Cyclopentadienyliron dicarbonyl dimer
Encyclopedia
Cyclopentadienyliron dicarbonyl dimer is an organometallic compound with the formula (C5H5)2Fe2(CO)4, also abbreviated Cp2Fe2(CO)4. It is called Fp2 or "fip dimer." It is a dark reddish-purple crystalline solid, which is readily soluble in moderately polar organic solvents such as chloroform and pyridine, but less soluble in carbon tetrachloride
and carbon disulfide
. Cp2Fe2(CO)4 is insoluble in but stable toward water.
complex. It exists in three isomeric forms: cis, trans, and unbridged. These isomeric forms are distinguished by the position of the ligands. Cis and trans differ in the relative position of C5H5 (Cp) ligands. And for both isomers, two CO ligands are terminal whereas the other two CO ligands bridge between the iron atoms. In the unbridged isomer, no ligands bridge between iron atoms - the metals are held together only by the Fe-Fe bond. Cis and trans isomers are the more abundant.
In solution, the three isomers interconvert. The phenomenon of rapidly interconverting structures is called fluxional
ity. Fluxional process for cyclopentadienyliron dicarbonyl dimer is so fast that only averaged single signal is observed in H NMR spectrum. However, the fluxional process is not fast enough for IR spectrum. Thus, three absorptions are seen for each isomer. The νco bands for bridging CO ligands are around 1780 cm-1 whereas νco bands for terminal CO ligands are about 1980 cm-1.
The solid state of molecular structure of both cis and trans isomers were determined and compared by X-ray and neutron diffraction. Surprisingly, cis and trans have the same metal-metal separation, identical Fe-C bond lengths in the Fe2C2 rhomboids, an exactly planar Fe2C2 four-membered ring in the trans isomer versus a folded rhomboid in cis with an angle of 164°, and significant distortions in the Cp ring of trans isomer reflecting different Cp orbital populations.
from iron pentacarbonyl
and dicyclopentadiene
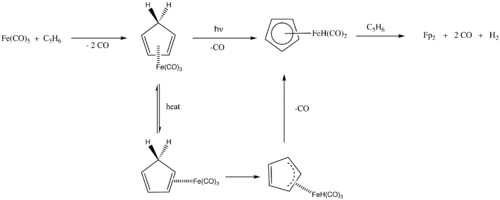
and has since been found as a byproduct of many organoiron reactions. Cp2Fe2(CO)4 is synthesized by the reaction of Fe(CO)5 and dicyclopentadiene.
In this preparation, dicyclopentadiene cracks to give cyclopentadiene, which reacts with Fe(CO)5. Cyclopentadiene reacts with Fe(CO)5 concomitant with loss of CO. Thereafter, the pathways differ for the photochemical and thermal routes differ subtly but both entail formation of a hydride intermediate.
; NaK
alloy, and alkali metal trialkylborohydrides have been used. CpFe(CO)2]Na is a widely studied reagent since it is readily alkylated, acylated, or metalated by treatment with an appropriate electrophile.
Treatment of NaFp with an alkyl halide
(RX, X = Br, I) produces FeR(C5H5)(CO)2
oxidatively cleaves the Fe-Fe bond in Fp2 to give FpBr, CpFe(CO)2Br.
CpFe(CO)2Br reacts with alkenes to afford cationic alkene-Fp complexes. The reactions require the addition of a Lewis acid
, such as AlBr3.
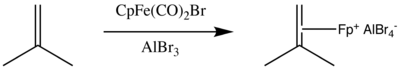
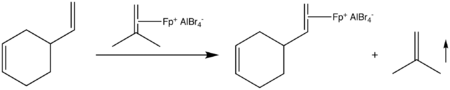 Alkene-Fp complexes can also be prepared from Fp anion indirectly. Thus, hydride abstraction from Fpalkyl compounds using the triphenylmethyl cation affords [Fp(isobutene)]+ complexes.
Alkene-Fp complexes can also be prepared from Fp anion indirectly. Thus, hydride abstraction from Fpalkyl compounds using the triphenylmethyl cation affords [Fp(isobutene)]+ complexes.
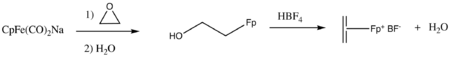
Reaction of NaFp with an epoxide
followed by acid-promoted dehydration also affords such alkene complexes.
 [CpFe(CO)2]- or Fp anion is a good alkene protecting group. Fp(alkene)+ are stable with respect to bromination, hydrogenation, and acetoxymercuration, but the alkene is easily released with sodium iodide
[CpFe(CO)2]- or Fp anion is a good alkene protecting group. Fp(alkene)+ are stable with respect to bromination, hydrogenation, and acetoxymercuration, but the alkene is easily released with sodium iodide
in acetone
or by warming with acetonitrile
.
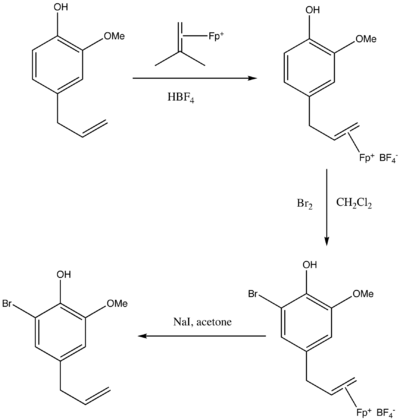 However, the coordinated alkene is strongly activated toward nucleophile addition, leading to number of carbon-carbon bond formation. Many nucleophile addition show regioselectivity, usually occurring at the more substituted carbon. This is due to the greater positive charge density at this position. However, the regiocontrol is not always good enough to be considered in the organic synthesis. The addition of the nucleophile is completely stereoselective, anti to the Fp group.
However, the coordinated alkene is strongly activated toward nucleophile addition, leading to number of carbon-carbon bond formation. Many nucleophile addition show regioselectivity, usually occurring at the more substituted carbon. This is due to the greater positive charge density at this position. However, the regiocontrol is not always good enough to be considered in the organic synthesis. The addition of the nucleophile is completely stereoselective, anti to the Fp group.
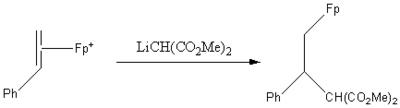
One advantage of [FpCH2S(CH3)2]BF4 is that its use does not require specialized conditions.
Ferric chloride is added to destroy any byproduct.
Carbon tetrachloride
Carbon tetrachloride, also known by many other names is the organic compound with the formula CCl4. It was formerly widely used in fire extinguishers, as a precursor to refrigerants, and as a cleaning agent...
and carbon disulfide
Carbon disulfide
Carbon disulfide is a colorless volatile liquid with the formula CS2. The compound is used frequently as a building block in organic chemistry as well as an industrial and chemical non-polar solvent...
. Cp2Fe2(CO)4 is insoluble in but stable toward water.
Structure
In solution, Cp2Fe2(CO)4 can be considered a dimeric half sandwichSandwich compound
In organometallic chemistry, a sandwich compound is a chemical compound featuring a metal bound by haptic covalent bonds to two arene ligands. The arenes have the formula CnHn, substituted derivatives and heterocyclic derivatives...
complex. It exists in three isomeric forms: cis, trans, and unbridged. These isomeric forms are distinguished by the position of the ligands. Cis and trans differ in the relative position of C5H5 (Cp) ligands. And for both isomers, two CO ligands are terminal whereas the other two CO ligands bridge between the iron atoms. In the unbridged isomer, no ligands bridge between iron atoms - the metals are held together only by the Fe-Fe bond. Cis and trans isomers are the more abundant.
In solution, the three isomers interconvert. The phenomenon of rapidly interconverting structures is called fluxional
Fluxional
Fluxional molecules are molecules that undergo dynamics such that some or all of their atoms interchange between symmetry-equivalent positions. Because virtually all molecules are fluxional in some respects, e.g. bond rotations in most organic compounds, the term fluxional depends on the context...
ity. Fluxional process for cyclopentadienyliron dicarbonyl dimer is so fast that only averaged single signal is observed in H NMR spectrum. However, the fluxional process is not fast enough for IR spectrum. Thus, three absorptions are seen for each isomer. The νco bands for bridging CO ligands are around 1780 cm-1 whereas νco bands for terminal CO ligands are about 1980 cm-1.
The solid state of molecular structure of both cis and trans isomers were determined and compared by X-ray and neutron diffraction. Surprisingly, cis and trans have the same metal-metal separation, identical Fe-C bond lengths in the Fe2C2 rhomboids, an exactly planar Fe2C2 four-membered ring in the trans isomer versus a folded rhomboid in cis with an angle of 164°, and significant distortions in the Cp ring of trans isomer reflecting different Cp orbital populations.
Synthesis
Cp2Fe2(CO)4 was first isolated as an intermediate in the synthesis of ferroceneFerrocene
Ferrocene is an organometallic compound with the formula Fe2. It is the prototypical metallocene, a type of organometallic chemical compound consisting of two cyclopentadienyl rings bound on opposite sides of a central metal atom. Such organometallic compounds are also known as sandwich compounds...
from iron pentacarbonyl
Iron pentacarbonyl
Iron pentacarbonyl, also known as iron carbonyl, is the compound with formula 5. Under standard conditions Fe5 is a free-flowing, straw-colored liquid with a pungent odour. This compound is a common precursor to diverse iron compounds, including many that are useful in organic synthesis. Fe5 is...
and dicyclopentadiene
Dicyclopentadiene
Dicyclopentadiene, abbreviated DCPD, is a chemical compound with formula C10H12. At room temperature, it is a white crystalline solid with a camphor-like odor. Its energy density is 10,975 Wh/l....
and has since been found as a byproduct of many organoiron reactions. Cp2Fe2(CO)4 is synthesized by the reaction of Fe(CO)5 and dicyclopentadiene.
- 2 Fe(CO)5 + C10H12 → (C5H5)2Fe2(CO)4 + 6 CO + H2
In this preparation, dicyclopentadiene cracks to give cyclopentadiene, which reacts with Fe(CO)5. Cyclopentadiene reacts with Fe(CO)5 concomitant with loss of CO. Thereafter, the pathways differ for the photochemical and thermal routes differ subtly but both entail formation of a hydride intermediate.
"Fp-"
Reductive cleavage of the Cp2Fe2(CO)4 produces derivatives formally derived from the cyclopentadienyliron dicarbonyl anion, [CpFe(CO)2]- or called Fp-. Such species are in fact covalent; there is no evidence for the existence of free Fp-. A typical reductant is sodium metal or sodium amalgamSodium amalgam
Sodium amalgam, commonly denoted Na, is an alloy of mercury and sodium. The term amalgam is used for alloys, intermetallic compounds, and solutions involving mercury as a major component. Sodium amalgam is often used in reactions as strong reducing agents with better handling properties compared...
; NaK
NaK
NaK, or sodium-potassium alloy, an alloy, of potassium , and sodium , is usually liquid at room temperature. Various commercial grades are available. NaK is highly reactive with water and may catch fire when exposed to air, so must be handled with special precautions...
alloy, and alkali metal trialkylborohydrides have been used. CpFe(CO)2]Na is a widely studied reagent since it is readily alkylated, acylated, or metalated by treatment with an appropriate electrophile.
- [CpFe(CO)2]2 + Na/Hg → 2 CpFe(CO)2Na
- [CpFe(CO)2]2 + 2 KBH(C2H5)3 → 2 CpFe(CO)2K + H2 + 2 B(C2H5)3
Treatment of NaFp with an alkyl halide
Halide
A halide is a binary compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative than the halogen, to make a fluoride, chloride, bromide, iodide, or astatide compound. Many salts are halides...
(RX, X = Br, I) produces FeR(C5H5)(CO)2
- CpFe(CO)2K + CH3I → CpFe(CO)2CH3 + KI
FpBr
BromineBromine
Bromine ") is a chemical element with the symbol Br, an atomic number of 35, and an atomic mass of 79.904. It is in the halogen element group. The element was isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig and Antoine Jerome Balard, in 1825–1826...
oxidatively cleaves the Fe-Fe bond in Fp2 to give FpBr, CpFe(CO)2Br.
- [CpFe(CO)2]2 + Br2 → 2 CpFe(CO)2Br
CpFe(CO)2Br reacts with alkenes to afford cationic alkene-Fp complexes. The reactions require the addition of a Lewis acid
Lewis acid
]The term Lewis acid refers to a definition of acid published by Gilbert N. Lewis in 1923, specifically: An acid substance is one which can employ a lone pair from another molecule in completing the stable group of one of its own atoms. Thus, H+ is a Lewis acid, since it can accept a lone pair,...
, such as AlBr3.
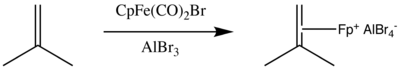
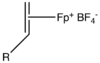
Fp(alkene)+
Salts of [Fp(isobutene)]+ are widely employed for the preparation of Fp-alkene complexes by alkene exchange. The exchange process is facilitated by the loss of gaseous isobutene.
- CpFe(CO)2Na + RCH2CH2I → FpCH2CH2R + NaI
- FpCH2CH2R + Ph3CBF4 →
Reaction of NaFp with an epoxide
Epoxide
An epoxide is a cyclic ether with three ring atoms. This ring approximately defines an equilateral triangle, which makes it highly strained. The strained ring makes epoxides more reactive than other ethers. Simple epoxides are named from the parent compound ethylene oxide or oxirane, such as in...
followed by acid-promoted dehydration also affords such alkene complexes.

Sodium iodide
Sodium iodide is a white, crystalline salt with chemical formula NaI used in radiation detection, treatment of iodine deficiency, and as a reactant in the Finkelstein reaction.-Uses:Sodium iodide is commonly used to treat and prevent iodine deficiency....
in acetone
Acetone
Acetone is the organic compound with the formula 2CO, a colorless, mobile, flammable liquid, the simplest example of the ketones.Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important solvent in its own right, typically as the solvent of choice for cleaning purposes in the laboratory...
or by warming with acetonitrile
Acetonitrile
Acetonitrile is the chemical compound with formula . This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile. It is produced mainly as a byproduct of acrylonitrile manufacture...
.


Fp-based cyclopropanation reagents
Fp-based reagents are useful for cyclopropanations. The key reagent is prepared from FpNa and has a good shelf-life, in contrast to typical Simmons-Smith intermediates and diazoalkanes.- CpFe(CO)2Na + ClCH2SCH3 → CpFe(CO)2CH2SCH3 + NaCl
- CpFe(CO)2CH2SCH3 + CH3I + NaBF4 → [CpFe(CO)2CH2S(CH3)2]BF4 + NaI
One advantage of [FpCH2S(CH3)2]BF4 is that its use does not require specialized conditions.
- CpFe(CO)2(CH2S+(CH3)2) BF4- + (Ph)2C=CH2 → 1,1-diphenylcyclopropane
Ferric chloride is added to destroy any byproduct.
Other specialized reactions
Under photochemical conditions, Fp2 reduces the C-C bond in 1-benzyl-1,4-dihydronicotinamide dimer, (BNA)2.- [CpFe(CO)2]2 + (BNA)2 + hv(λ=350nm) → 2[CpFe(CO)2]- + 2BNA+