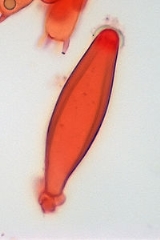
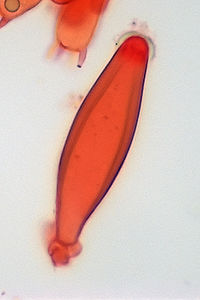
Cystidium
Encyclopedia
A cystidium is a relatively large cell found on the hymenium
of a basidiomycete (for example, on the surface of a mushroom gill), often between clusters of basidia
. Since cystidia have highly varied and distinct shapes that are often unique to a particular species or genus, they are a useful micromorphological characteristic in the identification of basidiomycetes. In general, the adaptive significance of cystidia is not well understood.
structure) (cheilocystidia), on the face of a lamella (pleurocystidia), on the surface of the cap (dermatocystidia or pileocystidia), on the margin of the cap (circumcystidia) or on the stipe
(caulocystidia). Especially the pleurocystidia and cheilocystidia are important for identification within many genera. Sometimes the cheilocystidia give the gill edge a distinct colour which is visible to the naked eye or with a hand lens.
or other alkaline compounds. Chrysocystidia are characteristic of many (though not all) members of the agaric
family Strophariaceae
.
Gloeocystidia have an oily or granular appearance under the microscope. Like gloeohyphae, they may be yellowish or clear (hyaline
) and can sometimes selectively be coloured by sulphovanillin or other reagents. Metuloids are thick-walled cystidia with an apex having any of several distinct shapes.
Hymenium
The hymenium is the tissue layer on the hymenophore of a fungal fruiting body where the cells develop into basidia or asci, which produce spores. In some species all of the cells of the hymenium develop into basidia or asci, while in others some cells develop into sterile cells called cystidia or...
of a basidiomycete (for example, on the surface of a mushroom gill), often between clusters of basidia
Basidium
thumb|right|500px|Schematic showing a basidiomycete mushroom, gill structure, and spore-bearing basidia on the gill margins.A basidium is a microscopic, spore-producing structure found on the hymenophore of fruiting bodies of basidiomycete fungi. The presence of basidia is one of the main...
. Since cystidia have highly varied and distinct shapes that are often unique to a particular species or genus, they are a useful micromorphological characteristic in the identification of basidiomycetes. In general, the adaptive significance of cystidia is not well understood.
Classification of cystidia

By position
Cystidia may occur on the edge of a lamella (or analogous hymenophoralHymenophore
A hymenophore refers to the hymenium-bearing structure of a fungal fruiting body. Hymenophores can be smooth surfaces, lamellae, folds, tubes, or teeth....
structure) (cheilocystidia), on the face of a lamella (pleurocystidia), on the surface of the cap (dermatocystidia or pileocystidia), on the margin of the cap (circumcystidia) or on the stipe
Stipe (mycology)
thumb|150px|right|Diagram of a [[basidiomycete]] stipe with an [[annulus |annulus]] and [[volva |volva]]In mycology a stipe refers to the stem or stalk-like feature supporting the cap of a mushroom. Like all tissues of the mushroom other than the hymenium, the stipe is composed of sterile hyphal...
(caulocystidia). Especially the pleurocystidia and cheilocystidia are important for identification within many genera. Sometimes the cheilocystidia give the gill edge a distinct colour which is visible to the naked eye or with a hand lens.
By morphology
Chrysocystidia are cystidia whose contents contain a distinct refractive yellow body, that becomes more deeply yellow when exposed to ammoniaAmmonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
or other alkaline compounds. Chrysocystidia are characteristic of many (though not all) members of the agaric
Agaric
An agaric is a type of fungal fruiting body characterized by the presence of a pileus that is clearly differentiated from the stipe , with lamellae on the underside of the pileus. "Agaric" can also refer to a basidiomycete species characterized by an agaric-type fruiting body...
family Strophariaceae
Strophariaceae
The Strophariaceae are a family of fungi in the order Agaricales. The family contains 18 genera and 1316 species. The species of Strophariaceae have a red-brown to dark brown spore print, while the spores themselves are smooth and have an apical germ pore. These agarics are also characterized by...
.
Gloeocystidia have an oily or granular appearance under the microscope. Like gloeohyphae, they may be yellowish or clear (hyaline
Hyaline
The term hyaline denotes a substance with a glass-like appearance.-Histopathology:In histopathological medical usage, a hyaline substance appears glassy and pink after being stained with haematoxylin and eosin — usually it is an acellular, proteinaceous material...
) and can sometimes selectively be coloured by sulphovanillin or other reagents. Metuloids are thick-walled cystidia with an apex having any of several distinct shapes.
External links
- BCERN Glossary: Cystidia
- "Using a Microscope: Basidia and Cystidia" by Michael Kuo. MushroomExpert.com
- Wild Mushrooms from Tokyo: Inocybe nodulosospora Includes very good photograph of cystidia.

