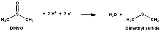
DMSO reductase
Encyclopedia
DMSO reductase is a molybdenum
-containing enzyme capable of reducing dimethyl sulfoxide
(DMSO) to dimethyl sulfide
(DMS). This enzyme serves as the terminal reductase
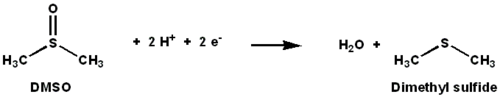
under anaerobic conditions in some bacteria, with DMSO being the terminal electron acceptor. During the course of the reaction, the oxygen atom in DMSO is transferred to molybdenum, and then is subsequently removed from molybdenum as water.
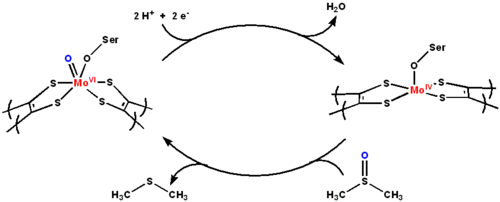
-containing core that supports molybdenum in its highest oxidation state (MoVI). The proposed mechanism of DMSO reductase cycles molybdenum between the +4 and +6 oxidation states.
Molybdenum
Molybdenum , is a Group 6 chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42. The name is from Neo-Latin Molybdaenum, from Ancient Greek , meaning lead, itself proposed as a loanword from Anatolian Luvian and Lydian languages, since its ores were confused with lead ores...
-containing enzyme capable of reducing dimethyl sulfoxide
Dimethyl sulfoxide
Dimethyl sulfoxide is an organosulfur compound with the formula 2SO. This colorless liquid is an important polar aprotic solvent that dissolves both polar and nonpolar compounds and is miscible in a wide range of organic solvents as well as water...
(DMSO) to dimethyl sulfide
Dimethyl sulfide
Dimethyl sulfide or methylthiomethane is an organosulfur compound with the formula 2S. Dimethyl sulfide is a water-insoluble flammable liquid that boils at and has a characteristic disagreeable odor. It is a component of the smell produced from cooking of certain vegetables, notably maize,...
(DMS). This enzyme serves as the terminal reductase
Oxidoreductase
In biochemistry, an oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule to another...
under anaerobic conditions in some bacteria, with DMSO being the terminal electron acceptor. During the course of the reaction, the oxygen atom in DMSO is transferred to molybdenum, and then is subsequently removed from molybdenum as water.

Active site and mechanism
The active site contains a molybdopterinMolybdopterin
Molybdopterins, when reacted with molybdenum or tungsten in the form of molybdate or tungstate, are a class of cofactors found in most molybdenum and all tungsten enzymes...
-containing core that supports molybdenum in its highest oxidation state (MoVI). The proposed mechanism of DMSO reductase cycles molybdenum between the +4 and +6 oxidation states.


