
DUT1
Encyclopedia
Universal Time
Universal Time is a time scale based on the rotation of the Earth. It is a modern continuation of Greenwich Mean Time , i.e., the mean solar time on the Prime Meridian at Greenwich, and GMT is sometimes used loosely as a synonym for UTC...
(UT1), which is defined by Earth's rotation, and Coordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is one of several closely related successors to Greenwich Mean Time. Computer servers, online services and other entities that rely on having a universally accepted time use UTC for that purpose...
(UTC), which is defined by a network of precision clocks.
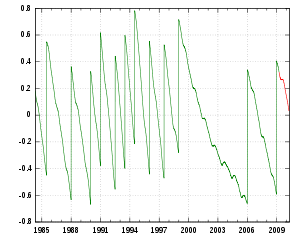
- DUT1 = UT1 − UTC
UTC is maintained via leap second
Leap second
A leap second is a positive or negative one-second adjustment to the Coordinated Universal Time time scale that keeps it close to mean solar time. UTC, which is used as the basis for official time-of-day radio broadcasts for civil time, is maintained using extremely precise atomic clocks...
s, such that UTC remains within the range −0.9 s < DUT1 < +0.9 s. The reason for this correction is partly that the rate of rotation of the Earth is not constant, due to tidal braking and the redistribution of mass within the Earth, including its oceans and atmosphere, and partly because the SI second
Second
The second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
(as now used for UTC) was already, when adopted, a little shorter than the current value of the second of mean solar time.
Forecast values of DUT1 are published by IERS
IERS
IERS may refer to:* International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service* Independent Electricity Retail Solutions Pty Ltd* Information Exchange Requirements - used within MODAF and DODAF as the OV-3 view - called Information Exchange Matrix....
Bulletin A.
Weekly updated values of DUT1 with 0.1 s precision are broadcast by several time signal services, including WWV and MSF. These services transmit one pulse per second of some sort. To represent positive DUT1 values from +0.1 to +0.8 seconds, the pulses sent during seconds 1 through 8 are "emphasized" in some way, generally by transmitting a double pulse. The number of emphasized pulses gives the value of DUT1. Negative DUT1 values, from −0.1 to −0.8 seconds, are similarly represented by emphasizing pulses 9 through 16. For example, a DUT1 value of −0.4 would be transmitted by emphasizing pulses 9 through 12.
The Russian time signal RWM
RWM
RWM is the callsign of a high frequency standard frequency and time signal radio station in Moscow, Russia. RWM transmits on 4996 kHz with 5 kW and on 9996 and 14996 kHz with 8 kW....
transmits an additional correction dUT1 in 0.02 s increments. Positive values of dUT1 from +0.02 to +0.08 s are encoded by emphasizing pulses 21 through 24; negative values are encoded by emphasizing pulses 31 through 34. The actual value of DUT1 is approximated by the sum of the transmitted DUT1 + dUT1.
The longwave RBU
RBU (radio station)
RBU is a time code radio station located in Moscow . It transmits a continuous 10 kW time code on 66⅔ kHz. According other sources the transmitter site may be or on the area of Taldom transmitter at...
time signal also transmits dUT1.
External links
- http://scienceworld.wolfram.com/astronomy/Time.html

