Daly detector
Encyclopedia
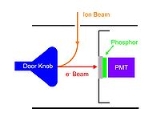
A Daly detector is a gas phase ion
detector that consists of a metal "doorknob", a scintillator
(phosphor
screen) and a photomultiplier
. It was named after its inventor Norman Richard Daly. Daly detectors are typically used in mass spectrometers.
.
The advantage of the Daly detector is that the photomultiplier can be separated by a window, which lets the photons through from the high vacuum of the mass spectrometer, which an otherwise possible contamination prevented and which extends detector life span. The Daly detector also allows for a higher acceleration after the field free region of a time-of-flight mass spectrometer flight tube, which can improve the sensitivity for high mass ions.
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
detector that consists of a metal "doorknob", a scintillator
Scintillator
A scintillator is a special material, which exhibits scintillation—the property of luminescence when excited by ionizing radiation. Luminescent materials, when struck by an incoming particle, absorb its energy and scintillate, i.e., reemit the absorbed energy in the form of light...
(phosphor
Phosphor
A phosphor, most generally, is a substance that exhibits the phenomenon of luminescence. Somewhat confusingly, this includes both phosphorescent materials, which show a slow decay in brightness , and fluorescent materials, where the emission decay takes place over tens of nanoseconds...
screen) and a photomultiplier
Photomultiplier
Photomultiplier tubes , members of the class of vacuum tubes, and more specifically phototubes, are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum...
. It was named after its inventor Norman Richard Daly. Daly detectors are typically used in mass spectrometers.
How it works
Ions that hit the doorknob release secondary electrons. A high voltage (ca. -20,000 V) between the doorknob and the scintillator accelerates the electrons onto the phosphor screen where they are converted to photons. These photons are detected by the photomultiplierPhotomultiplier
Photomultiplier tubes , members of the class of vacuum tubes, and more specifically phototubes, are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum...
.
The advantage of the Daly detector is that the photomultiplier can be separated by a window, which lets the photons through from the high vacuum of the mass spectrometer, which an otherwise possible contamination prevented and which extends detector life span. The Daly detector also allows for a higher acceleration after the field free region of a time-of-flight mass spectrometer flight tube, which can improve the sensitivity for high mass ions.

