
Data signaling rate
Encyclopedia
In telecommunication
, data signaling rate (DSR), also known as gross bit rate, is the aggregate rate at which data
pass a point in the transmission
path
of a data transmission system
.
Notes:
Based upon proposal from davisnetworks.com. 1 Mbit/s is defined as 1,000,000 bits per second signal data rate (OSI Layer 1).
Telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information over significant distances to communicate. In earlier times, telecommunications involved the use of visual signals, such as beacons, smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs, or audio messages via coded...
, data signaling rate (DSR), also known as gross bit rate, is the aggregate rate at which data
Data
The term data refers to qualitative or quantitative attributes of a variable or set of variables. Data are typically the results of measurements and can be the basis of graphs, images, or observations of a set of variables. Data are often viewed as the lowest level of abstraction from which...
pass a point in the transmission
Transmission (telecommunications)
Transmission, in telecommunications, is the process of sending, propagating and receiving an analogue or digital information signal over a physical point-to-point or point-to-multipoint transmission medium, either wired, optical fiber or wireless...
path
Data link
In telecommunication a data link is the means of connecting one location to another for the purpose of transmitting and receiving information. It can also refer to a set of electronics assemblies, consisting of a transmitter and a receiver and the interconnecting data telecommunication circuit...
of a data transmission system
Transmission system
In telecommunications a transmission system is a system that transmits a signal from one place to another. The signal can be an electrical, optical or radio signal....
.
Notes:
- The DSR is usually expressed in bits per second.
- The data signaling rate is given by
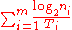 where m is the number of parallel channels, ni is the number of significant conditions of the modulationModulationIn electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
where m is the number of parallel channels, ni is the number of significant conditions of the modulationModulationIn electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
in the i-th channelChannel (communications)In telecommunications and computer networking, a communication channel, or channel, refers either to a physical transmission medium such as a wire, or to a logical connection over a multiplexed medium such as a radio channel...
, and Ti is the unit intervalUnit interval (data transmission)The unit interval is the minimum time interval between condition changes of a data transmission signal, also known as the symbol duration time....
, expressed in seconds, for the i-th channel. - For serial transmission in a single channel, the DSR reduces to (1/T)log2n; with a two-condition modulation, i. e. n = 2, the DSR is 1/T, according to Hartley's law.
- For parallel transmission with equal unit intervals and equal numbers of significant conditions on each channel, the DSR is (m/T)log2 n; in the case of a two-condition modulationModulationIn electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
, this reduces to m/T. - The DSR may be expressed in bauds, in which case, the factor log2ni in the above summation formula should be deleted when calculating bauds.
- In synchronous binaryBinary numeral systemThe binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, represents numeric values using two symbols, 0 and 1. More specifically, the usual base-2 system is a positional notation with a radix of 2...
signaling, the DSR in bits per second may be numerically the same as the modulation rate expressed in bauds. Signal processors, such as four-phasePhase (waves)Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:...
modems, cannot change the DSR, but the modulation rate depends on the lineTelephone lineA telephone line or telephone circuit is a single-user circuit on a telephone communication system...
modulation scheme, in accordance with Note 4. For example, in a 2400 bit/s 4-phase sending modemModemA modem is a device that modulates an analog carrier signal to encode digital information, and also demodulates such a carrier signal to decode the transmitted information. The goal is to produce a signal that can be transmitted easily and decoded to reproduce the original digital data...
, the signaling rate is 2400 bit/s on the serialSerial communicationsIn telecommunication and computer science, serial communication is the process of sending data one bit at a time, sequentially, over a communication channel or computer bus. This is in contrast to parallel communication, where several bits are sent as a whole, on a link with several parallel channels...
input side, but the modulation rate is only 1200 bauds on the 4-phase output side.
Transmission Data Rate Terminology
| Data Rate | Abbreviation | Lower | Upper |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extremely Low Data Rate | ELDR | 300 bit/s | 3 kbit/s |
| Very Low Data Rate | VLDR | 3 kbit/s | 30 kbit/s |
| Low Data Rate | LDR | 30 kbit/s | 300 kbit/s |
| Medium Data Rate | MDR | 300 kbit/s | 3 Mbit/s |
| High Data Rate | HDR | 3 Mbit/s | 30 Mbit/s |
| Very High Data Rate | VHDR | 30 Mbit/s | 300 Mbit/s |
| Ultra High Data Rate | UHDR | 300 Mbit/s | 3 Gbit/s |
| Super High Data Rate | SHDR | 3 Gbit/s | 30 Gbit/s |
| Extremely High Data Rate | EHDR | 30 Gbit/s | 300 Gbit/s |
Based upon proposal from davisnetworks.com. 1 Mbit/s is defined as 1,000,000 bits per second signal data rate (OSI Layer 1).
Data Rate and Standard
| Data Rate | Standard |
|---|---|
| 155 Mb/s | OC-3 |
| 622 Mb/s | OC-12 |
| 1063 Mb/s | Fibre Channel |
| 1250 Mb/s | GbE |
| 2125 Mb/s | 2xFibre Channel |
| 2488 Mb/s | OC-48 |
| 2500 Mb/s | 2xGbE, infiniband |
| 2666 Mb/s | OC-48(FEC) |
| 3125 Mb/s | 10 DbE LX-4 |
| 4250 Mb/s | 4xFibre Channel |
| 9.953 Gb/s | OC-192 |
| 10.3125 Gb/s | 10 GbE |
| 10.51875 Gb/s | 10 G Fibre Channel |
| 10.664 Gb/s | OC-192 (FEC) |
| 10.709 Gb/s | OC-192 (ITU-T G.709) |
| 11.100 Gb/s | 10 GbE FEC |
| 11.300 Gb/s | 10 G Fibre Channel |
See also
- Bit rateBit rateIn telecommunications and computing, bit rate is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time....
- Bandwidth (computing)Bandwidth (computing)In computer networking and computer science, bandwidth, network bandwidth, data bandwidth, or digital bandwidth is a measure of available or consumed data communication resources expressed in bits/second or multiples of it .Note that in textbooks on wireless communications, modem data transmission,...
- BaudBaudIn telecommunications and electronics, baud is synonymous to symbols per second or pulses per second. It is the unit of symbol rate, also known as baud rate or modulation rate; the number of distinct symbol changes made to the transmission medium per second in a digitally modulated signal or a...
- Line rate
- Maximum user signaling rateMaximum user signaling rateIn telecommunication, maximum user signaling rate, synonymous to gross bitrate or data signaling rate, is the maximum rate, in bits per second, at which binary information can be transferred in a given direction between users over the telecommunications system facilities dedicated to a particular...
- Transfer rate

