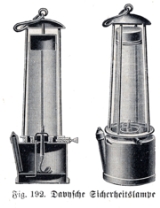
Davy lamp
Encyclopedia
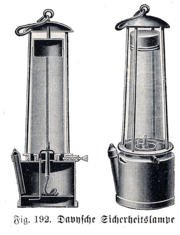
Safety lamp
A safety lamp is any of several types of lamp, which are designed to be safe to use in coal mines. These lamps are designed to operate in air that may contain coal dust, methane, or firedamp, all of which are potentially flammable or explosive...
with a wick and oil vessel burning originally a heavy vegetable oil, devised in 1815 by Sir Humphry Davy. It was created for use in coal mines, allowing deep seams to be mined despite the presence of methane
Methane
Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest alkane, the principal component of natural gas, and probably the most abundant organic compound on earth. The relative abundance of methane makes it an attractive fuel...
and other flammable gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
es, called firedamp
Firedamp
Firedamp is a flammable gas found in coal mines. It is the name given to a number of flammable gases, especially methane. It is particularly commonly found in areas where the coal is bituminous...
or minedamp.
Sir Humphry Davy had discovered that a flame enclosed inside a mesh of a certain fineness cannot ignite firedamp. The screen acts as a flame arrestor; air (and any firedamp present) can pass through the mesh freely enough to support combustion, but the holes are too fine to allow a flame to propagate through them and ignite any firedamp outside the mesh. The first trial of a Davy lamp with a wire sieve was at Hebburn
Hebburn
Hebburn is a small town situated on the south bank of the River Tyne in North East England, sandwiched between the towns of Jarrow and Bill Quay...
Colliery on 9 January 1816. Gas Detector
The lamp also provided a test for the presence of gases. If flammable gas mixtures were present, the flame of the Davy lamp burned higher with a blue tinge as shown by the gauge. Miners could place the safety lamp close to the ground to detect gases, such as carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
, that are denser than air and so could collect in depressions in the mine; if the mine air was oxygen-poor (asphyxiant gas
Asphyxiant gas
An asphyxiant gas is a non-toxic or minimally toxic gas which reduces or diplaces the normal oxygen concentration in breathing air. Prolonged breathing of oxygen depleted air can lead to death by asphyxiation...
), the lamp flame would be extinguished (black damp or chokedamp). A flame is extinguished at about 17% oxygen content, air which will still support life, so the lamp gave an early indication of a problem.
Comparison with Geordie lamp
There was some controversy, since George StephensonGeorge Stephenson
George Stephenson was an English civil engineer and mechanical engineer who built the first public railway line in the world to use steam locomotives...
also produced a similar safety lamp in 1816 called the Stephenson generally and locally within the North East coalfields the Geordie lamp
Geordie lamp
The Geordie lamp was invented by George Stephenson in 1815 as a solution to explosions due to firedamp in coal mines.Although controversy arose between Stephenson's design and the Davy lamp, , Stephenson's original design worked on significantly different principles...
.
Supporters of each man seem to have regarded the other as having plagiarised their man's idea. The Geordie lamp had a glass inside the tubular gauze with a copper cap; the air was fed from below. The Davy lamp was simpler and cheaper, and was popular with mine owners.
There were safety arguments on both sides: in principle, a poorly maintained (or badly designed) Davy lamp could overheat the gauze if it met a high concentration of methane. The gauze rusted easily in the damp mines, making the lamp hazardous. The Geordie lamp could become unsafe if the internal glass was broken (as it became an oversize Davy). Both original lamps were faulty, and led to attempts at improvement, by using multiple gauzes above the flame, and with a glass surround to improve illumination.
Accident rate
The introduction of the Davy lamp actually led to an increase in accidents in mines, as the lamp encouraged working mines that had previously been closed for safety reasons. The bare gauze was easily damaged, and once just a single wire broke or rusted away, the lamp became unsafe. Illumination from the safety lamps was very poor, and the problem was not resolved until electric lamps became widely available in the late 19th century.One reason why the lamp caused an increase in the accident rate was that the men continued to work in unsafe conditions due to the presence of methane gas. The other reason why there was an increase was that there should have been an installation of extractor ventilation fans installed at each mine to reduce the concentration of methane in the air. This would have been expensive, and thus they were not installed by mine owners. The lamps also had to be provided by the miners themselves, not the owners, as traditionally the miners bought their own candles from the company store. The installation of fans became required after laws requiring minimum air quality standards were introduced.
Modern lamps
The modern day equivalent of the Davy lamp is the Protector Garforth GR6S flame safety lamp which is used for firedamp testing in all UK coal mines. A modified version of this lamp is used to transport the Olympic Flame
Olympic Flame
The Olympic Flame or Olympic Torch is a symbol of the Olympic Games. Commemorating the theft of fire from the Greek god Zeus by Prometheus, its origins lie in ancient Greece, where a fire was kept burning throughout the celebration of the ancient Olympics. The fire was reintroduced at the 1928...
for the torch relays. They were used for the Sydney, Athens, Turin, Beijing, Vancouver and Singapore Youth Olympic Games relays. They were also used for the Special Olympics Shanghai, Pan American and Central African Games relays. They will also be used for the London 2012 relay. The lamps are still made in Eccles.
A modified version of the lamp has recently been produced which will burn ghee
Ghee
Ghee is a class of clarified butter that originated in South Asia and is commonly used in South Asian cuisine....
, as used in Hindu flame ceremonies.
Electronic gas detectors are now widely used in collieries and detect methane by its slow combustion on a catalyst chip. The rise in temperature is detected and a warning emitted by the device, known as a methanometer
Methanometer
A methanometer is an instrument used to measure methane gas in the air of a mine. The Mine Safety Appliances Company Ltd. manufactured the first type - W8 Methanometer around 1950.and it was approved for use by the Ventilation Regulations of 1947. The Methanometer could be powered by an Edison...
.
However it is still a legal requirement in operating a UK coal mine that a Protector Flame Safety Lamp is used for gas testing.
These are carried by Pit Deputies who are usually responsible for 15 men.
External links
- Popular Science video showing an experiment that demonstrates the principle of the Davy lamp

