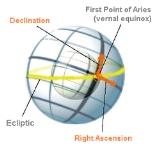
Declination
Overview
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
, declination (abbrev. dec or δ) is one of the two coordinates of the equatorial coordinate system
Equatorial coordinate system
The equatorial coordinate system is a widely-used method of mapping celestial objects. It functions by projecting the Earth's geographic poles and equator onto the celestial sphere. The projection of the Earth's equator onto the celestial sphere is called the celestial equator...
, the other being either right ascension
Right ascension
Right ascension is the astronomical term for one of the two coordinates of a point on the celestial sphere when using the equatorial coordinate system. The other coordinate is the declination.-Explanation:...
or hour angle
Hour angle
In astronomy and celestial navigation, the hour angle is one of the coordinates used in the equatorial coordinate system to give the position of a point on the celestial sphere....
. Declination in astronomy is comparable to geographic latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
, but projected onto the celestial sphere
Celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an imaginary sphere of arbitrarily large radius, concentric with the Earth and rotating upon the same axis. All objects in the sky can be thought of as projected upon the celestial sphere. Projected upward from Earth's equator and poles are the...
. Declination is measured in degrees north and south of the celestial equator
Celestial equator
The celestial equator is a great circle on the imaginary celestial sphere, in the same plane as the Earth's equator. In other words, it is a projection of the terrestrial equator out into space...
. Points north of the celestial equator have positive declinations, while those to the south have negative declinations.
- An object on the celestial equatorCelestial equatorThe celestial equator is a great circle on the imaginary celestial sphere, in the same plane as the Earth's equator. In other words, it is a projection of the terrestrial equator out into space...
has a declination of 0°. - An object at the celestial north poleNorth PoleThe North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is, subject to the caveats explained below, defined as the point in the northern hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface...
has a declination of +90°. - An object at the celestial south poleSouth PoleThe South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole or Terrestrial South Pole, is one of the two points where the Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on the surface of the Earth and lies on the opposite side of the Earth from the North Pole...
has a declination of −90°.
The sign is customarily included even if it is positive.

