Degree of polymerization
Encyclopedia
The degree of polymerization, or DP, is usually defined as the number of monomeric unit
s in a macromolecule
or polymer
or oligomer
molecule.
For a homopolymer, there is only one type of monomeric unit and
the number-average degree of polymerization is given by
For most industrial purposes, degrees of polymerization in the thousands or tens of thousands are desired.
Some authors, however, define DP as the number of repeat unit
s, where for copolymers the repeat unit may not be identical to the monomeric unit. For example, in nylon-6,6, the repeat unit contains the two monomeric units —NH(CH2)6NH— and —OC(CH2)4CO— , so that a chain of 1000 monomeric units corresponds to 500 repeat units. The degree of polymerization or chain length is then 1000 by the first (IUPAC) definition, but 500 by the second.
In polycondensation
, in order to achieve a high degree of polymerization (and hence molecular weight), Xn, a high fractional monomer conversion, p, is required, as per Carothers' equation: Xn = 1/(1−p). A monomer conversion of p = 99% would be required to achieve Xn = 100.
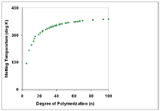
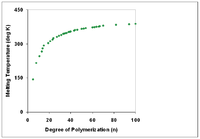 Polymers with identical composition but different total molecular weights may exhibit different physical properties. In general, increasing degree of polymerization correlates with higher melting temperature and higher mechanical strength.
Polymers with identical composition but different total molecular weights may exhibit different physical properties. In general, increasing degree of polymerization correlates with higher melting temperature and higher mechanical strength.
Structural unit
In polymer chemistry, a structural unit is a building block of a polymer chain. It is the result of a monomer which has been polymerized into a long chain....
s in a macromolecule
Macromolecule
A macromolecule is a very large molecule commonly created by some form of polymerization. In biochemistry, the term is applied to the four conventional biopolymers , as well as non-polymeric molecules with large molecular mass such as macrocycles...
or polymer
Polymer
A polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating structural units. These subunits are typically connected by covalent chemical bonds...
or oligomer
Oligomer
In chemistry, an oligomer is a molecule that consists of a few monomer units , in contrast to a polymer that, at least in principle, consists of an unlimited number of monomers. Dimers, trimers, and tetramers are oligomers. Many oils are oligomeric, such as liquid paraffin...
molecule.
For a homopolymer, there is only one type of monomeric unit and
the number-average degree of polymerization is given by
For most industrial purposes, degrees of polymerization in the thousands or tens of thousands are desired.
Some authors, however, define DP as the number of repeat unit
Repeat unit
An essential concept which defines polymer structure, the repeat unit or repeating unit is a part of a polymer chain whose repetition would produce the complete polymer by linking the repeat units together successively along the chain, like the beads of a necklace.A repeat unit is sometimes called...
s, where for copolymers the repeat unit may not be identical to the monomeric unit. For example, in nylon-6,6, the repeat unit contains the two monomeric units —NH(CH2)6NH— and —OC(CH2)4CO— , so that a chain of 1000 monomeric units corresponds to 500 repeat units. The degree of polymerization or chain length is then 1000 by the first (IUPAC) definition, but 500 by the second.
In polycondensation
Step-growth polymerization
Step-growth polymerization refers to a type of polymerization mechanism in which bi-functional or multifunctional monomers react to form first dimers, then trimers, longer oligomers and eventually long chain polymers. Many naturally occurring and some synthetic polymers are produced by step-growth...
, in order to achieve a high degree of polymerization (and hence molecular weight), Xn, a high fractional monomer conversion, p, is required, as per Carothers' equation: Xn = 1/(1−p). A monomer conversion of p = 99% would be required to achieve Xn = 100.
Correlation with physical properties



