Delta cell
Encyclopedia
Delta cells are somatostatin
-producing cell
s.
They can be found in the stomach
, intestine
and the Islets of Langerhans
in the pancreas
.
In rodents delta-cells are located in the periphery of the islets; in humans the islet architecture is generally less organized and delta-cells are frequently observed inside the islets as well.
In the electron microscope
, delta-cells can be identified as cells with smaller and slightly more compact granules
than beta cell
s.
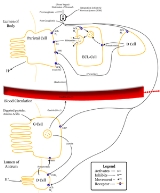
D cells contain CCKBR (which respond to gastrin) and M3 receptors (which respond to Ach). Respectively, these receptors will increase somatostatin
output and decrease somatostatin output from the D cells.
VIP, vasoactive intestinal peptide
, acts positively on D cells resulting in more somatostatin
being released.
".
Somatostatin
Somatostatin is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via interaction with G-protein-coupled somatostatin receptors and inhibition of the release of numerous secondary hormones.Somatostatin...
-producing cell
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
s.
They can be found in the stomach
Stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow, dilated part of the alimentary canal which functions as an important organ of the digestive tract in some animals, including vertebrates, echinoderms, insects , and molluscs. It is involved in the second phase of digestion, following mastication .The stomach is...
, intestine
Intestine
In human anatomy, the intestine is the segment of the alimentary canal extending from the pyloric sphincter of the stomach to the anus and, in humans and other mammals, consists of two segments, the small intestine and the large intestine...
and the Islets of Langerhans
Islets of Langerhans
The islets of Langerhans are the regions of the pancreas that contain its endocrine cells. Discovered in 1869 by German pathological anatomist Paul Langerhans at the age of 22, the islets of Langerhans constitute approximately 1 to 2% of the mass of the pancreas...
in the pancreas
Pancreas
The pancreas is a gland organ in the digestive and endocrine system of vertebrates. It is both an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin, as well as a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist...
.
In rodents delta-cells are located in the periphery of the islets; in humans the islet architecture is generally less organized and delta-cells are frequently observed inside the islets as well.
In the electron microscope
Electron microscope
An electron microscope is a type of microscope that uses a beam of electrons to illuminate the specimen and produce a magnified image. Electron microscopes have a greater resolving power than a light-powered optical microscope, because electrons have wavelengths about 100,000 times shorter than...
, delta-cells can be identified as cells with smaller and slightly more compact granules
Granule (cell biology)
In cell biology, a granule is a small particle. It can be any structure barely visible by light microscopy. The term is most often used to describe a secretory vesicle.-Leukocytes:...
than beta cell
Beta cell
Beta cells are a type of cell in the pancreas located in the so-called islets of Langerhans. They make up 65-80% of the cells in the islets.-Function:...
s.
D cells contain CCKBR (which respond to gastrin) and M3 receptors (which respond to Ach). Respectively, these receptors will increase somatostatin
Somatostatin
Somatostatin is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via interaction with G-protein-coupled somatostatin receptors and inhibition of the release of numerous secondary hormones.Somatostatin...
output and decrease somatostatin output from the D cells.
VIP, vasoactive intestinal peptide
Vasoactive intestinal peptide
Vasoactive intestinal peptide also known as the vasoactive intestinal polypeptide or VIP is a peptide hormone containing 29 amino acid residues that is produced in many tissues of vertebrates including the gut, pancreas and suprachiasmatic nuclei of the hypothalamus in the brain...
, acts positively on D cells resulting in more somatostatin
Somatostatin
Somatostatin is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via interaction with G-protein-coupled somatostatin receptors and inhibition of the release of numerous secondary hormones.Somatostatin...
being released.
Clinical significance
A tumor of the delta cells is called a "somatostatinomaSomatostatinoma
Somatostatinoma is a tumor of the delta cells of the endocrine pancreas that produces somatostatin.It is associated with diabetes mellitus and abnormal glucose tolerance.Triad of : Mild Diabetes mellitus, Steatorrhoea, Gall stones...
".

