Demographics of Uganda
Encyclopedia
This article is about the demographic
features of the population of Uganda
, including population density
, ethnicity
, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
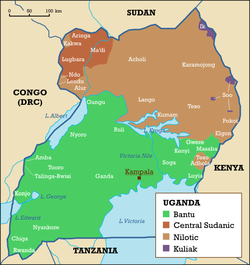
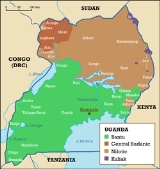
, and Central Sudanic—constitute most of the population.
Bantu peoples are the most numerous and include the Baganda
in the central area (17%), Basoga in the south-eastern area (8%), Banyankole in the south-western area (8%), Bakiga
in the most south-western area (8%), Banyoro in the mid-western area (3%), Batooro in the mid-western area (3%), Bagisu
in the eastern area, Bahima in the south-western area (2%), Bafumbira in the south-western area (6%), and other much smaller ethnic groups.
Nilotic
peoples, mainly in the north, are the next largest, including the Langi
, 6%, and the Acholi, 4%. In the northwest are the Lugbara
, 4%. The Karamojong
, 2%, occupy the considerably drier, largely pastoral territory in the northeast. Europeans, Asians, and Arab
s make up about 1% of the population with other groups accounting for the remainder.
More than half of the population is under the age of 15 more than any other country in the world. Uganda's population is predominantly rural, and its density population highest in the southern regions.
came to power in 1971, he declared "economic war" on the Indians, culminating in the Expulsion of Asians in Uganda in 1972
. Since Amin's overthrow in 1979 some Asians have returned. There are about 12,000 in Uganda today, nearly all in the capital Kampala
.
There are also about 3,000 Arabs of various national origins in Uganda.
note:
estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS
; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality and death rates, lower population and growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2009 estimate).
50% (male 8,152,830; female 8,034,366)
15-64 years:
47.9% (male 7,789,209; female 7,703,143)
65 years and over:
2.1% (male 286,693; female 403,317) (2009 estimate)
1.03 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.7 male(s)/female
total population:
1.01 male(s)/female (2009 estimate)
52.72 years
male:
51.66 years
female:
53.81 years (2009 estimate)
4.2%, Nyoro 2.7%, other 29.6% (2002 census)
1.5%, Muslim
12.1%, Sikhism
& other 3.1%, Baha'i 0.3%, None 0.9% (2002 census)
(official national language, taught in grade schools, used in courts of law and by most newspapers and some radio broadcasts), Luganda
(most widely used of the Niger–Congo languages
, preferred for native language publications in the capital and may be taught in school), other Bantu languages
, Nilo-Saharan languages
, English, Arabic.
Demographics
Demographics are the most recent statistical characteristics of a population. These types of data are used widely in sociology , public policy, and marketing. Commonly examined demographics include gender, race, age, disabilities, mobility, home ownership, employment status, and even location...
features of the population of Uganda
Uganda
Uganda , officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. Uganda is also known as the "Pearl of Africa". It is bordered on the east by Kenya, on the north by South Sudan, on the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, on the southwest by Rwanda, and on the south by...
, including population density
Population density
Population density is a measurement of population per unit area or unit volume. It is frequently applied to living organisms, and particularly to humans...
, ethnicity
Ethnic group
An ethnic group is a group of people whose members identify with each other, through a common heritage, often consisting of a common language, a common culture and/or an ideology that stresses common ancestry or endogamy...
, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

Ethnic Diversity
Africans mainly speaking languages of three families—Bantu, NiloticNilotic
Nilotic people or Nilotes, in its contemporary usage, refers to some ethnic groups mainly in South Sudan, Uganda, Kenya, and northern Tanzania, who speak Nilotic languages, a large sub-group of the Nilo-Saharan languages...
, and Central Sudanic—constitute most of the population.
Bantu peoples are the most numerous and include the Baganda
Baganda
The Ganda are an ethnic group native to Buganda, a subnational kingdom within Uganda. Traditionally comprising 52 tribes the Ganda have a rich history and culture...
in the central area (17%), Basoga in the south-eastern area (8%), Banyankole in the south-western area (8%), Bakiga
Bakiga
The Kiga people, or Abakiga , are an ethnic group located in northern Rwanda and southern Uganda. The Kiga speak a Bantu language called Rukiga. They are sometimes referred to as the Chiga or Kiga, while the singular form is Umukiga...
in the most south-western area (8%), Banyoro in the mid-western area (3%), Batooro in the mid-western area (3%), Bagisu
Bagisu
The Gisu people, or Bagisu , alternately Gishu, Masaba, or Sokwia, are a tribe of the Masaba nation of eastern Uganda, closely related to the Bukusu people of Kenya...
in the eastern area, Bahima in the south-western area (2%), Bafumbira in the south-western area (6%), and other much smaller ethnic groups.
Nilotic
Nilotic
Nilotic people or Nilotes, in its contemporary usage, refers to some ethnic groups mainly in South Sudan, Uganda, Kenya, and northern Tanzania, who speak Nilotic languages, a large sub-group of the Nilo-Saharan languages...
peoples, mainly in the north, are the next largest, including the Langi
Lango
-Lango of Uganda:The Lango or Jo Lango live in the Lango sub-region , north of Lake Kyoga. Lango sub-region comprises the districts of Amolatar, Alebtong, Apac, Dokolo, Kole, Lira, Oyam, and Otuke...
, 6%, and the Acholi, 4%. In the northwest are the Lugbara
Lugbara
The Lugbara are an ethnic group who live mainly in the West Nile region of Uganda and in the adjoining area of the Democratic Republic of the Congo...
, 4%. The Karamojong
Karamojong
The Karamojong or Karimojong, are an ethnic group of agro-pastoral herders living mainly in the north-east of Uganda. Their language is also known as Karamojong or Karimojong, and is part of the Nilo-Saharan language group.-History:...
, 2%, occupy the considerably drier, largely pastoral territory in the northeast. Europeans, Asians, and Arab
Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
s make up about 1% of the population with other groups accounting for the remainder.
More than half of the population is under the age of 15 more than any other country in the world. Uganda's population is predominantly rural, and its density population highest in the southern regions.
South Asians and Arabs
During the Uganda Protectorate period, the British colonialists used South Asian immigrants as intermediaries. Following independence they constituted the largest non-indigenous ethnic group in Uganda, at around 80,000 people, and they dominated trade, industry, and the professions. This caused resentment among the Black majority, which was exploited by post-Independence leaders. After Idi AminIdi Amin
Idi Amin Dada was a military leader and President of Uganda from 1971 to 1979. Amin joined the British colonial regiment, the King's African Rifles in 1946. Eventually he held the rank of Major General in the post-colonial Ugandan Army and became its Commander before seizing power in the military...
came to power in 1971, he declared "economic war" on the Indians, culminating in the Expulsion of Asians in Uganda in 1972
Expulsion of Asians in Uganda in 1972
On 4 August 1972, the then President of Uganda, Idi Amin, ordered the expulsion of his country's Indian minority, giving them 90 days to leave Uganda...
. Since Amin's overthrow in 1979 some Asians have returned. There are about 12,000 in Uganda today, nearly all in the capital Kampala
Kampala
Kampala is the largest city and capital of Uganda. The city is divided into five boroughs that oversee local planning: Kampala Central Division, Kawempe Division, Makindye Division, Nakawa Division and Lubaga Division. The city is coterminous with Kampala District.-History: of Buganda, had chosen...
.
There are also about 3,000 Arabs of various national origins in Uganda.
CIA World Factbook demographic statistics
The following demographic statistics are from the CIA World Factbook, unless otherwise indicated.Population
32,369,558note:
estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS
AIDS
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is a disease of the human immune system caused by the human immunodeficiency virus...
; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality and death rates, lower population and growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2009 estimate).
Age structure
0-14 years:50% (male 8,152,830; female 8,034,366)
15-64 years:
47.9% (male 7,789,209; female 7,703,143)
65 years and over:
2.1% (male 286,693; female 403,317) (2009 estimate)
Sex ratio
at birth:1.03 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.7 male(s)/female
total population:
1.01 male(s)/female (2009 estimate)
Life expectancy at birth
total population:52.72 years
male:
51.66 years
female:
53.81 years (2009 estimate)
Total fertility rate
- 6.73 children born/woman (2010 estimate)
- 6.77 children born/woman (2009 estimate)
Ethnic groups
Ganda 16.9%, Nkole 9.5%, Soga 8.4%, Kiga 6.9%, Teso 6.4%, Langi 6.1%, Acholi 4.7%, Gisu 4.6%, LugbaraLugbara people
The Lugbara are an ethnic group who live mainly in the West Nile region of Uganda and in the adjoining area of the Democratic Republic of the Congo...
4.2%, Nyoro 2.7%, other 29.6% (2002 census)
Religions
Roman Catholic 41.9%, Anglican 35.9%, Pentecostal 4.6%, Seventh-day AdventistSeventh-day Adventist Church
The Seventh-day Adventist Church is a Protestant Christian denomination distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the original seventh day of the Judeo-Christian week, as the Sabbath, and by its emphasis on the imminent second coming of Jesus Christ...
1.5%, Muslim
Muslim
A Muslim, also spelled Moslem, is an adherent of Islam, a monotheistic, Abrahamic religion based on the Quran, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God as revealed to prophet Muhammad. "Muslim" is the Arabic term for "submitter" .Muslims believe that God is one and incomparable...
12.1%, Sikhism
Sikhism
Sikhism is a monotheistic religion founded during the 15th century in the Punjab region, by Guru Nanak Dev and continued to progress with ten successive Sikh Gurus . It is the fifth-largest organized religion in the world and one of the fastest-growing...
& other 3.1%, Baha'i 0.3%, None 0.9% (2002 census)
Languages
SwahiliSwahili language
Swahili or Kiswahili is a Bantu language spoken by various ethnic groups that inhabit several large stretches of the Mozambique Channel coastline from northern Kenya to northern Mozambique, including the Comoro Islands. It is also spoken by ethnic minority groups in Somalia...
(official national language, taught in grade schools, used in courts of law and by most newspapers and some radio broadcasts), Luganda
Luganda language
Ganda, or Luganda , is the major language of Uganda, spoken by over sixteen million Ganda and other people mainly in Southern Uganda, including the capital Kampala. It belongs to the Bantu branch of the Niger–Congo language family...
(most widely used of the Niger–Congo languages
Niger–Congo languages
The Niger–Congo languages constitute one of the world's major language families, and Africa's largest in terms of geographical area, number of speakers, and number of distinct languages. They may constitute the world's largest language family in terms of distinct languages, although this question...
, preferred for native language publications in the capital and may be taught in school), other Bantu languages
Bantu languages
The Bantu languages constitute a traditional sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages. There are about 250 Bantu languages by the criterion of mutual intelligibility, though the distinction between language and dialect is often unclear, and Ethnologue counts 535 languages...
, Nilo-Saharan languages
Nilo-Saharan languages
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of African languages spoken by some 50 million people, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers , including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributaries of Nile meet...
, English, Arabic.

