
Dermatoscopy
Encyclopedia
Skin
-Dermis:The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis that consists of connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis by a basement membrane. It also harbors many Mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and heat...
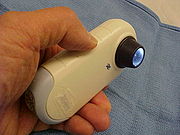
, and allows inspection of skin lesions unobstructed by skin surface reflections. Modern dermatoscopes dispense with the use of liquid medium and instead use polarised light to cancel out skin surface reflections.
This instrument is useful to dermatologists in distinguishing benign from malignant
Malignant
Malignancy is the tendency of a medical condition, especially tumors, to become progressively worse and to potentially result in death. Malignancy in cancers is characterized by anaplasia, invasiveness, and metastasis...
(cancerous) lesions, especially in the diagnosis of melanoma.
Advantages of dermatoscopy
With doctors who are experts in the specific field of dermoscopy, the diagnostic accuracy for melanoma is significantly better than for those dermatologists who do not have any specialized training in dermatoscopy. Thus, with specialists trained in dermoscopy, there is considerable improvement in the sensitivity (detection of melanomas) as well as specificity (percentage of non-melanomas correctly diagnosed as benign), compared with naked eye examination. The accuracy by dermatoscopy was increased up to 20% in the case of sensitivity and up to 10% in the case of specificity, compared with naked eye examiation. By using dermatoscopy the specificity is thereby increased, reducing the frequency of unnecessary surgical excisions of benign lesions.In the studies referred to, a comparison is made between dermatoscopy and an artificial situation of only naked eye examination. In reality, most of the 80% of US dermatologists who do not employ dermatoscopy work in bright rooms and use various magnifiers.
Application of dermatoscopy
- The typical application of dermatoscopy is early detection of melanomaMelanomaMelanoma is a malignant tumor of melanocytes. Melanocytes are cells that produce the dark pigment, melanin, which is responsible for the color of skin. They predominantly occur in skin, but are also found in other parts of the body, including the bowel and the eye...
(see above) - Digital dermatoscopy (videodermatoscopy) is used for monitoring skin lesions suspicious of melanoma. Digital dermatoscopy images are stored and compared to images obtained during the patient’s next visit. Suspicious changes in such a lesion are an indication for excision. Skin lesions, which appear unchanged over time are considered benign. Common systems for digital dermoscopy are FotofinderFotofinderFotoFinder is a worldwide brand for medical imaging systems. The German company FotoFinder Systems GmbH was founded in 1991 and has developed imaging solutions for the early detection of melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer....
, MolemaxMolemaxMoleMax was the first digital epiluminescence microscopy system developed in cooperation with the medical faculty of the university Vienna, department of dermatology...
or Easyscan. - Aid in the diagnosis of skin tumors - such as basal cell carcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas, cylindromas, dermatofibromas, angiomas, seborrheic keratosis and many other common skin tumors have classical dermtoscopic findings.
- Aid in the diagnosis of scabies and pubic louse. By staining the skin with India ink, a dermatoscope can help identify the location of the mite in the burrow, facilitating scraping of the scabetic burrow. By magnifying pubic louse, it allows for rapid diagnosis of the difficult to see small insects.
- Aid in the diagnosis of warts. By allowing a physician to visualize the structure of a wart, to distinguish it from corn, callouses, trauma, or foreign bodies. By examining warts at late stages of treatment, to assure that therapy is not stopped prematurely due to difficult to visualize wart structures.
- Aid in the diagnosis of fungal infections. To differentiate "black dot" tinea, or tinea capitis (fungal scalp infection) from alopecia areataAlopecia areataAlopecia areata is a medical condition in which hair is lost from some or all areas of the body, usually from the scalp. Because it causes bald spots on the scalp, especially in the first stages, it is sometimes called spot baldness. In 1–2% of cases, the condition can spread to the entire scalp ...
. - Aid in the diagnosis of hair and scalp diseases, such as alopecia areata, female androgenic alopecia, monilethrixMonilethrixMonilethrix is a rare autosomal dominant hair disease that results in short, fragile, broken hair that appears beaded. It comes from the Latin word for necklace and the Greek word for hair ....
, Netherton syndromeNetherton syndromeNetherton syndrome is a severe, autosomal recessive form of ichthyosis associated with mutations in the SPINK5 gene. It is named after E.W. Netherton.- Characteristics :...
, and woolly hair syndrome. Dermoscopy of hair and scalp is called trichoscopyTrichoscopyTrichoscopy is a method of hair and scalp evaluation and is used for diagnosing hair and scalp diseases. The method is based on dermoscopy and videodermoscopy. In trichoscopy hair and scalp structures may be visualized at many-fold magnification...
.
- Determination of surgical margin of hard to define skin cancers. Examples would be Bowen’s disease, superficial basal cell carcinomas, and lentigo malignas. These tumors have very indistinct margins. By allowing the surgeon to correctly identify the true extent of the tumor, repeat surgery often is decreased.
History
Skin surface microscopy started in 1663 by Kolhaus and was improved with the addition of immersion oil in 1878 by Ernst Abbe. The German dermatologist, Johann Saphier, added a built-in light source to the instrument. GoldmanGoldman
Goldman is the surname of several people:* Albert Goldman, American professor and author* Albert Goldman , American Trotskyist and lawyer* Alvin Ira Goldman, philosopher* Charley Goldman, boxing trainer...
was the first dermatologist to coin the term "dermascopy" and to use the dermatoscope to evaluate pigmented cutaneous lesions.
In 2001, a California medical device manufacturer, 3Gen, introduced the first polarized dermatoscope, the DermLite. Polarised illumination, coupled with a cross-polarised viewer, reduces (polarised) skin surface reflection, thus allowing visualisation of skin structures (the light from which is depolarised) without using an immersion fluid. Examination of several lesions is thus more convenient because physicians no longer have to stop and apply immersion oil, alcohol, or water to the skin before examining each lesion. With the marketing of polarised dermatoscopes, dermatoscopy increased in popularity among physicians worldwide. Although images produced by polarised light dermatoscopes are slightly different from those produced by a traditional skin contact glass dermatoscope, they have certain advantages, such as vascular patterns not being potentially missed through compression of the skin by a glass contact plate.

