
Descent direction
Encyclopedia
In optimization
, a descent direction is a vector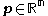 that, in the sense below, moves us closer towards a local minimum
that, in the sense below, moves us closer towards a local minimum 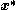 of our objective function
of our objective function 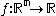 .
.
Suppose we are computing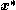 by an iterative method, such as line search. We define a descent direction
by an iterative method, such as line search. We define a descent direction 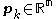 at the
at the 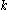 th iterate to be any
th iterate to be any 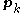 such that
such that 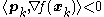 , where
, where 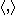 denotes the inner product. The motivation for such an approach is that small steps along
denotes the inner product. The motivation for such an approach is that small steps along 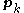 guarantee that
guarantee that 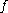 is reduced, by Taylor's theorem
is reduced, by Taylor's theorem
.
Using this definition, the negative of a non-zero gradient is always a
descent direction, as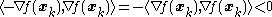 .
.
Numerous methods exist to compute descent directions, all with differing merits. For example, one could use gradient descent
or the conjugate gradient method
.
Optimization (mathematics)
In mathematics, computational science, or management science, mathematical optimization refers to the selection of a best element from some set of available alternatives....
, a descent direction is a vector
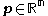 that, in the sense below, moves us closer towards a local minimum
that, in the sense below, moves us closer towards a local minimum 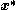 of our objective function
of our objective function 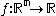 .
.Suppose we are computing
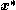 by an iterative method, such as line search. We define a descent direction
by an iterative method, such as line search. We define a descent direction 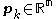 at the
at the 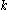 th iterate to be any
th iterate to be any 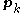 such that
such that 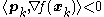 , where
, where 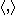 denotes the inner product. The motivation for such an approach is that small steps along
denotes the inner product. The motivation for such an approach is that small steps along 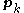 guarantee that
guarantee that 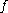 is reduced, by Taylor's theorem
is reduced, by Taylor's theoremTaylor's theorem
In calculus, Taylor's theorem gives an approximation of a k times differentiable function around a given point by a k-th order Taylor-polynomial. For analytic functions the Taylor polynomials at a given point are finite order truncations of its Taylor's series, which completely determines the...
.
Using this definition, the negative of a non-zero gradient is always a
descent direction, as
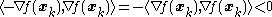 .
.Numerous methods exist to compute descent directions, all with differing merits. For example, one could use gradient descent
Gradient descent
Gradient descent is a first-order optimization algorithm. To find a local minimum of a function using gradient descent, one takes steps proportional to the negative of the gradient of the function at the current point...
or the conjugate gradient method
Conjugate gradient method
In mathematics, the conjugate gradient method is an algorithm for the numerical solution of particular systems of linear equations, namely those whose matrix is symmetric and positive-definite. The conjugate gradient method is an iterative method, so it can be applied to sparse systems that are too...
.

