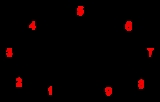
Dibenzofuran
Encyclopedia
Dibenzofuran, is a heterocyclic organic compound
with the chemical structure
shown at right. It is an aromatic compound that has two benzene
rings fused to one furan
ring in the middle. All of the numbered carbon
atoms have a hydrogen
atom bonded to each of them (not shown in the image). Dibenzofuran is an aromatic ether
having the chemical formula C12H8O.
(PCDFs), a family of organic compounds which are polyhalogenated compound
s which have atom or group substitutions made for the hydrogens on any of the numbered carbon atoms in the dibenzofuran structure. For example, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzofuran (TCDF) has chlorine
atoms substituted for each of the hydrogens on the number 2, 3, 7, and 8 carbons (see structure below). Polychlorinated dibenzofurans are very toxic
chemicals with properties and chemical structures similar to polychlorinated dibenzodioxins, often simply called dioxin
.
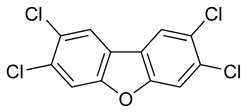 The dibenzofuran TCDF (2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzofuran) is the dibenzofuran analog of the polychlorinated dibenzodioxin TCDD (2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxin
The dibenzofuran TCDF (2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzofuran) is the dibenzofuran analog of the polychlorinated dibenzodioxin TCDD (2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxin
), the poison released in the Seveso disaster
.
It is a white crystal-like solid created from production of coal tar. It is used as an insecticide, in the production of PVC, industrial bleaching and incineration.
Production and Producers: Dibenzofuran is recovered from a wash oil fraction of coal tar that boils between 275 °C and 290 °C. Redistillation separates dibenzofuran from acenaphthene, which boils at a lower temperature. Crystallization of the redistilled fraction then produces technically pure dibenzofuran. Typical wood preservative creosote is approximately 3.5% dibenzofuran. Dibenzofuran occurs at levels of 0.19-1.50 wt % of dry tar in commercial coal tars. It also is a by-product of smoking and affects both the smoker and second hand smokers.
Pathways of exposure
Occupational exposure to dibenzofuran may occur through inhalation and dermal contact, particularly at sites where coal tar, coal tar derivatives, and creosote are produced and used.
General Population Exposure: Fish and dairy intake also have been studied to be related with body burden of dibenzofuran in pregnant women. Consumption of contaminated water and food are the primary sources of exposure.
Excretion:
Dibenzofuran is excreted 22% the daily intake of dioxins from meals is excreted from feces and 29% from sebum.
Regulatory Status:
Dibenzofuran is cited in the Clean Air Act 1990 Amendments -Hazardous Air Pollutants as a volatile hazardous air pollutant of potential concern. The Superfund Amendment Reauthorization Act (SARA) Section 110 placed dibenzofuran on the revised Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry
(ATSDR) priority list of hazardous substances to be the subject of a toxicological profile. The listing was based on the substance’s frequency of occurrence at Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA) National Priorities List sites, its toxicity, and/or its potential for human exposure. Dibenzofuran is also listed in the Massachusetts Substance List for Right-to-Know Law, the New Jersey Department of Health Hazard Right-to-Know Program Hazardous Substance List, and the Pennsylvania Department of Labor and Industry Hazardous Substance List. California’s Air Toxics “Hot Spots” List (Assembly Bill).
Testing process
No medical test exists to identify dibenzofuran. But if symptoms of eye, nose, throat or skin irritation occurs after exposure (accidentally / workplace) medical attention is recommended. EPA uses High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) to monitor samples.
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
with the chemical structure
Chemical structure
A chemical structure includes molecular geometry, electronic structure and crystal structure of molecules. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together. Molecular geometry can range from the very simple, such as...
shown at right. It is an aromatic compound that has two benzene
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
rings fused to one furan
Furan
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen. The class of compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans....
ring in the middle. All of the numbered carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
atoms have a hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
atom bonded to each of them (not shown in the image). Dibenzofuran is an aromatic ether
Ether
Ethers are a class of organic compounds that contain an ether group — an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups — of general formula R–O–R'. A typical example is the solvent and anesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether"...
having the chemical formula C12H8O.
Dibenzofurans
Dibenzofurans can also refer to polychlorinated dibenzofuransPolychlorinated dibenzofurans
Polychlorinated dibenzofurans are a group of halogenated organic compounds which are toxic environmental pollutants. They are known teratogens, mutagens, and suspected human carcinogens. PCDFs tend to co-occur with polychlorinated dibenzodioxins...
(PCDFs), a family of organic compounds which are polyhalogenated compound
Polyhalogenated compound
Polyhalogenated compounds are any compounds with multiple substitutions of halogens. They are of particular interest and importance because halogens generally are highly reactive and also bioaccumulate in humans, and comprise a superset of which has many toxic and carcinogenic industrial...
s which have atom or group substitutions made for the hydrogens on any of the numbered carbon atoms in the dibenzofuran structure. For example, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzofuran (TCDF) has chlorine
Chlorine
Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine...
atoms substituted for each of the hydrogens on the number 2, 3, 7, and 8 carbons (see structure below). Polychlorinated dibenzofurans are very toxic
Toxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a substance can damage a living or non-living organisms. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a substructure of the organism, such as a cell or an organ , such as the liver...
chemicals with properties and chemical structures similar to polychlorinated dibenzodioxins, often simply called dioxin
Dioxins and dioxin-like compounds
Dioxins and dioxin-like compounds are by-products of various industrial processes, and are commonly regarded as highly toxic compounds that are environmental pollutants and persistent organic pollutants . They include:...
.

2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzodioxin
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin is a polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin . It is the most potent compound of the series and became known as a contaminant in Agent Orange, a herbicide used in the Vietnam War, as well as the Seveso disaster...
), the poison released in the Seveso disaster
Seveso disaster
The Seveso disaster was an industrial accident that occurred around 12:37 pm July 10, 1976, in a small chemical manufacturing plant approximately north of Milan in the Lombardy region in Italy...
.
Environmental and health consequences
Probable places of originIt is a white crystal-like solid created from production of coal tar. It is used as an insecticide, in the production of PVC, industrial bleaching and incineration.
Production and Producers: Dibenzofuran is recovered from a wash oil fraction of coal tar that boils between 275 °C and 290 °C. Redistillation separates dibenzofuran from acenaphthene, which boils at a lower temperature. Crystallization of the redistilled fraction then produces technically pure dibenzofuran. Typical wood preservative creosote is approximately 3.5% dibenzofuran. Dibenzofuran occurs at levels of 0.19-1.50 wt % of dry tar in commercial coal tars. It also is a by-product of smoking and affects both the smoker and second hand smokers.
Pathways of exposure
Occupational exposure to dibenzofuran may occur through inhalation and dermal contact, particularly at sites where coal tar, coal tar derivatives, and creosote are produced and used.
General Population Exposure: Fish and dairy intake also have been studied to be related with body burden of dibenzofuran in pregnant women. Consumption of contaminated water and food are the primary sources of exposure.
Excretion:
Dibenzofuran is excreted 22% the daily intake of dioxins from meals is excreted from feces and 29% from sebum.
Regulatory Status:
Dibenzofuran is cited in the Clean Air Act 1990 Amendments -Hazardous Air Pollutants as a volatile hazardous air pollutant of potential concern. The Superfund Amendment Reauthorization Act (SARA) Section 110 placed dibenzofuran on the revised Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry
Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry
The Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry is a federal public health agency within the United States Department of Health and Human Services. The agency focuses on minimizing human health risks associated with exposure to hazardous substances...
(ATSDR) priority list of hazardous substances to be the subject of a toxicological profile. The listing was based on the substance’s frequency of occurrence at Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA) National Priorities List sites, its toxicity, and/or its potential for human exposure. Dibenzofuran is also listed in the Massachusetts Substance List for Right-to-Know Law, the New Jersey Department of Health Hazard Right-to-Know Program Hazardous Substance List, and the Pennsylvania Department of Labor and Industry Hazardous Substance List. California’s Air Toxics “Hot Spots” List (Assembly Bill).
Testing process
No medical test exists to identify dibenzofuran. But if symptoms of eye, nose, throat or skin irritation occurs after exposure (accidentally / workplace) medical attention is recommended. EPA uses High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) to monitor samples.

