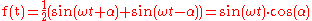Differential gain
Encyclopedia
Differential gain is a kind of linearity distortion which affects the color saturation in TV broadcasting.
The first two terms are usually called composite video signal (CVS)
The modulation technique of the color subcarrier is quadrature amplitude modulation
(QUAM ) both in PAL
and NTSC
systems. The amplitude of the color signal represents the saturation (purity) in both systems. On the other hand, the level of the CVS represents the brightness. So in order to reproduce the original vision in the receiver the ratio between these two pieces of information should be kept constant in the receiver.
In cable broadcasting
and satellite broadcasting some of the above maybe replaced by other equipment.
All of the above circuitry include active circuit devices. These devices are only approximatelly linear devices. In particular, amplification factor is not constant for all levels. Usually the amplification factor decreases as the input level increases. This is known as gain nonlinearity
. In system specifications, the nonlinearity in percentage is almost always specified. It must be under a tolerable level depending on the required sensitivity of the system.
The output of an ideal amplifier with the amplification factor of A is;
However, in practice this goal is almost never attained. The amplification factor of color signal is always slightly different than that of CVS. (The color signal is superimposed on CVS.)
According to European standarts DG should be less than % 10.
 be the phase lag.
be the phase lag.
So the phase differences between two consecutive lines (so called differential phase
) are converted to differential gain distortions. ( Hue is preserved at the risk of decreased saturation)
For example, a differential phase of 100 introduces an additional gain loss of % 2.
Composite color video signal
Composite color video signal (CCVS) consists of three terms:- LuminanceLuminanceLuminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle. The SI unit for luminance is candela per square...
(monochrome) signal - Auxiliary signals (sync pulse and blanking level signals )
- ChrominanceChrominanceChrominance is the signal used in video systems to convey the color information of the picture, separately from the accompanying luma signal . Chrominance is usually represented as two color-difference components: U = B' − Y' and V = R' − Y'...
, which is actually a subcarrier modulated by chromaChrominanceChrominance is the signal used in video systems to convey the color information of the picture, separately from the accompanying luma signal . Chrominance is usually represented as two color-difference components: U = B' − Y' and V = R' − Y'...
information
The first two terms are usually called composite video signal (CVS)
The modulation technique of the color subcarrier is quadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation is both an analog and a digital modulation scheme. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit streams, by changing the amplitudes of two carrier waves, using the amplitude-shift keying digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation analog...
(QUAM ) both in PAL
PAL
PAL, short for Phase Alternating Line, is an analogue television colour encoding system used in broadcast television systems in many countries. Other common analogue television systems are NTSC and SECAM. This page primarily discusses the PAL colour encoding system...
and NTSC
NTSC
NTSC, named for the National Television System Committee, is the analog television system that is used in most of North America, most of South America , Burma, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, the Philippines, and some Pacific island nations and territories .Most countries using the NTSC standard, as...
systems. The amplitude of the color signal represents the saturation (purity) in both systems. On the other hand, the level of the CVS represents the brightness. So in order to reproduce the original vision in the receiver the ratio between these two pieces of information should be kept constant in the receiver.
Non linearity in the broadcast system
The main steps of visual signal from the scene to receiver screen (for terrestrial broadcasting) are as follows:- Cameras and associated bufferBuffer amplifierA buffer amplifier is one that provides electrical impedance transformation from one circuit to another...
stages - Recording circuits and storage medium (CDs, tapes etc.)
- Playback units and studio equipment
- Cable, microwave or TVRO equipment
- Transmitters (and sometimes also transposerTransposerIn broadcasting, a transposer is a device in the service area of a transmitter which rebroadcasts signals to the receivers which can’t properly receive the signals of the transmitter because of a physical obstruction . A transposer receives the signals of the transmitter and rebroadcasts the...
s) - Receivers (and sometimes also antenna amplifierAntenna amplifierIn electronics, an antenna amplifier, also called antenna preamplifier, antenna preamp or antenna booster, is a device that amplifies an antenna signal, usually into an output with the same impedance as the input impedance....
s and distribution units)
In cable broadcasting
Cable television
Cable television is a system of providing television programs to consumers via radio frequency signals transmitted to televisions through coaxial cables or digital light pulses through fixed optical fibers located on the subscriber's property, much like the over-the-air method used in traditional...
and satellite broadcasting some of the above maybe replaced by other equipment.
All of the above circuitry include active circuit devices. These devices are only approximatelly linear devices. In particular, amplification factor is not constant for all levels. Usually the amplification factor decreases as the input level increases. This is known as gain nonlinearity
Nonlinearity
In mathematics, a nonlinear system is one that does not satisfy the superposition principle, or one whose output is not directly proportional to its input; a linear system fulfills these conditions. In other words, a nonlinear system is any problem where the variable to be solved for cannot be...
. In system specifications, the nonlinearity in percentage is almost always specified. It must be under a tolerable level depending on the required sensitivity of the system.
Differential gain
Differential gain is a special case of gain nonlinearity. Let CCVS is given byThe output of an ideal amplifier with the amplification factor of A is;
However, in practice this goal is almost never attained. The amplification factor of color signal is always slightly different than that of CVS. (The color signal is superimposed on CVS.)
Problems caused by differential gain
Any color can be totally described by luminance, saturation and hue. When the gain of the reproduced color signal is lower than that of luminance, the perceived colors are paler than their originals. Conversely, when the gain of the reproduced color signal is higher than the luminance, the perceived colors are too loud.Measuring
To measure the percentage of differential gain, the standart sawtooth signal with superimposed color carrier is used. (4.43 MHz. in PAL and 3.58 MHz. in NTSC) The sawtooth represents the CVS with all possible levels between 0.3 v to 1 V. The waveforms are shown in the accompanying image frame.The top figure shows the input. Note that the amplitude of the superimposed color signal is constant. The middle figure shows the distorted output. In this example, color signal superimposed on a high level luminance signal has been attenuated.The bottom figure shows the same waveform after passing through a high pass filter to facilitate measuring. (CVS is filtered out leaving only color signal) .According to European standarts DG should be less than % 10.
A special case of PAL
DG is a problem both in NTSC and PAL. But PAL is more sensetive to this kind of distortion. System PAL averages phase differences of color signal in two consecutive lines. Let be the phase lag.
be the phase lag.So the phase differences between two consecutive lines (so called differential phase
Differential phase
Differential phase is a kind of linearity distortion which affects the color hue in TV broadcasting.- Composite color video signal :Composite color video signal consists of three terms:*Monochrome signal...
) are converted to differential gain distortions. ( Hue is preserved at the risk of decreased saturation)
For example, a differential phase of 100 introduces an additional gain loss of % 2.
Further reading
- Measuring Differential Gain and Phase, Texas InstrumentsTexas InstrumentsTexas Instruments Inc. , widely known as TI, is an American company based in Dallas, Texas, United States, which develops and commercializes semiconductor and computer technology...
- Doc.Dr.Mümtaz Yılmaz:Renkli Televizyon Tekniği,TRT yayınları, Ankara, 1979, pp. 32–47