
Diffusing-wave spectroscopy
Encyclopedia
Diffusing-wave spectroscopy (DWS) is an optical technique derived from dynamic light scattering
(DLS) that studies the dynamics of scattered light in the limit of strong multiple scattering. It has been widely used in the past to study colloidal suspension
s, emulsions, foams, gels, biological media and other forms of soft matter
. If carefully calibrated, DWS allows the quantitative measurement of microscopic motion in a soft material, from which the rheological properties of the complex medium can be extracted via the so-called microrheology
approach.
The signal is analysed by calculating the intensity autocorrelation
function called g2.
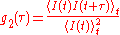
For the case of non-interacting particles suspended in a (complex) fluid a direct relation between g2-1 and the mean square displacement of the particles <Δr2> can be established. Let's note P(s) the probability density function (PDF) of the photon path length s. The relation can be written as follows:
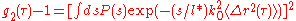
with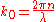 and
and 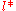 is the transport mean free path of scattered light.
is the transport mean free path of scattered light.
For simple cell geometries, it is thus possible to calculate the mean square displacement of the particles <Δr2> from the measured g2-1 values analytically. For example, for the backscattering geometry, an infinitely thick cell, large laser spot illumination and detection of photons coming from the center of the spot, the relation ship between g2-1 and <Δr2> is:
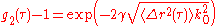 , γ value is around 2.
, γ value is around 2.
For less thick cells and in transmission, the relationship depends also on l* (the transport length).
) or a ground glass to create a large number of speckle realizations (Echo-DWS ). In both cases an average over a large number of statistically independent intensity values is obtained, allowing a much faster data acquisition time.
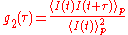
MSDWS is particularly adapted for the study of slow dynamics and non ergodic media. Echo-DWS allows seamless integration of MSDWS in a traditional DWS-scheme with superior temporal resolution down to 12 ns. Camera based adaptive image processing allows online measurement of particle dynamics for example during drying.
Dynamic light scattering
thumb|right|350px|Hypothetical Dynamic light scattering of two samples: Larger particles on the top and smaller particle on the bottomDynamic light scattering is a technique in physics that can be used to determine the size distribution profile of small particles in suspension or polymers...
(DLS) that studies the dynamics of scattered light in the limit of strong multiple scattering. It has been widely used in the past to study colloidal suspension
Suspension
Suspension may refer to:In science and engineering:*Suspension , in mathematics*Suspension , in mathematics*Suspension , mixture of two chemicals with the property that one does not rapidly settle out...
s, emulsions, foams, gels, biological media and other forms of soft matter
Soft matter
Soft matter is a subfield of condensed matter comprising a variety of physical states that are easily deformed by thermal stresses or thermal fluctuations. They include liquids, colloids, polymers, foams, gels, granular materials, and a number of biological materials...
. If carefully calibrated, DWS allows the quantitative measurement of microscopic motion in a soft material, from which the rheological properties of the complex medium can be extracted via the so-called microrheology
Microrheology
Microrheology is a technique to measure the rheological properties of a medium, such as microviscosity, via the measurement of the trajectory of a flow tracer . It is a new way of doing rheology, traditionally done using a rheometer. The size of the tracer is around a micrometre...
approach.
One-speckle diffusing-wave spectroscopy
Laser light is sent to the sample and the outcoming transmitted or backscattered light is detected by an optoelectric sensor. The light intensity detected is the result of the interference of all the optical waves coming from the different light paths.The signal is analysed by calculating the intensity autocorrelation
Autocorrelation
Autocorrelation is the cross-correlation of a signal with itself. Informally, it is the similarity between observations as a function of the time separation between them...
function called g2.
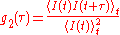
For the case of non-interacting particles suspended in a (complex) fluid a direct relation between g2-1 and the mean square displacement of the particles <Δr2> can be established. Let's note P(s) the probability density function (PDF) of the photon path length s. The relation can be written as follows:
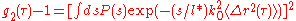
with
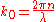 and
and 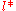 is the transport mean free path of scattered light.
is the transport mean free path of scattered light.For simple cell geometries, it is thus possible to calculate the mean square displacement of the particles <Δr2> from the measured g2-1 values analytically. For example, for the backscattering geometry, an infinitely thick cell, large laser spot illumination and detection of photons coming from the center of the spot, the relation ship between g2-1 and <Δr2> is:
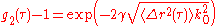 , γ value is around 2.
, γ value is around 2.For less thick cells and in transmission, the relationship depends also on l* (the transport length).
Multispeckle Diffusing-Wave Spectroscopy (MSDWS)
This technique either uses a camera to detect many speckle grains (see speckle patternSpeckle pattern
A speckle pattern is a random intensity pattern produced by the mutual interference of a set of wavefronts. This phenomenon has been investigated by scientists since the time of Newton, but speckles have come into prominence since the invention of the laser and have now found a variety of...
) or a ground glass to create a large number of speckle realizations (Echo-DWS ). In both cases an average over a large number of statistically independent intensity values is obtained, allowing a much faster data acquisition time.
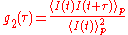
MSDWS is particularly adapted for the study of slow dynamics and non ergodic media. Echo-DWS allows seamless integration of MSDWS in a traditional DWS-scheme with superior temporal resolution down to 12 ns. Camera based adaptive image processing allows online measurement of particle dynamics for example during drying.

