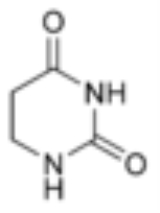
Dihydrouracil
Encyclopedia
Dihydrouracil is an intermediate in the catabolism of uracil
.
Uracil
Uracil is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of RNA that are represented by the letters A, G, C and U. The others are adenine, cytosine, and guanine. In RNA, uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds. In DNA, the uracil nucleobase is replaced by thymine.Uracil is a common and...
.
See also
- Dihydrouracil dehydrogenase (NAD+)Dihydrouracil dehydrogenase (NAD+)In enzymology, a dihydrouracil dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactionThus, the two substrates of this enzyme are 5,6-dihydrouracil and NAD+, whereas its 3 products are uracil, NADH, and H+....
- Dihydrouracil oxidaseDihydrouracil oxidaseIn enzymology, a dihydrouracil oxidase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactionThus, the two substrates of this enzyme are 5,6-dihydrouracil and O2, whereas its two products are uracil and H2O2....
- DihydropyrimidinaseDihydropyrimidinaseIn enzymology, a dihydropyrimidinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactionThus, the two substrates of this enzyme are 5,6-dihydrouracil and H2O, whereas its product is 3-ureidopropanoate....

