
Direct Stream Digital
Encyclopedia
Direct-Stream Digital is the trademark
name used by Sony
and Philips
for their system of recreating audible signals which uses pulse-density modulation
encoding
, a technology
to store audio
signal
s on digital
storage media which is used for the Super Audio CD
(SACD).
The signal is stored as delta-sigma modulated
digital audio
, a sequence of single bit values at a sampling rate
of 64 times the CD Audio sampling rates of 44.1 kHz, for a rate of 2.8224 MHz (1 bit times 64 times 44.1 kHz). Noise shaping
occurs by use of the 64× oversampled
signal to reduce noise/distortion
caused by the inaccuracy of quantization
of the audio signal to a single bit. Therefore it is a topic of discussion whether it is possible to eliminate distortion
in 1-bit Sigma-Delta conversion.
Practical DSD converter implementations were pioneered by Andreas Koch and Ed Meitner, the original founders of EMM Labs. Andreas Koch later left EMM Labs and along with Jonathan Tinn, founded Playback Designs who have pioneered the transfer of DSD files over USB connections. Global DSD technology was developed by Sony and Philips, the designers of the audio CD
. Philips' DSD tool division was transferred to Sonic Studio, LLC in 2005 for on-going design and development.
DSD technology may also have potential for video applications. A similar structure based on pulse-width modulation
, which is decoded in the same way as DSD, has been used in Laserdisc
video.
 SACD
SACD
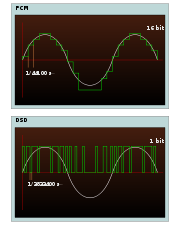
audio is stored in a format called Direct Stream Digital (DSD), which differs from the conventional PCM
used by the compact disc
or conventional computer audio systems.
DSD is 1-bit
, has a sampling rate of 2.8224 MHz, and makes use of noise shaping
quantization
techniques in order to push 1-bit quantization noise up to inaudible ultrasonic frequencies. This gives the format a greater dynamic range
and wider frequency response
than the CD. The SACD format is capable of delivering a dynamic range
of 120 dB
from 20 Hz to 20 kHz and an extended frequency response
up to 100 kHz
, although most currently available players list an upper limit of 80–90 kHz and 20 kHz is the upper limit of human hearing.
The process of creating a DSD signal is conceptually similar to taking a 1-bit delta-sigma
analog-to-digital
(A/D) converter and removing the decimator, which converts the 1-bit bitstream into multibit PCM. Instead, the 1-bit signal is recorded directly and in theory only requires a lowpass filter to reconstruct the original analog waveform. In reality it is a little more complex, and the analogy is incomplete in that 1-bit sigma-delta converters are these days rather unusual, one reason being that a 1-bit signal cannot be dither
ed properly: most modern sigma-delta converters are multibit.
Because of the nature of sigma-delta converters, one cannot make a direct comparison between DSD and PCM. An approximation is possible, though, and would place DSD in some aspects comparable to a PCM format that has a bit depth of 20 bits and a sampling frequency of 96 kHz. PCM sampled at 24 bits provides a (theoretical) additional 24 dB of dynamic range.
Because it has been extremely difficult to carry out DSP operations (for example performing EQ, balance, panning and other changes in the digital domain) in a 1-bit environment, and because of the prevalence of studio equipment such as Pro Tools
, which is solely PCM-based, the vast majority of SACDs — especially rock and contemporary music which relies on multitrack techniques — are in fact mixed in PCM (or mixed analog and recorded on PCM recorders) and then converted to DSD for SACD mastering.
To address some of these issues, a new studio format has been developed, usually referred to as "DSD-wide", which retains standard DSD's high sample rate but uses an 8-bit
, rather than single-bit digital word length, but still relies heavily on the noise shaping
principle. It becomes almost the same as PCM (it's sometimes disparagingly referred to as "PCM-narrow") but has the added benefit of making DSP operations in the studio a great deal more practical. The main difference is that "DSD-wide" still retains 2.8224 MHz (64Fs) sampling frequency while the highest frequency in which PCM is being edited is 352.8 kHz (8Fs). The "DSD-wide" signal is down-converted to regular DSD for SACD mastering. As a result of this technique and other developments there are now a few digital audio workstation
s (DAWs) that operate, or can operate, in the DSD domain, notably Pyramix and some SADiE systems.
Another format for DSD editing is DXD (Digital eXtreme Definition
), a "PCM-like" signal with 24-bit resolution sampled at 352.8 kHz.
Note that high-resolution PCM (DVD-Audio
, HD DVD
and Blu-ray Disc
) and DSD (SACD) may still technically differ at high frequencies. A reconstruction filter is typically used in PCM decoding systems, much the same way that bandwidth-limiting filters are normally used in PCM encoding systems. Any error or unwanted artifact introduced by such filters will typically affect the end-result. A claimed advantage of DSD is that product designers commonly choose to have no filtering, or modest filtering. Instead DSD leads to constant high levels of noise at these frequencies. DSD's dynamic range decreases quickly at frequencies over 20 kHz due to the use of strong noise shaping
techniques which push the noise out of the audio band resulting in a rising noise floor just above 20 kHz. PCM's dynamic range, on the other hand, is the same at all frequencies. (Some high-end SACD players employ an optional low-pass filter set at 30 kHz for compatibility and safety reasons, suitable for situations where amplifiers or loudspeakers cannot deliver an undistorted output if noise above 30 kHz is present in the signal.)
. HQPlayer from Feb 16 2011 ver 2.6.0 beta includes support for direct/native playback from DSDIFF and DSF files to ASIO devices with DSD support. Moreover, Sony produces two SACD-players, the SCD-XA5400ES and the SCD-XE800, that fully support the DSD-disc format. Only so-called DSF format is supported. DSF is a stereo-only, simplified form of DFF, the format used for SACD mastering and 5.1-channel downloads.
Playback Designs' players and converters and pro-audio company 'Mytek Digitals 192 Stereo DAC both sport DSD over USB capability. Apparently, this would provide owners of DSD-recorders from Korg, Tascam and others with a computer-based playback option for their (non-encrypted) DSD-files. Whether these USB-DAC will be compatible with the DSD-disc specification still remains to be seen.
audio CD standard. DSD-CDs are fully compatible with CD.
DSD-CD has been marketed as an audiophile
medium, primarily in Hong Kong with music by Cantopop
artists such as Sally Yeh
.
The Korg MR-1000 1-bit digital recorder samples at 5.6 MHz, twice the SACD rate. It's also referred to as DSD128 because of the sample rate 128x that of CD.
over which encoding system is superior. Professors Stanley Lipshitz and John Vanderkooy from the University of Waterloo
, in Audio Engineering Society Convention Paper 5395 (2001), stated that 1-bit converters (as employed by DSD) are unsuitable for high-end applications due to their high distortion. Even 8-bit, four-times-oversampled PCM with noise shaping, proper dithering and half data rate of DSD has better noise floor and frequency response. However, in 2002, Philips published a convention paper arguing against this in Convention Paper 5616. Lipshitz and Vanderkooy's paper has been criticized in detail by Professor Jamie Angus at an Audio Engineering Society presentation in Convention Paper 5619. Lipshitz and Vanderkooy responded in Convention Paper 5620.
When comparing a DSD and PCM recording of the same origin, the same number of channels and similar bandwidth/SNR, some still think that there are differences. A study conducted at the Erik-Thienhaus Institute in Detmold, Germany, seems to contradict this, concluding that "hardly any of the subjects could make a reproducible distinction between the two encoding systems. Hence it may be concluded that no significant differences are audible."
Trademark
A trademark, trade mark, or trade-mark is a distinctive sign or indicator used by an individual, business organization, or other legal entity to identify that the products or services to consumers with which the trademark appears originate from a unique source, and to distinguish its products or...
name used by Sony
Sony
, commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues....
and Philips
Philips
Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. , more commonly known as Philips, is a multinational Dutch electronics company....
for their system of recreating audible signals which uses pulse-density modulation
Pulse-density modulation
Pulse-density modulation, or PDM, is a form of modulation used to represent an analog signal with digital data. In a PDM signal, specific amplitude values are not encoded into pulses of different size as they would be in PCM. Instead, it is the relative density of the pulses that corresponds to...
encoding
Encoder
An encoder is a device, circuit, transducer, software program, algorithm or person that converts information from one format or code to another, for the purposes of standardization, speed, secrecy, security, or saving space by shrinking size.-Media:...
, a technology
Technology
Technology is the making, usage, and knowledge of tools, machines, techniques, crafts, systems or methods of organization in order to solve a problem or perform a specific function. It can also refer to the collection of such tools, machinery, and procedures. The word technology comes ;...
to store audio
Sound
Sound is a mechanical wave that is an oscillation of pressure transmitted through a solid, liquid, or gas, composed of frequencies within the range of hearing and of a level sufficiently strong to be heard, or the sensation stimulated in organs of hearing by such vibrations.-Propagation of...
signal
Signal processing
Signal processing is an area of systems engineering, electrical engineering and applied mathematics that deals with operations on or analysis of signals, in either discrete or continuous time...
s on digital
Digital
A digital system is a data technology that uses discrete values. By contrast, non-digital systems use a continuous range of values to represent information...
storage media which is used for the Super Audio CD
Super Audio CD
Super Audio CD is a high-resolution, read-only optical disc for audio storage. Sony and Philips Electronics jointly developed the technology, and publicized it in 1999. It is designated as the Scarlet Book standard. Sony and Philips previously collaborated to define the Compact Disc standard...
(SACD).
The signal is stored as delta-sigma modulated
Delta-sigma modulation
Delta-sigma modulation is a method for encoding high-resolution or analog signals into lower-resolution digital signals. The conversion is done using error feedback, where the difference between the two signals is measured and used to improve the conversion...
digital audio
Digital audio
Digital audio is sound reproduction using pulse-code modulation and digital signals. Digital audio systems include analog-to-digital conversion , digital-to-analog conversion , digital storage, processing and transmission components...
, a sequence of single bit values at a sampling rate
Sampling rate
The sampling rate, sample rate, or sampling frequency defines the number of samples per unit of time taken from a continuous signal to make a discrete signal. For time-domain signals, the unit for sampling rate is hertz , sometimes noted as Sa/s...
of 64 times the CD Audio sampling rates of 44.1 kHz, for a rate of 2.8224 MHz (1 bit times 64 times 44.1 kHz). Noise shaping
Noise shaping
Noise shaping is a technique typically used in digital audio, image, and video processing, usually in combination with dithering, as part of the process of quantization or bit-depth reduction of a digital signal...
occurs by use of the 64× oversampled
Oversampling
In signal processing, oversampling is the process of sampling a signal with a sampling frequency significantly higher than twice the bandwidth or highest frequency of the signal being sampled...
signal to reduce noise/distortion
Distortion
A distortion is the alteration of the original shape of an object, image, sound, waveform or other form of information or representation. Distortion is usually unwanted, and often many methods are employed to minimize it in practice...
caused by the inaccuracy of quantization
Quantization (sound processing)
In signal processing and digital audio, quantization is the process of approximating a continuous range of values by a relatively small set of discrete symbols or integer values...
of the audio signal to a single bit. Therefore it is a topic of discussion whether it is possible to eliminate distortion
Distortion
A distortion is the alteration of the original shape of an object, image, sound, waveform or other form of information or representation. Distortion is usually unwanted, and often many methods are employed to minimize it in practice...
in 1-bit Sigma-Delta conversion.
Practical DSD converter implementations were pioneered by Andreas Koch and Ed Meitner, the original founders of EMM Labs. Andreas Koch later left EMM Labs and along with Jonathan Tinn, founded Playback Designs who have pioneered the transfer of DSD files over USB connections. Global DSD technology was developed by Sony and Philips, the designers of the audio CD
Compact Disc
The Compact Disc is an optical disc used to store digital data. It was originally developed to store and playback sound recordings exclusively, but later expanded to encompass data storage , write-once audio and data storage , rewritable media , Video Compact Discs , Super Video Compact Discs ,...
. Philips' DSD tool division was transferred to Sonic Studio, LLC in 2005 for on-going design and development.
DSD technology may also have potential for video applications. A similar structure based on pulse-width modulation
Pulse-width modulation
Pulse-width modulation , or pulse-duration modulation , is a commonly used technique for controlling power to inertial electrical devices, made practical by modern electronic power switches....
, which is decoded in the same way as DSD, has been used in Laserdisc
Laserdisc
LaserDisc was a home video format and the first commercial optical disc storage medium. Initially licensed, sold, and marketed as MCA DiscoVision in North America in 1978, the technology was previously referred to interally as Optical Videodisc System, Reflective Optical Videodisc, Laser Optical...
video.
History
DSD is a method of storing a Delta-Sigma signal before applying a "decimation" process that converts the signal to a PCM signal. When Delta-Sigma conversion was originally described in patent 2,927,962 filed by C. C. Cutler in 1954 (But not named as such until a 1962 paper by H. Inose, Y. Yasuda, and J. Murakami), decimation did not exist and the intention was to have oversampled data sent as-is. Indeed, the first proposal to decimate oversampled delta-sigma data to convert it in to PCM audio did not appear until 1969, in D. J. Goodman's paper "The Application of Delta Modulation of Analog-to-PCM encoding".DSD

Super Audio CD
Super Audio CD is a high-resolution, read-only optical disc for audio storage. Sony and Philips Electronics jointly developed the technology, and publicized it in 1999. It is designated as the Scarlet Book standard. Sony and Philips previously collaborated to define the Compact Disc standard...
audio is stored in a format called Direct Stream Digital (DSD), which differs from the conventional PCM
Pulse-code modulation
Pulse-code modulation is a method used to digitally represent sampled analog signals. It is the standard form for digital audio in computers and various Blu-ray, Compact Disc and DVD formats, as well as other uses such as digital telephone systems...
used by the compact disc
Compact Disc
The Compact Disc is an optical disc used to store digital data. It was originally developed to store and playback sound recordings exclusively, but later expanded to encompass data storage , write-once audio and data storage , rewritable media , Video Compact Discs , Super Video Compact Discs ,...
or conventional computer audio systems.
DSD is 1-bit
Bit
A bit is the basic unit of information in computing and telecommunications; it is the amount of information stored by a digital device or other physical system that exists in one of two possible distinct states...
, has a sampling rate of 2.8224 MHz, and makes use of noise shaping
Noise shaping
Noise shaping is a technique typically used in digital audio, image, and video processing, usually in combination with dithering, as part of the process of quantization or bit-depth reduction of a digital signal...
quantization
Quantization (sound processing)
In signal processing and digital audio, quantization is the process of approximating a continuous range of values by a relatively small set of discrete symbols or integer values...
techniques in order to push 1-bit quantization noise up to inaudible ultrasonic frequencies. This gives the format a greater dynamic range
Dynamic range
Dynamic range, abbreviated DR or DNR, is the ratio between the largest and smallest possible values of a changeable quantity, such as in sound and light. It is measured as a ratio, or as a base-10 or base-2 logarithmic value.-Dynamic range and human perception:The human senses of sight and...
and wider frequency response
Frequency response
Frequency response is the quantitative measure of the output spectrum of a system or device in response to a stimulus, and is used to characterize the dynamics of the system. It is a measure of magnitude and phase of the output as a function of frequency, in comparison to the input...
than the CD. The SACD format is capable of delivering a dynamic range
Dynamic range
Dynamic range, abbreviated DR or DNR, is the ratio between the largest and smallest possible values of a changeable quantity, such as in sound and light. It is measured as a ratio, or as a base-10 or base-2 logarithmic value.-Dynamic range and human perception:The human senses of sight and...
of 120 dB
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
from 20 Hz to 20 kHz and an extended frequency response
Frequency response
Frequency response is the quantitative measure of the output spectrum of a system or device in response to a stimulus, and is used to characterize the dynamics of the system. It is a measure of magnitude and phase of the output as a function of frequency, in comparison to the input...
up to 100 kHz
Hertz
The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
, although most currently available players list an upper limit of 80–90 kHz and 20 kHz is the upper limit of human hearing.
The process of creating a DSD signal is conceptually similar to taking a 1-bit delta-sigma
Delta-sigma modulation
Delta-sigma modulation is a method for encoding high-resolution or analog signals into lower-resolution digital signals. The conversion is done using error feedback, where the difference between the two signals is measured and used to improve the conversion...
analog-to-digital
Analog-to-digital converter
An analog-to-digital converter is a device that converts a continuous quantity to a discrete time digital representation. An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement...
(A/D) converter and removing the decimator, which converts the 1-bit bitstream into multibit PCM. Instead, the 1-bit signal is recorded directly and in theory only requires a lowpass filter to reconstruct the original analog waveform. In reality it is a little more complex, and the analogy is incomplete in that 1-bit sigma-delta converters are these days rather unusual, one reason being that a 1-bit signal cannot be dither
Dither
Dither is an intentionally applied form of noise used to randomize quantization error, preventing large-scale patterns such as color banding in images...
ed properly: most modern sigma-delta converters are multibit.
Because of the nature of sigma-delta converters, one cannot make a direct comparison between DSD and PCM. An approximation is possible, though, and would place DSD in some aspects comparable to a PCM format that has a bit depth of 20 bits and a sampling frequency of 96 kHz. PCM sampled at 24 bits provides a (theoretical) additional 24 dB of dynamic range.
Because it has been extremely difficult to carry out DSP operations (for example performing EQ, balance, panning and other changes in the digital domain) in a 1-bit environment, and because of the prevalence of studio equipment such as Pro Tools
Pro Tools
Pro Tools is a digital audio workstation platform for Microsoft Windows and Mac OS X operating systems, developed and manufactured by Avid Technology. It is widely used by professionals throughout the audio industries for recording and editing in music production, film scoring, film, and television...
, which is solely PCM-based, the vast majority of SACDs — especially rock and contemporary music which relies on multitrack techniques — are in fact mixed in PCM (or mixed analog and recorded on PCM recorders) and then converted to DSD for SACD mastering.
To address some of these issues, a new studio format has been developed, usually referred to as "DSD-wide", which retains standard DSD's high sample rate but uses an 8-bit
Bit
A bit is the basic unit of information in computing and telecommunications; it is the amount of information stored by a digital device or other physical system that exists in one of two possible distinct states...
, rather than single-bit digital word length, but still relies heavily on the noise shaping
Noise shaping
Noise shaping is a technique typically used in digital audio, image, and video processing, usually in combination with dithering, as part of the process of quantization or bit-depth reduction of a digital signal...
principle. It becomes almost the same as PCM (it's sometimes disparagingly referred to as "PCM-narrow") but has the added benefit of making DSP operations in the studio a great deal more practical. The main difference is that "DSD-wide" still retains 2.8224 MHz (64Fs) sampling frequency while the highest frequency in which PCM is being edited is 352.8 kHz (8Fs). The "DSD-wide" signal is down-converted to regular DSD for SACD mastering. As a result of this technique and other developments there are now a few digital audio workstation
Digital audio workstation
A digital audio workstation is an electronic system designed solely or primarily for recording, editing and playing back digital audio. DAWs were originally tape-less, microprocessor-based systems such as the Synclavier and Fairlight CMI...
s (DAWs) that operate, or can operate, in the DSD domain, notably Pyramix and some SADiE systems.
Another format for DSD editing is DXD (Digital eXtreme Definition
Digital eXtreme Definition
Digital eXtreme Definition is an audio encoding scheme for professional use that was developed for editing high-resolution recordings because DSD, the audio standard used on Super Audio CD is not ideally suited for editing...
), a "PCM-like" signal with 24-bit resolution sampled at 352.8 kHz.
Note that high-resolution PCM (DVD-Audio
DVD-Audio
DVD-Audio is a digital format for delivering high-fidelity audio content on a DVD. DVD-Audio is not intended to be a video delivery format and is not the same as video DVDs containing concert films or music videos....
, HD DVD
HD DVD
HD DVD is a discontinued high-density optical disc format for storing data and high-definition video.Supported principally by Toshiba, HD DVD was envisioned to be the successor to the standard DVD format...
and Blu-ray Disc
Blu-ray Disc
Blu-ray Disc is an optical disc storage medium designed to supersede the DVD format. The plastic disc is 120 mm in diameter and 1.2 mm thick, the same size as DVDs and CDs. Blu-ray Discs contain 25 GB per layer, with dual layer discs being the norm for feature-length video discs...
) and DSD (SACD) may still technically differ at high frequencies. A reconstruction filter is typically used in PCM decoding systems, much the same way that bandwidth-limiting filters are normally used in PCM encoding systems. Any error or unwanted artifact introduced by such filters will typically affect the end-result. A claimed advantage of DSD is that product designers commonly choose to have no filtering, or modest filtering. Instead DSD leads to constant high levels of noise at these frequencies. DSD's dynamic range decreases quickly at frequencies over 20 kHz due to the use of strong noise shaping
Noise shaping
Noise shaping is a technique typically used in digital audio, image, and video processing, usually in combination with dithering, as part of the process of quantization or bit-depth reduction of a digital signal...
techniques which push the noise out of the audio band resulting in a rising noise floor just above 20 kHz. PCM's dynamic range, on the other hand, is the same at all frequencies. (Some high-end SACD players employ an optional low-pass filter set at 30 kHz for compatibility and safety reasons, suitable for situations where amplifiers or loudspeakers cannot deliver an undistorted output if noise above 30 kHz is present in the signal.)
DSD Disc Format
Some professional audio recorders can record in DSD format. Transferring this signal to a recordable DVD with the appropriate tools, such as the Korg MR-1/2/1000/2000-bundled 'AudioGate'-software, will render a DSD Disc. Such discs can be played back/transcoded to PCM on the fly on PCs with the proper software plug-ins (for Windows Media Player or foobar2000), and in native DSD on certain Sony VAIO laptops and PlayStation 3PlayStation 3
The is the third home video game console produced by Sony Computer Entertainment and the successor to the PlayStation 2 as part of the PlayStation series. The PlayStation 3 competes with Microsoft's Xbox 360 and Nintendo's Wii as part of the seventh generation of video game consoles...
. HQPlayer from Feb 16 2011 ver 2.6.0 beta includes support for direct/native playback from DSDIFF and DSF files to ASIO devices with DSD support. Moreover, Sony produces two SACD-players, the SCD-XA5400ES and the SCD-XE800, that fully support the DSD-disc format. Only so-called DSF format is supported. DSF is a stereo-only, simplified form of DFF, the format used for SACD mastering and 5.1-channel downloads.
Playback Designs' players and converters and pro-audio company 'Mytek Digitals 192 Stereo DAC both sport DSD over USB capability. Apparently, this would provide owners of DSD-recorders from Korg, Tascam and others with a computer-based playback option for their (non-encrypted) DSD-files. Whether these USB-DAC will be compatible with the DSD-disc specification still remains to be seen.
DSD-CD
DSD-CD is a variant of the Compact Disc Digital Audio format. The difference from the standard version of CD is that the sound is derived from a DSD master. A DSD-CD however does not achieve the same sound resolution as SACD because the high-resolution DSD sound has to be down-converted to 44.1 kHz, 16-bit PCM in order to be compliant with the 'Red Book'Red Book (audio CD standard)
Red Book is the standard for audio CDs . It is named after one of the Rainbow Books, a series of books that contain the technical specifications for all CD and CD-ROM formats.The first edition of the Red Book was released in 1980 by Philips and Sony; it was adopted by the Digital Audio Disc...
audio CD standard. DSD-CDs are fully compatible with CD.
DSD-CD has been marketed as an audiophile
Audiophile
An audiophile is a person who enjoys listening to recorded music, usually in a home. Some audiophiles are more interested in collecting and listening to music, while others are more interested in collecting and listening to audio components, whose "sound quality" they consider as important as the...
medium, primarily in Hong Kong with music by Cantopop
Cantopop
Cantopop is a colloquialism for "Cantonese popular music". It is sometimes referred to as HK-pop, short for "Hong Kong popular music". It is categorized as a subgenre of Chinese popular music within C-pop...
artists such as Sally Yeh
Sally Yeh
Sally Yeh , sometimes written as Sally Yip or Yip Sin-Man, is a Cantopop singer in the Hong Kong music industry and an actress in the Hong Kong film industry.-Overview:...
.
Double-rate DSD
The Korg MR-1000 1-bit digital recorder samples at 5.6 MHz, twice the SACD rate. It's also referred to as DSD128 because of the sample rate 128x that of CD.
DSD vs. PCM
There has been much controversy between proponents of DSD and PCMPulse-code modulation
Pulse-code modulation is a method used to digitally represent sampled analog signals. It is the standard form for digital audio in computers and various Blu-ray, Compact Disc and DVD formats, as well as other uses such as digital telephone systems...
over which encoding system is superior. Professors Stanley Lipshitz and John Vanderkooy from the University of Waterloo
University of Waterloo
The University of Waterloo is a comprehensive public university in the city of Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. The school was founded in 1957 by Drs. Gerry Hagey and Ira G. Needles, and has since grown to an institution of more than 30,000 students, faculty, and staff...
, in Audio Engineering Society Convention Paper 5395 (2001), stated that 1-bit converters (as employed by DSD) are unsuitable for high-end applications due to their high distortion. Even 8-bit, four-times-oversampled PCM with noise shaping, proper dithering and half data rate of DSD has better noise floor and frequency response. However, in 2002, Philips published a convention paper arguing against this in Convention Paper 5616. Lipshitz and Vanderkooy's paper has been criticized in detail by Professor Jamie Angus at an Audio Engineering Society presentation in Convention Paper 5619. Lipshitz and Vanderkooy responded in Convention Paper 5620.
When comparing a DSD and PCM recording of the same origin, the same number of channels and similar bandwidth/SNR, some still think that there are differences. A study conducted at the Erik-Thienhaus Institute in Detmold, Germany, seems to contradict this, concluding that "hardly any of the subjects could make a reproducible distinction between the two encoding systems. Hence it may be concluded that no significant differences are audible."
External links
- Audio Engineering Society Convention Paper 5396: Why Direct Stream Digital is the best choice as a digital audio format
- Audio Engineering Society Convention Paper 5616: Enhanced Sigma Delta Structures for Super Audio CD Applications
- Audio Engineering Society Convention Paper 5619: The Effect of Idle Tone Structure on Effective Dither in Delta-Sigma Modulation Systems
- Audio Engineering Society Convention Paper 5620: Toward a Better Understanding of 1-Bit Sigma-Delta Modulators - Part 3 - DSD vs PCM comparison
- DSF and DSD Disc Format specifications by Sony
- 'How to create a DSD Disc' guide including DSD plug-in for Windows Media PlayerWindows Media PlayerWindows Media Player is a media player and media library application developed by Microsoft that is used for playing audio, video and viewing images on personal computers running the Microsoft Windows operating system, as well as on Pocket PC and Windows Mobile-based devices...
- Mutlti-channel DSD over USB DSD recording playback over USB software and hardware development kit
- DSD downloads

