
Direction, position, or indication sign
Encyclopedia
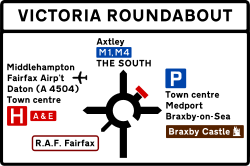
Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals
The Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals is an international treaty designed to increase road safety and aid international road traffic by standardising the signing system for road traffic in use internationally.This convention was agreed upon by the United Nations Economic and Social...
, is any road sign used primarily to give information about the location of either the driver or possible destinations, and are considered a subset of the informative signs group. Direction signs are far more varied internationally than other classes of sign, as the Vienna Convention does not specify sizes, colours, symbols or positions of such signs.
Direction signs are the oldest type of road sign; Plutarch
Plutarch
Plutarch then named, on his becoming a Roman citizen, Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus , c. 46 – 120 AD, was a Greek historian, biographer, essayist, and Middle Platonist known primarily for his Parallel Lives and Moralia...
writes about milestones being placed in the 3rd century BC, while some fingerpost
Fingerpost
A fingerpost is a name given to traditional British and Irish sign posts comprising a post with one or more arms — known as fingers — pointing in the direction of travel to named places on the fingers...
s in the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
date back to at least the 1690s. However, it was not until the invention of the motor car at the turn of the 20th century that modern direction signs, with fewer words and clear design, allowing them to be read at speed, evolved.
Pre-automobile

Milestone
A milestone is one of a series of numbered markers placed along a road or boundary at intervals of one mile or occasionally, parts of a mile. They are typically located at the side of the road or in a median. They are alternatively known as mile markers, mileposts or mile posts...
s on the Roman road
Roman road
The Roman roads were a vital part of the development of the Roman state, from about 500 BC through the expansion during the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. Roman roads enabled the Romans to move armies and trade goods and to communicate. The Roman road system spanned more than 400,000 km...
network; finding one's location on the long, straight roads was difficult, and hence, large stones were placed at intervals along the roads, giving the distance in Roman miles to nearby major cities, and usually to the capitals of major provinces. As most Roman roads diverged from Rome
Rome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
, one of the numbers was usually the distance to the Milliarium Aureum, a large golden milestone in the centre of Rome, although sometimes other stones, such as the London Stone
London Stone
The London Stone is a historic stone that is now set within a Portland stone surround and iron grille on Cannon Street, in the City of London.-Features:...
, were used in places where measuring distances from Rome was impossible or not useful.
The use of milestones continued following the decline of the Roman Empire. However, as trading between towns and regions increased, milestones were found to be inconvenient for giving directions at crossroad
Junction (road)
A road junction is a location where vehicular traffic going in different directions can proceed in a controlled manner designed to minimize accidents. In some cases, vehicles can change between different routes or directions of travel.-Origins:...
s. As a result, the fingerpost developed. Built by local parish
Parish
A parish is a territorial unit historically under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of one parish priest, who might be assisted in his pastoral duties by a curate or curates - also priests but not the parish priest - from a more or less central parish church with its associated organization...
es, fingerposts were easier to read from horseback and were cheaper to make. With the development of the turnpike
Turnpike trust
Turnpike trusts in the United Kingdom were bodies set up by individual Acts of Parliament, with powers to collect road tolls for maintaining the principal highways in Britain from the 17th but especially during the 18th and 19th centuries...
and the stagecoach
Stagecoach
A stagecoach is a type of covered wagon for passengers and goods, strongly sprung and drawn by four horses, usually four-in-hand. Widely used before the introduction of railway transport, it made regular trips between stages or stations, which were places of rest provided for stagecoach travelers...
, the Turnpike Roads Act 1773 was passed, making signposting compulsory to allow the riders to judge their speed and prevent them from becoming lost. Similar signs were developed in other countries and remained in use until the early-20th century, when development of the motor car made the small and often wordy signs impractical.

Modernisation
Most early direction signs were based on the traditional styles in use in area; the United Kingdom used adapted, cast ironCast iron
Cast iron is derived from pig iron, and while it usually refers to gray iron, it also identifies a large group of ferrous alloys which solidify with a eutectic. The color of a fractured surface can be used to identify an alloy. White cast iron is named after its white surface when fractured, due...
fingerposts for signing directions, while the United States adopted an ad hoc scheme based on traditional trail markings. These proved unwieldy, and modernisation efforts quickly sprung up to change them. However, the changes faced opposition, both from traditionalists who preferred the style or charm of older signs, and from businesses along affected routes, who feared that standardised direction signs would favour the new highway
Highway
A highway is any public road. In American English, the term is common and almost always designates major roads. In British English, the term designates any road open to the public. Any interconnected set of highways can be variously referred to as a "highway system", a "highway network", or a...
s, causing rural routes to fade into obscurity.
The advent of World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
halted sign modernisation efforts across Europe however, and governments, fearing that invading forces or enemy spies could use such signs to navigate, removed all direction signs from the road networks. The end of the war was however used as an opportunity by many European nations to redevelop direction signs. The construction of high speed motorways meant that traditional road signs were no longer practical, and so new, modern signs with bold, sans serif typeface
Typeface
In typography, a typeface is the artistic representation or interpretation of characters; it is the way the type looks. Each type is designed and there are thousands of different typefaces in existence, with new ones being developed constantly....
s and diagrams indicating lanes and sliproads ahead were developed. The British Worboys Committee
Worboys Committee
The Worboys Committee was formed by the British government in July 1963 to review signage on all British roads. This was in response to two articles published in 1961 by graphic designer Herbert Spencer, illustrating the shortcomings of non-motorway British road signs.The committee was chaired by...
went even further, and created signs with detailed maps of junctions. Such signs have been in use almost unchanged for over half a century.
Design
The Vienna Convention on Road Signs and SignalsVienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals
The Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals is an international treaty designed to increase road safety and aid international road traffic by standardising the signing system for road traffic in use internationally.This convention was agreed upon by the United Nations Economic and Social...
divides the direction, position, or indication sign category into direction signs, which are only those giving distances or directions to a given location; road identification signs (also known as "reassurance signs
Reassurance marker
A reassurance marker or road identification sign is a road sign that repeats the name or number of the current route. Typically posted at intervals alongside a numbered highway, the signs are intended to reassure drivers that they are traveling on the desired road .- North America :In the United...
"), which repeat the name or number of the road, and place identification signs, which give the name of a landmark, such as a town
Town
A town is a human settlement larger than a village but smaller than a city. The size a settlement must be in order to be called a "town" varies considerably in different parts of the world, so that, for example, many American "small towns" seem to British people to be no more than villages, while...
, river
River
A river is a natural watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, a lake, a sea, or another river. In a few cases, a river simply flows into the ground or dries up completely before reaching another body of water. Small rivers may also be called by several other names, including...
or border
Border
Borders define geographic boundaries of political entities or legal jurisdictions, such as governments, sovereign states, federated states and other subnational entities. Some borders—such as a state's internal administrative borders, or inter-state borders within the Schengen Area—are open and...
. Unlike the other classes of sign, direction signs remain broadly undefined by the convention; the only restrictions given are that direction signs must be either a rectangle or an arrow shaped pentagon
Pentagon
In geometry, a pentagon is any five-sided polygon. A pentagon may be simple or self-intersecting. The sum of the internal angles in a simple pentagon is 540°. A pentagram is an example of a self-intersecting pentagon.- Regular pentagons :In a regular pentagon, all sides are equal in length and...
, and that they may not contain placenames in more than two languages. Additionally, direction signs on motorways must be blue or green, while temporary direction signs are yellow or orange.
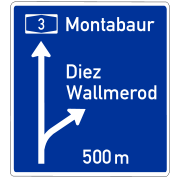



Road signs in the Republic of Ireland
Road signs in Ireland mostly differ from the traffic signs used elsewhere in Europe. Directional signage is similar to that of the United Kingdom, but is bilingual. Distances are in kilometres. Apart from directional signage, the basic prohibitory signs such as "no left turn" and "no right turn"...
and Iceland use signs with fewer words but detailed maps of the approaching junctions. Most areas use different colours to show different road types, but the implementation varies: the United Kingdom (and Ireland) uses full colour boards, colour coded to match the type of road they are placed on, with relevant text highlighted within patches of other colours to indicate different road types using the Guildford Rules. The United States, Canada, and Australia on the other hand almost universally use the plain green signs, but some signs use different colours to highlight certain types of destination such as hospital
Hospital
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment by specialized staff and equipment. Hospitals often, but not always, provide for inpatient care or longer-term patient stays....
s and rest stops, or, in Australia that the road is a tollway. Road signs in Israel and the Palestinian territories are of similar design to North American signage, but vary in color depending on whether the sign indicates direction for through traffic, exiting traffic, etc.
Direction signs can also be used in conjunction with other types of sign: for example, in the United Kingdom, if a warning
Warning sign
A traffic warning sign is a type of traffic sign that indicates a hazard ahead on the road that may not be readily apparent to a driver.In most countries, they usually take the shape of an equilateral triangle with a white background and a thick red border...
or prohibitory sign
Prohibitory traffic sign
Prohibitory traffic signs are used to prohibit certain types of manoeuvres or some types of traffic.-No entry:No admittance to unauthorised personnel, usually shown as a red circle with a white rectangle across its face.-Speed limits:...
appears on a direction sign, it means that the route indicates by the sign contains the hazard or prohibition sign posted.
See also
- Bilingual signBilingual signA bilingual sign is the representation on a panel of texts in more than one language...
- CairnCairnCairn is a term used mainly in the English-speaking world for a man-made pile of stones. It comes from the or . Cairns are found all over the world in uplands, on moorland, on mountaintops, near waterways and on sea cliffs, and also in barren desert and tundra areas...
- Exit numberExit numberAn exit number is a number assigned to a road junction, usually an exit from a freeway. It is usually marked on the same sign as the destinations of the exit, as well as a sign in the gore....
- Highway route markersHighway route markersHighway route markers are the modern-day equivalent of milestones. Unlike traditional milestones, however, which were originally carved from stone and sited at one-mile intervals, modern highway route markers are made from a variety of materials and are almost invariably spaced at intervals of a...
- Driver location signsDriver location signsDriver location signs are English highway route markers, first introduced in 2003, that complement distance marker posts. Both types of marker post display the distances from a nominal start point in kilometres...

