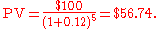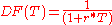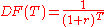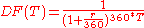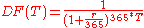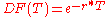Discount
Encyclopedia
Discounting is a financial mechanism in which a debtor
obtains the right to delay payments to a creditor
, for a defined period of time, in exchange for a charge or fee. Essentially, the party that owes money in the present purchases the right to delay the payment until some future date. The discount, or charge, is simply the difference between the original amount owed in the present and the amount that has to be paid in the future to settle the debt.
The discount is usually associated with a discount rate, which is also called the discount yield. The discount yield is simply the proportional share of the initial amount owed (initial liability) that must be paid to delay payment for 1 year.
It is also the rate at which the amount owed must rise to delay payment for 1 year.
Since a person can earn a return on money invested over some period of time, most economic and financial models assume the "Discount Yield" is the same as the Rate of Return
the person could receive by investing this money elsewhere (in assets of similar risk
) over the given period of time covered by the delay in payment. The Concept is associated with the Opportunity Cost
of not having use of the money for the period of time covered by the delay in payment. The relationship between the "Discount Yield" and the Rate of Return
on other financial assets is usually discussed in such economic and financial theories involving the inter-relation between various Market Prices
, and the achievement of Pareto Optimality
through the operations in the Capitalistic Price Mechanism, as well as in the discussion of the "Efficient (Financial) Market Hypothesis". Competition from other firms who offer other Financial Assets that promise the Market Rate of Return
forces the person who is asking for a delay in payment to offer a "Discount Yield" that is the same as the Market Rate of Return
. The person delaying the payment of the current Liability is essentially compensating the person to whom he/she owes money for the lost revenue that could be earned from an investment during the time period covered by the delay in payment. Accordingly, it is the relevant "Discount Yield" that determines the "Discount", and not the other way around.
As indicated, the Rate of Return
is usually calculated in accordance to an annual return on investment
. Since an investor earns a return on the original principal amount of the investment as well as on any prior period Investment income, investment earnings are "compounded" as time advances. Therefore, considering the fact that the "Discount" must match the benefits obtained from a similar Investment Asset
, the "Discount Yield" must be used within the same compounding mechanism to negotiate an increase in the size of the "Discount" whenever the time period the payment is delayed or extended. The “Discount Rate” is the rate at which the “Discount” must grow as the delay in payment is extended.Alpha C Chiang, "Fundamental Methods of Mathematical Economics, Third Edition", McGraw Hill Book Company, 1984. This fact is directly tied into the "Time Value of Money
" and its calculations.
The "Time Value of Money
" indicates there is a difference between the "Future Value" of a payment and the "Present Value" of the same payment. The Rate of Return
on investment should be the dominant factor in evaluating the market's assessment of the difference between the "Future Value" and the "Present Value" of a payment; and it is the Market's assessment that counts the most. Therefore, the "Discount Yield", which is predetermined by a related Return on Investment
that is found in the financial markets, is what is used within the "Time Value of Money
" calculations to determine the "Discount" required to delay payment of a financial liability for a given period of time.
BASIC CALCULATION
If we consider the value of the original payment presently due to be $P, and the debtor wants to delay the payment for t years, then an r% Market Rate of Return
on a similar Investment Assets
means the "Future Value" of $P is $P * (1 + r%)t , and the "Discount" would be calculated as
where r% is also the "Discount Yield".
If $F is a payment that will be made t years in the future, then the "Present Value" of this Payment, also called the "Discounted Value" of the payment, is
of a single cash flow, it is divided by one plus the interest rate for each period of time that will pass. This is expressed mathematically as raising the divisor to the power of the number of units of time.
Consider the task to find the present value PV of $100 that will be received in five years. Or equivalently, which amount of money today will grow to $100 in five years when subject to a constant discount rate?
Assuming a 12% per year interest rate it follows
. The Cost of Capital
, in a financial market equilibrium, will be the same as the Market Rate of Return
on the financial asset mixture the firm uses to finance capital investment. Some adjustment may be made to the discount rate to take account of risks associated with uncertain cash flows, with other developments.
The discount rates typically applied to different types of companies show significant differences:
Reason for high discount rates for startups:
One method that looks into a correct discount rate is the capital asset pricing model
.
This model takes in account three variables that make up the discount rate:
1. Risk Free Rate: The percentage of return generated by investing in risk free securities such as government bonds.
2. Beta: The measurement of how a company’s stock price reacts to a change in the market. A beta higher than 1 means that a change in share price is exaggerated compared to the rest of shares in the same market. A beta less than 1 means that the share is stable and not very responsive to changes in the market. Less than 0 means that a share is moving in the opposite of the market change.
3. Equity Market Risk Premium: The return on investment that investors require above the risk free rate.
Discount rate= risk free rate + beta*(equity market risk premium)
 , taken from a yield curve
, taken from a yield curve
, and a time to cashflow (in years), the discount factor is:
(in years), the discount factor is:
In the case where the only discount rate you have is not a zero-rate (neither taken from a zero-coupon bond nor converted from a swap rate
to a zero-rate through bootstrapping
) but an annually-compounded rate (for example if your benchmark is a US Treasury bond with annual coupons and you only have its yield to maturity
, you would use an annually-compounded discount factor:
However, when operating in a bank, where the amount the bank can lend (and therefore get interest) is linked to the value of its assets (including accrued interest
), traders usually use daily compounding to discount cashflows. Indeed, even if the interest of the bonds it holds (for example) is paid semi-annually, the value of its book of bond will increase daily, thanks to accrued interest
being accounted for, and therefore the bank will be able to re-invest these daily accrued interest (by lending additional money or buying more financial products). In that case, the discount factor is then (if the usual money market
day count convention
for the currency is ACT/360, in case of currencies such as USD, EUR, JPY), with the zero-rate and
the zero-rate and  the time to cashflow in years:
the time to cashflow in years:
or, in case the market convention for the currency being discounted is ACT/365 (AUD, CAD, GBP):
Sometimes, for manual calculation, the continuously-compounded hypothesis is a close-enough approximation of the daily-compounding hypothesis, and makes calculation easier (even though it does not have any real application as no financial instrument is continuously compounded). In that case, the discount factor is:
----
, see discounts and allowances
, sales promotion
, and pricing
. The article on Discounted Cash Flow
provides a nice example about discounting and risks in real estate investments.
Debtor
A debtor is an entity that owes a debt to someone else. The entity may be an individual, a firm, a government, a company or other legal person. The counterparty is called a creditor...
obtains the right to delay payments to a creditor
Creditor
A creditor is a party that has a claim to the services of a second party. It is a person or institution to whom money is owed. The first party, in general, has provided some property or service to the second party under the assumption that the second party will return an equivalent property or...
, for a defined period of time, in exchange for a charge or fee. Essentially, the party that owes money in the present purchases the right to delay the payment until some future date. The discount, or charge, is simply the difference between the original amount owed in the present and the amount that has to be paid in the future to settle the debt.
The discount is usually associated with a discount rate, which is also called the discount yield. The discount yield is simply the proportional share of the initial amount owed (initial liability) that must be paid to delay payment for 1 year.
Discount Yield = "Charge" to Delay Payment for 1 year / Debt Liability
It is also the rate at which the amount owed must rise to delay payment for 1 year.
Since a person can earn a return on money invested over some period of time, most economic and financial models assume the "Discount Yield" is the same as the Rate of Return
Rate of return
In finance, rate of return , also known as return on investment , rate of profit or sometimes just return, is the ratio of money gained or lost on an investment relative to the amount of money invested. The amount of money gained or lost may be referred to as interest, profit/loss, gain/loss, or...
the person could receive by investing this money elsewhere (in assets of similar risk
Risk
Risk is the potential that a chosen action or activity will lead to a loss . The notion implies that a choice having an influence on the outcome exists . Potential losses themselves may also be called "risks"...
) over the given period of time covered by the delay in payment. The Concept is associated with the Opportunity Cost
Opportunity cost of capital
The opportunity cost of capital is the expected rate of return forgone by bypassing of other potential investment activities for a given capital.It is a rate of return that investors could earn in financial markets....
of not having use of the money for the period of time covered by the delay in payment. The relationship between the "Discount Yield" and the Rate of Return
Rate of return
In finance, rate of return , also known as return on investment , rate of profit or sometimes just return, is the ratio of money gained or lost on an investment relative to the amount of money invested. The amount of money gained or lost may be referred to as interest, profit/loss, gain/loss, or...
on other financial assets is usually discussed in such economic and financial theories involving the inter-relation between various Market Prices
Market price
In economics, market price is the economic price for which a good or service is offered in the marketplace. It is of interest mainly in the study of microeconomics...
, and the achievement of Pareto Optimality
Pareto efficiency
Pareto efficiency, or Pareto optimality, is a concept in economics with applications in engineering and social sciences. The term is named after Vilfredo Pareto, an Italian economist who used the concept in his studies of economic efficiency and income distribution.Given an initial allocation of...
through the operations in the Capitalistic Price Mechanism, as well as in the discussion of the "Efficient (Financial) Market Hypothesis". Competition from other firms who offer other Financial Assets that promise the Market Rate of Return
Rate of return
In finance, rate of return , also known as return on investment , rate of profit or sometimes just return, is the ratio of money gained or lost on an investment relative to the amount of money invested. The amount of money gained or lost may be referred to as interest, profit/loss, gain/loss, or...
forces the person who is asking for a delay in payment to offer a "Discount Yield" that is the same as the Market Rate of Return
Rate of return
In finance, rate of return , also known as return on investment , rate of profit or sometimes just return, is the ratio of money gained or lost on an investment relative to the amount of money invested. The amount of money gained or lost may be referred to as interest, profit/loss, gain/loss, or...
. The person delaying the payment of the current Liability is essentially compensating the person to whom he/she owes money for the lost revenue that could be earned from an investment during the time period covered by the delay in payment. Accordingly, it is the relevant "Discount Yield" that determines the "Discount", and not the other way around.
As indicated, the Rate of Return
Rate of return
In finance, rate of return , also known as return on investment , rate of profit or sometimes just return, is the ratio of money gained or lost on an investment relative to the amount of money invested. The amount of money gained or lost may be referred to as interest, profit/loss, gain/loss, or...
is usually calculated in accordance to an annual return on investment
Return on investment
Return on investment is one way of considering profits in relation to capital invested. Return on assets , return on net assets , return on capital and return on invested capital are similar measures with variations on how “investment” is defined.Marketing not only influences net profits but also...
. Since an investor earns a return on the original principal amount of the investment as well as on any prior period Investment income, investment earnings are "compounded" as time advances. Therefore, considering the fact that the "Discount" must match the benefits obtained from a similar Investment Asset
Investment
Investment has different meanings in finance and economics. Finance investment is putting money into something with the expectation of gain, that upon thorough analysis, has a high degree of security for the principal amount, as well as security of return, within an expected period of time...
, the "Discount Yield" must be used within the same compounding mechanism to negotiate an increase in the size of the "Discount" whenever the time period the payment is delayed or extended. The “Discount Rate” is the rate at which the “Discount” must grow as the delay in payment is extended.Alpha C Chiang, "Fundamental Methods of Mathematical Economics, Third Edition", McGraw Hill Book Company, 1984. This fact is directly tied into the "Time Value of Money
Time value of money
The time value of money is the value of money figuring in a given amount of interest earned over a given amount of time. The time value of money is the central concept in finance theory....
" and its calculations.
The "Time Value of Money
Time value of money
The time value of money is the value of money figuring in a given amount of interest earned over a given amount of time. The time value of money is the central concept in finance theory....
" indicates there is a difference between the "Future Value" of a payment and the "Present Value" of the same payment. The Rate of Return
Rate of return
In finance, rate of return , also known as return on investment , rate of profit or sometimes just return, is the ratio of money gained or lost on an investment relative to the amount of money invested. The amount of money gained or lost may be referred to as interest, profit/loss, gain/loss, or...
on investment should be the dominant factor in evaluating the market's assessment of the difference between the "Future Value" and the "Present Value" of a payment; and it is the Market's assessment that counts the most. Therefore, the "Discount Yield", which is predetermined by a related Return on Investment
Return on investment
Return on investment is one way of considering profits in relation to capital invested. Return on assets , return on net assets , return on capital and return on invested capital are similar measures with variations on how “investment” is defined.Marketing not only influences net profits but also...
that is found in the financial markets, is what is used within the "Time Value of Money
Time value of money
The time value of money is the value of money figuring in a given amount of interest earned over a given amount of time. The time value of money is the central concept in finance theory....
" calculations to determine the "Discount" required to delay payment of a financial liability for a given period of time.
BASIC CALCULATION
If we consider the value of the original payment presently due to be $P, and the debtor wants to delay the payment for t years, then an r% Market Rate of Return
Rate of return
In finance, rate of return , also known as return on investment , rate of profit or sometimes just return, is the ratio of money gained or lost on an investment relative to the amount of money invested. The amount of money gained or lost may be referred to as interest, profit/loss, gain/loss, or...
on a similar Investment Assets
Investment
Investment has different meanings in finance and economics. Finance investment is putting money into something with the expectation of gain, that upon thorough analysis, has a high degree of security for the principal amount, as well as security of return, within an expected period of time...
means the "Future Value" of $P is $P * (1 + r%)t , and the "Discount" would be calculated as
Discount = $P * (1+r%)t - $P
where r% is also the "Discount Yield".
If $F is a payment that will be made t years in the future, then the "Present Value" of this Payment, also called the "Discounted Value" of the payment, is
$P = $F / (1+r%)t
Example
To calculate the present valuePresent value
Present value, also known as present discounted value, is the value on a given date of a future payment or series of future payments, discounted to reflect the time value of money and other factors such as investment risk...
of a single cash flow, it is divided by one plus the interest rate for each period of time that will pass. This is expressed mathematically as raising the divisor to the power of the number of units of time.
Consider the task to find the present value PV of $100 that will be received in five years. Or equivalently, which amount of money today will grow to $100 in five years when subject to a constant discount rate?
Assuming a 12% per year interest rate it follows
Discount rate
The discount rate which is used in financial calculations is usually chosen to be equal to the Cost of CapitalCost of capital
The cost of capital is a term used in the field of financial investment to refer to the cost of a company's funds , or, from an investor's point of view "the shareholder's required return on a portfolio of all the company's existing securities"...
. The Cost of Capital
Cost of capital
The cost of capital is a term used in the field of financial investment to refer to the cost of a company's funds , or, from an investor's point of view "the shareholder's required return on a portfolio of all the company's existing securities"...
, in a financial market equilibrium, will be the same as the Market Rate of Return
Rate of return
In finance, rate of return , also known as return on investment , rate of profit or sometimes just return, is the ratio of money gained or lost on an investment relative to the amount of money invested. The amount of money gained or lost may be referred to as interest, profit/loss, gain/loss, or...
on the financial asset mixture the firm uses to finance capital investment. Some adjustment may be made to the discount rate to take account of risks associated with uncertain cash flows, with other developments.
The discount rates typically applied to different types of companies show significant differences:
- Startups seeking money: 50 – 100 %
- Early Startups: 40 – 60 %
- Late Startups: 30 – 50%
- Mature Companies: 10 – 25%
Reason for high discount rates for startups:
- Reduced marketability of ownerships because stocks are not traded publicly.
- Limited number of investors willing to invest.
- Startups face high risks.
- Over optimistic forecasts by enthusiastic founders.
One method that looks into a correct discount rate is the capital asset pricing model
Capital asset pricing model
In finance, the capital asset pricing model is used to determine a theoretically appropriate required rate of return of an asset, if that asset is to be added to an already well-diversified portfolio, given that asset's non-diversifiable risk...
.
This model takes in account three variables that make up the discount rate:
1. Risk Free Rate: The percentage of return generated by investing in risk free securities such as government bonds.
2. Beta: The measurement of how a company’s stock price reacts to a change in the market. A beta higher than 1 means that a change in share price is exaggerated compared to the rest of shares in the same market. A beta less than 1 means that the share is stable and not very responsive to changes in the market. Less than 0 means that a share is moving in the opposite of the market change.
3. Equity Market Risk Premium: The return on investment that investors require above the risk free rate.
Discount rate= risk free rate + beta*(equity market risk premium)
Discount factor
The discount factor, DF(T), is the factor by which a future cash flow must be multiplied in order to obtain the present value. For a zero-rate (also called spot rate) , taken from a yield curve
, taken from a yield curveYield curve
In finance, the yield curve is the relation between the interest rate and the time to maturity, known as the "term", of the debt for a given borrower in a given currency. For example, the U.S. dollar interest rates paid on U.S...
, and a time to cashflow
 (in years), the discount factor is:
(in years), the discount factor is:In the case where the only discount rate you have is not a zero-rate (neither taken from a zero-coupon bond nor converted from a swap rate
Swap rate
Swap rate is the fixed rate that makes the market value of a given swap at initiation zero. They are the borrowing rates between financial institutions, usually with credit ratings of A/AA equivalent. Swap rates are calculated using the fixed rate leg of interest rate swaps. Swap rates form the...
to a zero-rate through bootstrapping
Bootstrapping (finance)
Bootstrapping is a method for constructing a fixed-income yield curve from the prices of a set of coupon-bearing products by forward substitution....
) but an annually-compounded rate (for example if your benchmark is a US Treasury bond with annual coupons and you only have its yield to maturity
Yield to maturity
The Yield to maturity or redemption yield of a bond or other fixed-interest security, such as gilts, is the internal rate of return earned by an investor who buys the bond today at the market price, assuming that the bond will be held until maturity, and that all coupon and principal payments...
, you would use an annually-compounded discount factor:
However, when operating in a bank, where the amount the bank can lend (and therefore get interest) is linked to the value of its assets (including accrued interest
Accrued interest
In finance, accrued Interest is the interest that has accumulated since the principal investment, or since the previous interest payment if there has been one already. For a financial instrument such as a bond, interest is calculated and paid in set intervals...
), traders usually use daily compounding to discount cashflows. Indeed, even if the interest of the bonds it holds (for example) is paid semi-annually, the value of its book of bond will increase daily, thanks to accrued interest
Accrued interest
In finance, accrued Interest is the interest that has accumulated since the principal investment, or since the previous interest payment if there has been one already. For a financial instrument such as a bond, interest is calculated and paid in set intervals...
being accounted for, and therefore the bank will be able to re-invest these daily accrued interest (by lending additional money or buying more financial products). In that case, the discount factor is then (if the usual money market
Money market
The money market is a component of the financial markets for assets involved in short-term borrowing and lending with original maturities of one year or shorter time frames. Trading in the money markets involves Treasury bills, commercial paper, bankers' acceptances, certificates of deposit,...
day count convention
Day count convention
In finance, a day count convention determines how interest accrues over time for a variety of investments, including bonds, notes, loans, mortgages, medium-term notes, swaps, and forward rate agreements . This determines the amount transferred on interest payment dates, and also the calculation of...
for the currency is ACT/360, in case of currencies such as USD, EUR, JPY), with
 the zero-rate and
the zero-rate and  the time to cashflow in years:
the time to cashflow in years:or, in case the market convention for the currency being discounted is ACT/365 (AUD, CAD, GBP):
Sometimes, for manual calculation, the continuously-compounded hypothesis is a close-enough approximation of the daily-compounding hypothesis, and makes calculation easier (even though it does not have any real application as no financial instrument is continuously compounded). In that case, the discount factor is:
----
Other discounts
For discounts in marketingMarketing
Marketing is the process used to determine what products or services may be of interest to customers, and the strategy to use in sales, communications and business development. It generates the strategy that underlies sales techniques, business communication, and business developments...
, see discounts and allowances
Discounts and allowances
Discounts and allowances are reductions to a basic price of goods or services.They can occur anywhere in the distribution channel, modifying either the manufacturer's list price , the retail price , or the list price Discounts and allowances are reductions to a basic price of goods or services.They...
, sales promotion
Sales promotion
Sales promotion is one of the four aspects of promotional mix. Media and non-media marketing communication are employed for a pre-determined, limited time to increase consumer demand, stimulate market demand or improve product availability...
, and pricing
Pricing
Pricing is the process of determining what a company will receive in exchange for its products. Pricing factors are manufacturing cost, market place, competition, market condition, and quality of product. Pricing is also a key variable in microeconomic price allocation theory. Pricing is a...
. The article on Discounted Cash Flow
Discounted cash flow
In finance, discounted cash flow analysis is a method of valuing a project, company, or asset using the concepts of the time value of money...
provides a nice example about discounting and risks in real estate investments.