
Districts of India
Encyclopedia
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
n state or territory. Districts are further subdivided, in some cases into Sub-Divisions
Subdivisions of India
The Administrative divisions of India are Indian subnational administrative units; they compose a nested hierarchy of country subdivisions. Indian states and territories frequently use different local titles for the same level of subdivision The Administrative divisions of India are Indian...
, and otherwise directly into tehsils or talukas
Tehsil
A Tehsil or Tahsil/Tahasil , also known as Taluk and Mandal, is an administrative division of some country/countries of South Asia....
.
District officials include:
- the Deputy CommissionerDeputy Commissioner (India)The deputy commissioner or district magistrate or district collector or district magistrate and collector is the head of the revenue administration of an Indian district. The DC is required to be an Indian Administrative Service officer who is in charge of governmental assets in his district of...
or District Magistrate or District CollectorDistrict collectorThe District Collector is the district head of administration of the bureaucracy in a state of India. Though he/she is appointed and is under general supervision of the state government, he/she has to be a member of the elite IAS recruited by the Central Government...
, an officer of the Indian Administrative ServiceIndian Administrative ServiceThe Indian Administrative Service is the administrative civil service of the Government of India. It is one of the three All India Services....
, in charge of administrationPublic administrationPublic Administration houses the implementation of government policy and an academic discipline that studies this implementation and that prepares civil servants for this work. As a "field of inquiry with a diverse scope" its "fundamental goal.....
and revenueRevenueIn business, revenue is income that a company receives from its normal business activities, usually from the sale of goods and services to customers. In many countries, such as the United Kingdom, revenue is referred to as turnover....
collection - the Superintendent of Police or Deputy Commissioner of Police, an officer belonging to the Indian Police ServiceIndian Police ServiceThe Indian Police Service , simply known as Indian Police or IPS, is one of the three All India Services of the Government of India...
, responsible for maintaining law and orderLaw and order (politics)In politics, law and order refers to demands for a strict criminal justice system, especially in relation to violent and property crime, through harsher criminal penalties... - the Deputy Conservator of ForestsDeputy Conservator of Forests (India)A Deputy Conservator of Forests or, equivalently a Divisional Forest Officer is an officer belonging to the elite Indian Forest Service. The Deputy Conservator of Forests is responsible for managing the Forests, Environment and Wild-Life related issues of a Forest Division of a state or a union...
, an officer belonging to the Indian Forest ServiceIndian Forest ServiceThe Indian Forest Service is the Forestry service of India. It is one of the three All India Services of the Indian government, along with the Indian Administrative Service and Indian Police Service; its employees are recruited by the national government but serve under the state governments or...
, entrusted with the management of the forestForestA forest, also referred to as a wood or the woods, is an area with a high density of trees. As with cities, depending where you are in the world, what is considered a forest may vary significantly in size and have various classification according to how and what of the forest is composed...
s, environmentNatural environmentThe natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species....
and wildlifeWildlifeWildlife includes all non-domesticated plants, animals and other organisms. Domesticating wild plant and animal species for human benefit has occurred many times all over the planet, and has a major impact on the environment, both positive and negative....
of the district
Each of these officials is aided by officers of the appropriate branches of state government.
Most districts have a distinct headquarters
Headquarters
Headquarters denotes the location where most, if not all, of the important functions of an organization are coordinated. In the United States, the corporate headquarters represents the entity at the center or the top of a corporation taking full responsibility managing all business activities...
; Mumbai
Mumbai
Mumbai , formerly known as Bombay in English, is the capital of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the most populous city in India, and the fourth most populous city in the world, with a total metropolitan area population of approximately 20.5 million...
is an example of a city which, despite coming under a district, does not have a district headquarters, though it does have a Collector.
Overview
|
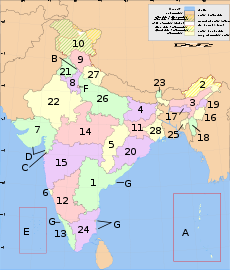 |
Naming
The majority of districts are named after their administrative center. Some are referred to by two names, a traditional one and one that uses the name of the town that is the headquarters. Since most of the districts are named after a town, the word "district" or "District" is appended to distinguish between the town and the district. Official websites very often use District with a capital D in this context.Ambiguous names
The names of the 640 districts are mostly unique. There are some exceptions:- Within India five names are ambiguous, representing 10 districts: Aurangabad (BRBiharBihar is a state in eastern India. It is the 12th largest state in terms of geographical size at and 3rd largest by population. Almost 58% of Biharis are below the age of 25, which is the highest proportion in India....
, MHMaharashtraMaharashtra is a state located in India. It is the second most populous after Uttar Pradesh and third largest state by area in India...
), Bijapur (CT, KA), Bilaspur (CT, HP), Hamirpur (HP, UP), Pratapgarh (RJ, UP). - Seven districts share names with districts in other countries in South Asia: Bhojpur (BR/Nepal), Daman (DD, Afghanistan), Ghaziabad (UP, Afghanistan), Gopalganj (BR, Bangladesh), Hyderabad (AP/Pakistan), Lalitpur (UP/Nepal), Poonch (JK, Pakistan)
- One outside South Asia: Mansa District (PB, Zambia)
City districts
- Bangalore Urban district
- Ahmedabad District
- Calcutta District
- ChandigarhChandigarhChandigarh is a union territory of India that serves as the capital of two states, Haryana and Punjab. The name Chandigarh translates as "The Fort of Chandi". The name is from an ancient temple called Chandi Mandir, devoted to the Hindu goddess Chandi, in the city...
- Mumbai City DistrictMumbai City DistrictMumbai City District is a district of Maharashtra in Konkan Division. As a city district, it has no headquarters or subdivisions. It, along with the Mumbai Suburban District make up the metropolis of Mumbai. The city area is called the "island city" or South Mumbai or Old Mumbai. It extends from...
- Kanpur (city)
- Hyderabad
- In Pondicherry U.T.
- Pondicherry district
- Karaikal districtKaraikal districtKaraikal district is one of the four regions of the Union Territory of Pondicherry in India.Karaikal town about 16 km. north of Nagappattinam and 9 km.south of Tarangambadi is the regional headquarters...
- Mahe districtMahe districtMahe district, one of the four districts of the Union Territory of Pondicherry in India, has an area of 9 km2. It consists of the whole of the Mahé region....
- Yanam districtYanam districtYanam district is one of the four districts of the Union Territory of Pondicherry in India.-Revenue Villages:Apart from the town of Yanam itself, the following villages fall under the district's jurisdiction:* Agraharam* Darialatippa* Farampeta...
Note: Chandigarh is the capital of two states and 1 Union territory.
See also
- List of districts of India
- Subdivisions of IndiaSubdivisions of IndiaThe Administrative divisions of India are Indian subnational administrative units; they compose a nested hierarchy of country subdivisions. Indian states and territories frequently use different local titles for the same level of subdivision The Administrative divisions of India are Indian...
- Local Governance in IndiaLocal Governance in IndiaUrban Local Bodies of India are the constitutionally provided administrative units that provide basic infrastructure and services in cities and towns...
External links
- 2001 maps; provides maps of social, economic and demographic data of India in 2001

