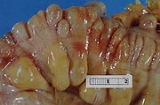
Diverticulitis
Encyclopedia
Diverticulitis is a common digestive disease
particularly found in the large intestine
. Diverticulitis develops from diverticulosis
, which involves the formation of pouches (diverticula) on the outside of the colon
. Diverticulitis results if one of these diverticula becomes inflamed.
, and leukocytosis
(an elevation of the white cell
count in blood tests). Patients may also complain of nausea
or diarrhea
; others may be constipated.
Less commonly, an individual with diverticulitis may present with right-sided abdominal pain
. This may be due to the less prevalent right-sided diverticula or a very redundant sigmoid colon.
as small pains and/or diarrhea
, and may slowly turn into vomiting and sharp pains.
do not have any discomfort or symptoms; however, symptoms may include mild cramps, bloating, and constipation. Other diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease
(IBD) and stomach ulcers cause similar problems, so these symptoms do not always mean a person has diverticulosis.
(Section 4) has the smallest diameter of any portion of the colon, and therefore the portion which would be expected to have the highest intraluminal pressure. The claim that a lack of dietary fiber, particularly non-soluble fiber (also known in older parlance as "roughage") predisposes individuals to diverticular disease is supported within the medical literature
.
Other studies, such as barium enema
and colonoscopy
are contraindicated
in the acute phase of diverticulitis due to the risk of perforation.
includes colon cancer, inflammatory bowel disease
, ischemic colitis
, and irritable bowel syndrome
, as well as a number of urological and gynecological processes. Some patients report bleeding from the rectum.
, abscess
, or fistula may require surgery, either immediately or on an elective basis.
People may be placed on a low residue diet
. This low-fiber diet gives the colon adequate time to heal without needing to be overworked. Later, patients are placed on a high-fiber diet.
. Whether the elective surgery should be performed is decided based on external factors such as the stage of the disease, the age of the patient and his or her general medical condition, as well as the severity and frequency of attacks or if the symptoms persisted after a first acute episode
. In most cases, the decision to perform elective surgery is taken when the risks of the surgery are smaller than the ones resulted from the complication of the condition. Elective surgery may be performed at least six weeks after recovery from acute diverticulitis.
Emergency surgery is necessary for people whose intestine
has ruptured; intestinal rupture always results in infection of the abdominal cavity. During a diverticulitis surgery, the ruptured section is removed and a colostomy
is performed. This means that the surgeon
will create an opening between the large intestine and the surface of the skin. The colostomy is closed in about 10 or 12 weeks in a subsequent surgery in which the cut ends of the intestine are rejoined.
The first surgical approach consists in the resection
and primary anastomosis
. This first stage of surgery is performed on patients with a well vascularized, nonedematous and tension-free bowel. The proximal margin should be an area of pliable colon without hypertrophy
or inflammation. The distal margin should extend to the upper third of the rectum
where the taenia
coalesces. Not all of the diverticula-bearing colon must be removed, since diverticula proximal to the descending or sigmoid colon are unlikely to result in further symptoms.
Diverticulitis surgery can be done in two ways: through a primary bowel resection
or through a bowel resection with colostomy. Both bowel resections may be done in the traditional way or by laparoscopic surgery
.
The traditional bowel resection is made using an open surgical approach, called colectomy
. During a colectomy, the patient is placed under general anesthesia. A surgeon performing a colectomy will make a lower midline incision in the abdomen or a lateral lower transverse incision. The diseased section of the large intestine is removed and then the two healthy ends are sewn or stapled back together. A colostomy may be performed when the bowel has to be relieved of its normal digestive work as it heals. A colostomy implies creating a temporary opening of the colon on the skin surface and the end of the colon is passed through the abdominal wall and a removable bag is attached to it. The waste will be collected in the bag.
However, most of the surgeons prefer performing the bowel resection laparoscopically mainly because the postoperative pain is reduced and the patient's recovery is faster. The laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure in which three to four smaller incisions are made in the abdomen or navel
.
All colon surgery involves only three maneuvers that may vary in complexity depending on the region of the bowel and the nature of the disease which are the retraction of the colon, the division of the attachments to the colon and the dissection of the mesentery
. After the resection of the colon, the surgeon normally divides the attachments to the liver and the small intestine. After the mesenteric vessels are dissected, the colon is divided with special surgical staplers that close off the bowel while cutting between the staple lines.
. Depending on the patient's general medical condition, the procedure may be done traditionally, via a colectomy
or laparoscopically, which requires smaller incisions and a faster recovery.
remains an option. Also known as the Hartmann's operation
, this is a more complicated surgery typically reserved for life-threatening cases.
The bowel resection with colostomy implies a temporary colostomy which is followed by a second operation which has the purpose to reverse the colostomy. The surgeon makes an opening in the abdominal wall (a colostomy) which helps clearing the infection and inflammation
. The colon is brought out through the opening and all waste is collected into an external bag.
The colostomy is usually temporary but it may be permanent depending on the severity of the case. Most of the time, several months later after the inflammation has healed, the patient undergoes another major surgery during which the surgeon rejoins the colon and rectum and reverses the colostomy.
may subsequently infect the outside of the colon
if an inflamed diverticulum bursts open. If the infection
spreads to the lining of the abdominal cavity
, (peritoneum
), this can cause a potentially fatal peritonitis
. Sometimes inflamed diverticula can cause narrowing of the bowel, leading to an obstruction
. Also, the affected part of the colon could adhere to the bladder
or other organ
in the pelvic cavity
, causing a fistula, or abnormal connection between an organ and adjacent structure or organ, in this case the colon and an adjacent organ.
may be associated with diverticulitis in younger patients, with some being as young as 20 years old.
In Western countries, diverticular disease most commonly involves the sigmoid colon
- section 4 - (95% of patients). The prevalence of diverticular disease has increased from an estimated 10% in the 1920s to between 35 and 50% by the late 1960s. 65% of those currently 85 years of age and older can be expected to have some form of diverticular disease of the colon. Less than 5% of those aged 40 years and younger may also be affected by diverticular disease.
Left-sided diverticular disease (involving the sigmoid colon) is most common in the West, while right-sided diverticular disease is more prevalent in Asia and Africa. Among patients with diverticulosis, 10–25% patients will go on to develop diverticulitis within their lifetimes.
Digestive disease
All diseases that pertain to the gastrointestinal tract are labelled as digestive diseases. This includes diseases of the esophagus, stomach, first, second, and third part of the duodenum, jejunum, ileum, the ileo-cecal complex, large intestine , sigmoid colon, and rectum.-Esophagus:*Esophagitis -...
particularly found in the large intestine
Large intestine
The large intestine is the third-to-last part of the digestive system — — in vertebrate animals. Its function is to absorb water from the remaining indigestible food matter, and then to pass useless waste material from the body...
. Diverticulitis develops from diverticulosis
Diverticulosis
Diverticulosis also known as "diverticular disease" is the condition of having diverticula in the colon, which are outpocketings of the colonic mucosa and submucosa through weaknesses of muscle layers in the colon wall. These are more common in the sigmoid colon, which is a common place for...
, which involves the formation of pouches (diverticula) on the outside of the colon
Colon (anatomy)
The colon is the last part of the digestive system in most vertebrates; it extracts water and salt from solid wastes before they are eliminated from the body, and is the site in which flora-aided fermentation of unabsorbed material occurs. Unlike the small intestine, the colon does not play a...
. Diverticulitis results if one of these diverticula becomes inflamed.
Signs and symptoms
Patients often present with the classic triad of left lower quadrant pain, feverFever
Fever is a common medical sign characterized by an elevation of temperature above the normal range of due to an increase in the body temperature regulatory set-point. This increase in set-point triggers increased muscle tone and shivering.As a person's temperature increases, there is, in...
, and leukocytosis
Leukocytosis
Leukocytosis is a raised white blood cell count above the normal range in the blood. It is frequently a sign of an inflammatory response, most commonly the result of infection, and is observed in certain parasitic infections...
(an elevation of the white cell
White blood cell
White blood cells, or leukocytes , are cells of the immune system involved in defending the body against both infectious disease and foreign materials. Five different and diverse types of leukocytes exist, but they are all produced and derived from a multipotent cell in the bone marrow known as a...
count in blood tests). Patients may also complain of nausea
Nausea
Nausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
or diarrhea
Diarrhea
Diarrhea , also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having three or more loose or liquid bowel movements per day. It is a common cause of death in developing countries and the second most common cause of infant deaths worldwide. The loss of fluids through diarrhea can cause dehydration and...
; others may be constipated.
Less commonly, an individual with diverticulitis may present with right-sided abdominal pain
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain can be one of the symptoms associated with transient disorders or serious disease. Making a definitive diagnosis of the cause of abdominal pain can be difficult, because many diseases can result in this symptom. Abdominal pain is a common problem...
. This may be due to the less prevalent right-sided diverticula or a very redundant sigmoid colon.
Diverticulitis
The most common symptom of diverticulitis is abdominal pain. The most common sign is tenderness around the left side of the lower abdomen. If infection is the cause, then nausea, vomiting, fever, cramping, and constipation may occur as well. The severity of symptoms depends on the extent of the infection and complications. Diverticulitis may worsen throughout the first day, as it startsProdrome
In medicine, a prodrome is an early symptom that might indicate the start of a disease before specific symptoms occur. It is derived from the Greek word prodromos or precursor...
as small pains and/or diarrhea
Diarrhea
Diarrhea , also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having three or more loose or liquid bowel movements per day. It is a common cause of death in developing countries and the second most common cause of infant deaths worldwide. The loss of fluids through diarrhea can cause dehydration and...
, and may slowly turn into vomiting and sharp pains.
Diverticulosis
Most people with diverticulosisDiverticulosis
Diverticulosis also known as "diverticular disease" is the condition of having diverticula in the colon, which are outpocketings of the colonic mucosa and submucosa through weaknesses of muscle layers in the colon wall. These are more common in the sigmoid colon, which is a common place for...
do not have any discomfort or symptoms; however, symptoms may include mild cramps, bloating, and constipation. Other diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease
In medicine, inflammatory bowel disease is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine. The major types of IBD are Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.-Classification:...
(IBD) and stomach ulcers cause similar problems, so these symptoms do not always mean a person has diverticulosis.
Causes
The development of colonic diverticulum is thought to be a result of raised intraluminal colonic pressures. The sigmoid colonSigmoid colon
The sigmoid colon is the part of the large intestine that is closest to the rectum and anus. It forms a loop that averages about 40 cm...
(Section 4) has the smallest diameter of any portion of the colon, and therefore the portion which would be expected to have the highest intraluminal pressure. The claim that a lack of dietary fiber, particularly non-soluble fiber (also known in older parlance as "roughage") predisposes individuals to diverticular disease is supported within the medical literature
Medical literature
Medical literature refers to articles in journals and texts in books devoted to the field of medicine.Contemporary and historic views regarding diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of medical conditions have been documented for thousands of years. The Edwin Smith papyrus is the first known medical...
.
Diet
Foods such as seeds, nuts, and corn were, in the past, thought by many health care professionals to possibly aggravate diverticulitis. However, recent studies have found no evidence that suggests the avoidance of nuts and seeds prevents the progression of diverticulosis to an acute case of diverticulitis. Not only has this research shown that they do not appear to be aggravating the diverticulitis, but it appears that a higher intake of nuts and corn could in fact help to avoid diverticulitis in male adults.Diagnosis
People with the above symptoms are commonly studied with a computed tomography, or CT scan. The CT scan is very accurate (98%) in diagnosing diverticulitis. In order to extract the most information possible about the patient's condition, thin section (5mm) transverse images are obtained through the entire abdomen and pelvis after the patient has been administered oral and intravascular contrast. Images reveal localized thickening and hyperemia (increased blood flow) involving a segment of the colon wall, with inflammatory changes extending into the fatty tissues surrounding the colon. The diagnosis of acute diverticulitis is made confidently when the involved segment contains diverticulae. CT may also identify patients with more complicated diverticulitis, such as those with an associated abscess. It may even allow for radiologically guided drainage of an associated abscess, sparing a patient from immediate surgical intervention.Other studies, such as barium enema
Barium enema
A lower gastrointestinal series, also called a barium enema, is a medical procedure used to examine and diagnose problems with the human colon . X-ray pictures are taken while barium sulfate fills the colon via the rectum.-Procedure:...
and colonoscopy
Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is the endoscopic examination of the large bowel and the distal part of the small bowel with a CCD camera or a fiber optic camera on a flexible tube passed through the anus. It may provide a visual diagnosis and grants the opportunity for biopsy or removal of suspected...
are contraindicated
Contraindication
In medicine, a contraindication is a condition or factor that serves as a reason to withhold a certain medical treatment.Some contraindications are absolute, meaning that there are no reasonable circumstances for undertaking a course of action...
in the acute phase of diverticulitis due to the risk of perforation.
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosisDifferential diagnosis
A differential diagnosis is a systematic diagnostic method used to identify the presence of an entity where multiple alternatives are possible , and may also refer to any of the included candidate alternatives A differential diagnosis (sometimes abbreviated DDx, ddx, DD, D/Dx, or ΔΔ) is a...
includes colon cancer, inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease
In medicine, inflammatory bowel disease is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine. The major types of IBD are Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.-Classification:...
, ischemic colitis
Colitis
In medicine, colitis refers to an inflammation of the colon and is often used to describe an inflammation of the large intestine .Colitides may be acute and self-limited or chronic, i.e...
, and irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome is a diagnosis of exclusion. It is a functional bowel disorder characterized by chronic abdominal pain, discomfort, bloating, and alteration of bowel habits in the absence of any detectable organic cause. In some cases, the symptoms are relieved by bowel movements...
, as well as a number of urological and gynecological processes. Some patients report bleeding from the rectum.
Treatment
Most cases of simple, uncomplicated diverticulitis respond to conservative therapy with bowel rest and antibiotics. The evidence for antibiotics however in mild cases is poor. However, recurring acute attacks or complications, such as peritonitisPeritonitis
Peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum, the serous membrane that lines part of the abdominal cavity and viscera. Peritonitis may be localised or generalised, and may result from infection or from a non-infectious process.-Abdominal pain and tenderness:The main manifestations of...
, abscess
Abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has accumulated in a cavity formed by the tissue in which the pus resides due to an infectious process or other foreign materials...
, or fistula may require surgery, either immediately or on an elective basis.
People may be placed on a low residue diet
Low residue diet
A low residue diet is a diet designed to reduce the frequency and volume of stools while prolonging intestinal transit time. It is similar to a low fiber diet, but typically includes restrictions on foods that increase bowel activity, such as milk, milk products, and prune juice. A low residue diet...
. This low-fiber diet gives the colon adequate time to heal without needing to be overworked. Later, patients are placed on a high-fiber diet.
Surgery
Diverticulitis surgery may be elective or may be a medical emergencyMedical emergency
A medical emergency is an injury or illness that is acute and poses an immediate risk to a person's life or long term health. These emergencies may require assistance from another person, who should ideally be suitably qualified to do so, although some of these emergencies can be dealt with by the...
. Whether the elective surgery should be performed is decided based on external factors such as the stage of the disease, the age of the patient and his or her general medical condition, as well as the severity and frequency of attacks or if the symptoms persisted after a first acute episode
Acute (medicine)
In medicine, an acute disease is a disease with either or both of:# a rapid onset, as in acute infection# a short course ....
. In most cases, the decision to perform elective surgery is taken when the risks of the surgery are smaller than the ones resulted from the complication of the condition. Elective surgery may be performed at least six weeks after recovery from acute diverticulitis.
Emergency surgery is necessary for people whose intestine
Intestine
In human anatomy, the intestine is the segment of the alimentary canal extending from the pyloric sphincter of the stomach to the anus and, in humans and other mammals, consists of two segments, the small intestine and the large intestine...
has ruptured; intestinal rupture always results in infection of the abdominal cavity. During a diverticulitis surgery, the ruptured section is removed and a colostomy
Colostomy
A colostomy is a surgical procedure in which a stoma is formed by drawing the healthy end of the large intestine or colon through an incision in the anterior abdominal wall and suturing it into place. This opening, in conjunction with the attached stoma appliance, provides an alternative channel...
is performed. This means that the surgeon
Surgeon
In medicine, a surgeon is a specialist in surgery. Surgery is a broad category of invasive medical treatment that involves the cutting of a body, whether human or animal, for a specific reason such as the removal of diseased tissue or to repair a tear or breakage...
will create an opening between the large intestine and the surface of the skin. The colostomy is closed in about 10 or 12 weeks in a subsequent surgery in which the cut ends of the intestine are rejoined.
The first surgical approach consists in the resection
Segmental resection
Segmental resection is a surgical procedure to remove part of an organ or gland. It may also be used to remove a tumor and normal tissue around it. In lung cancer surgery, segmental resection refers to removing a section of a lobe of the lung.- External links :* entry in the public domain NCI...
and primary anastomosis
Anastomosis
An anastomosis is the reconnection of two streams that previously branched out, such as blood vessels or leaf veins. The term is used in medicine, biology, mycology and geology....
. This first stage of surgery is performed on patients with a well vascularized, nonedematous and tension-free bowel. The proximal margin should be an area of pliable colon without hypertrophy
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy is the increase in the volume of an organ or tissue due to the enlargement of its component cells. It should be distinguished from hyperplasia, in which the cells remain approximately the same size but increase in number...
or inflammation. The distal margin should extend to the upper third of the rectum
Rectum
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in some mammals, and the gut in others, terminating in the anus. The human rectum is about 12 cm long...
where the taenia
Taenia
Taenia can refer to:* Taenia of Doric columnsIn medicine and anatomy* Taenia coli of the large intestine* Taenia thalami of the mammal brain* Taenia of fourth ventricle of the mammal brain...
coalesces. Not all of the diverticula-bearing colon must be removed, since diverticula proximal to the descending or sigmoid colon are unlikely to result in further symptoms.
Diverticulitis surgery can be done in two ways: through a primary bowel resection
Bowel resection
A bowel resection is a surgical procedure in which a part of the large or small intestine is removed. It may be performed due to cancer, necrosis, enteritis, diverticular disease, or a block in the intestine due to scar tissue...
or through a bowel resection with colostomy. Both bowel resections may be done in the traditional way or by laparoscopic surgery
Laparoscopic surgery
Laparoscopic surgery, also called minimally invasive surgery , bandaid surgery, or keyhole surgery, is a modern surgical technique in which operations in the abdomen are performed through small incisions as opposed to the larger incisions needed in laparotomy.Keyhole surgery makes use of images...
.
The traditional bowel resection is made using an open surgical approach, called colectomy
Colectomy
Colectomy consists of the surgical resection of any extent of the large intestine .-History:Sir William Arbuthnot-Lane was one of the early proponents of the usefulness of total colectomies, although his overuse of the procedure called the wisdom of the surgery into question.-Indications:Some of...
. During a colectomy, the patient is placed under general anesthesia. A surgeon performing a colectomy will make a lower midline incision in the abdomen or a lateral lower transverse incision. The diseased section of the large intestine is removed and then the two healthy ends are sewn or stapled back together. A colostomy may be performed when the bowel has to be relieved of its normal digestive work as it heals. A colostomy implies creating a temporary opening of the colon on the skin surface and the end of the colon is passed through the abdominal wall and a removable bag is attached to it. The waste will be collected in the bag.
However, most of the surgeons prefer performing the bowel resection laparoscopically mainly because the postoperative pain is reduced and the patient's recovery is faster. The laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure in which three to four smaller incisions are made in the abdomen or navel
Navel
The navel is a scar on the abdomen caused when the umbilical cord is removed from a newborn baby...
.
All colon surgery involves only three maneuvers that may vary in complexity depending on the region of the bowel and the nature of the disease which are the retraction of the colon, the division of the attachments to the colon and the dissection of the mesentery
Mesentery
In anatomy, the mesentery is the double layer of peritoneum that suspends the jejunum and ileum from the posterior wall of the abdomen. Its meaning, however, is frequently extended to include double layers of peritoneum connecting various components of the abdominal cavity.-Mesentery :The...
. After the resection of the colon, the surgeon normally divides the attachments to the liver and the small intestine. After the mesenteric vessels are dissected, the colon is divided with special surgical staplers that close off the bowel while cutting between the staple lines.
Primary bowel resection
The primary bowel resection is the standard procedure for diverticulitis. It consists of the removal of the diseased or ruptured part of the intestine which is then reconnected to healthy segments of the colon. This is called anastomosisAnastomosis
An anastomosis is the reconnection of two streams that previously branched out, such as blood vessels or leaf veins. The term is used in medicine, biology, mycology and geology....
. Depending on the patient's general medical condition, the procedure may be done traditionally, via a colectomy
Colectomy
Colectomy consists of the surgical resection of any extent of the large intestine .-History:Sir William Arbuthnot-Lane was one of the early proponents of the usefulness of total colectomies, although his overuse of the procedure called the wisdom of the surgery into question.-Indications:Some of...
or laparoscopically, which requires smaller incisions and a faster recovery.
Bowel resection with colostomy
When excessive inflammation of the colon renders primary bowel resection too risky, bowel resection with colostomyColostomy
A colostomy is a surgical procedure in which a stoma is formed by drawing the healthy end of the large intestine or colon through an incision in the anterior abdominal wall and suturing it into place. This opening, in conjunction with the attached stoma appliance, provides an alternative channel...
remains an option. Also known as the Hartmann's operation
Hartmann's operation
Hartmann's operation is the surgical resection of the rectosigmoid colon with closure of the rectal stump and formation of an end colostomy. It was used to treat colon cancer or diverticulitis. These days its use is limited to emergency surgery when immediate anastomosis is not possible, or more...
, this is a more complicated surgery typically reserved for life-threatening cases.
The bowel resection with colostomy implies a temporary colostomy which is followed by a second operation which has the purpose to reverse the colostomy. The surgeon makes an opening in the abdominal wall (a colostomy) which helps clearing the infection and inflammation
Inflammation
Inflammation is part of the complex biological response of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. Inflammation is a protective attempt by the organism to remove the injurious stimuli and to initiate the healing process...
. The colon is brought out through the opening and all waste is collected into an external bag.
The colostomy is usually temporary but it may be permanent depending on the severity of the case. Most of the time, several months later after the inflammation has healed, the patient undergoes another major surgery during which the surgeon rejoins the colon and rectum and reverses the colostomy.
Complications
In complicated diverticulitis, bacteriaBacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
may subsequently infect the outside of the colon
Colon (anatomy)
The colon is the last part of the digestive system in most vertebrates; it extracts water and salt from solid wastes before they are eliminated from the body, and is the site in which flora-aided fermentation of unabsorbed material occurs. Unlike the small intestine, the colon does not play a...
if an inflamed diverticulum bursts open. If the infection
Infection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
spreads to the lining of the abdominal cavity
Abdominal cavity
The abdominal cavity is the body cavity of the human body that holds the bulk of the viscera. It is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity. Its dome-shaped roof is the thoracic diaphragm , and its oblique floor is the pelvic inlet...
, (peritoneum
Peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane that forms the lining of the abdominal cavity or the coelom — it covers most of the intra-abdominal organs — in amniotes and some invertebrates...
), this can cause a potentially fatal peritonitis
Peritonitis
Peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum, the serous membrane that lines part of the abdominal cavity and viscera. Peritonitis may be localised or generalised, and may result from infection or from a non-infectious process.-Abdominal pain and tenderness:The main manifestations of...
. Sometimes inflamed diverticula can cause narrowing of the bowel, leading to an obstruction
Obstruction
Obstruction may refer to:* Obstruction theory, in mathematics* Obstruction of justice, the crime of interfering with law enforcement* Obstructing government administration* Propagation path obstruction** Single Vegetative Obstruction Model-Medical:...
. Also, the affected part of the colon could adhere to the bladder
Urinary bladder
The urinary bladder is the organ that collects urine excreted by the kidneys before disposal by urination. A hollow muscular, and distensible organ, the bladder sits on the pelvic floor...
or other organ
Organ (anatomy)
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in structural unit to serve a common function. Usually there is a main tissue and sporadic tissues . The main tissue is the one that is unique for the specific organ. For example, main tissue in the heart is the myocardium, while sporadic are...
in the pelvic cavity
Pelvic cavity
-External links:* * *...
, causing a fistula, or abnormal connection between an organ and adjacent structure or organ, in this case the colon and an adjacent organ.
- Bowel obstructionBowel obstructionBowel obstruction is a mechanical or functional obstruction of the intestines, preventing the normal transit of the products of digestion. It can occur at any level distal to the duodenum of the small intestine and is a medical emergency...
- PeritonitisPeritonitisPeritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum, the serous membrane that lines part of the abdominal cavity and viscera. Peritonitis may be localised or generalised, and may result from infection or from a non-infectious process.-Abdominal pain and tenderness:The main manifestations of...
- AbscessAbscessAn abscess is a collection of pus that has accumulated in a cavity formed by the tissue in which the pus resides due to an infectious process or other foreign materials...
- Fistula
- BleedingBleedingBleeding, technically known as hemorrhaging or haemorrhaging is the loss of blood or blood escape from the circulatory system...
- Strictures
Epidemiology
Diverticulitis most often affects middle-aged and elderly persons, though it can strike younger patients as well. Central obesityCentral obesity
Abdominal obesity, colloquially known as belly fat or clinically as central obesity, is the accumulation of abdominal fat resulting in an increase in waist size...
may be associated with diverticulitis in younger patients, with some being as young as 20 years old.
In Western countries, diverticular disease most commonly involves the sigmoid colon
Sigmoid colon
The sigmoid colon is the part of the large intestine that is closest to the rectum and anus. It forms a loop that averages about 40 cm...
- section 4 - (95% of patients). The prevalence of diverticular disease has increased from an estimated 10% in the 1920s to between 35 and 50% by the late 1960s. 65% of those currently 85 years of age and older can be expected to have some form of diverticular disease of the colon. Less than 5% of those aged 40 years and younger may also be affected by diverticular disease.
Left-sided diverticular disease (involving the sigmoid colon) is most common in the West, while right-sided diverticular disease is more prevalent in Asia and Africa. Among patients with diverticulosis, 10–25% patients will go on to develop diverticulitis within their lifetimes.
External links
- Health and Disease Information on Diverticulitis at Penn State University
- Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis at NIDDK
- Diverticulitis at Mayo ClinicMayo ClinicMayo Clinic is a not-for-profit medical practice and medical research group specializing in treating difficult patients . Patients are referred to Mayo Clinic from across the U.S. and the world, and it is known for innovative and effective treatments. Mayo Clinic is known for being at the top of...

