Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine
Encyclopedia
Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O. or DO) is a professional doctoral degree for physician
s in the United States
. Holders of the MD degree, Doctor of Medicine, have the same rights, privileges and responsibilities as osteopathic physicians in the United States.
The American Osteopathic Association’s Commission on Osteopathic College Accreditation (COCA) accredits 26 colleges of osteopathic medicine offering instruction at 34 locations in 25 states, compared with 134 medical schools that offer the MD degree.
(MD
) medical schools. The first two years focus on the biomedical and clinical sciences, followed by core clinical training in the clinical specialties. Osteopathic medical school accreditation standards require training in internal medicine
, obstetrics/gynecology
, pediatrics
, family practice, surgery
, psychiatry
, emergency medicine
, radiology
, preventive medicine
and public health
. According to Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine
, "the training, practice, credentialing, licensure, and reimbursement of osteopathic physicians is virtually indistinguishable from those of allopathic physicians, with 4 years of osteopathic medical school followed by specialty and subspecialty training and [board] certification." However, osteopathic physicians also receive an additional 300 – 500 hours in the study of hands-on manual medicine and the body's musculoskeletal system integrated into the medical curriculum, which is referred to as Osteopathic manipulative medicine
.
Upon graduation from medical school, many DOs attend the same internship and residency
training programs as their MD counterparts and then take MD specialty board exams. In addition, the osteopathic medical profession has its own specialty training programs and specialty board examinations for DO graduates.
Upon completion of internship and residency requirements for their chosen medical specialty, and depending on whether the program attended as ACGME or AOA accredited, holders of the DO may elect to be board certified by either an allopathic specialty board (through the American Medical Association
's American Board of Medical Specialties
) or an osteopathic specialty board (through the American Osteopathic Association Bureau of Osteopathic Specialists
certifying boards).
The following is an International Licensure Summary for US-trained Doctors of Osteopathic Medicine, as listed by the American Osteopathic Association
:
Physician
A physician is a health care provider who practices the profession of medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring human health through the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, injury and other physical and mental impairments...
s in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
. Holders of the MD degree, Doctor of Medicine, have the same rights, privileges and responsibilities as osteopathic physicians in the United States.
The American Osteopathic Association’s Commission on Osteopathic College Accreditation (COCA) accredits 26 colleges of osteopathic medicine offering instruction at 34 locations in 25 states, compared with 134 medical schools that offer the MD degree.
Education and training
Osteopathic medical school curricula closely mirror those of allopathicAllopathic medicine
Allopathic medicine refers to the practice of conventional medicine that uses pharmacologically active agents or physical interventions to treat or suppress symptoms or pathophysiologic processes of diseases or conditions. It was coined by Samuel Hahnemann , a homeopath, in 1810...
(MD
Doctor of Medicine
Doctor of Medicine is a doctoral degree for physicians. The degree is granted by medical schools...
) medical schools. The first two years focus on the biomedical and clinical sciences, followed by core clinical training in the clinical specialties. Osteopathic medical school accreditation standards require training in internal medicine
Internal medicine
Internal medicine is the medical specialty dealing with the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of adult diseases. Physicians specializing in internal medicine are called internists. They are especially skilled in the management of patients who have undifferentiated or multi-system disease processes...
, obstetrics/gynecology
Obstetrics and gynaecology
Obstetrics and gynaecology are the two surgical–medical specialties dealing with the female reproductive organs in their pregnant and non-pregnant state, respectively, and as such are often combined to form a single medical specialty and postgraduate training programme...
, pediatrics
Pediatrics
Pediatrics or paediatrics is the branch of medicine that deals with the medical care of infants, children, and adolescents. A medical practitioner who specializes in this area is known as a pediatrician or paediatrician...
, family practice, surgery
Surgery
Surgery is an ancient medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a patient to investigate and/or treat a pathological condition such as disease or injury, or to help improve bodily function or appearance.An act of performing surgery may be called a surgical...
, psychiatry
Psychiatry
Psychiatry is the medical specialty devoted to the study and treatment of mental disorders. These mental disorders include various affective, behavioural, cognitive and perceptual abnormalities...
, emergency medicine
Emergency medicine
Emergency medicine is a medical specialty in which physicians care for patients with acute illnesses or injuries which require immediate medical attention. While not usually providing long-term or continuing care, emergency medicine physicians diagnose a variety of illnesses and undertake acute...
, radiology
Radiology
Radiology is a medical specialty that employs the use of imaging to both diagnose and treat disease visualized within the human body. Radiologists use an array of imaging technologies to diagnose or treat diseases...
, preventive medicine
Preventive medicine
Preventive medicine or preventive care refers to measures taken to prevent diseases, rather than curing them or treating their symptoms...
and public health
Public health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals" . It is concerned with threats to health based on population health...
. According to Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine
Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine
Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine is an American textbook of internal medicine. First published in 1950, it is presently in its eighteenth edition...
, "the training, practice, credentialing, licensure, and reimbursement of osteopathic physicians is virtually indistinguishable from those of allopathic physicians, with 4 years of osteopathic medical school followed by specialty and subspecialty training and [board] certification." However, osteopathic physicians also receive an additional 300 – 500 hours in the study of hands-on manual medicine and the body's musculoskeletal system integrated into the medical curriculum, which is referred to as Osteopathic manipulative medicine
Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine
Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine is the application of the distinct osteopathic philosophy, structural diagnosis and use of Osteopathic Manipulative Technique in the diagnosis and management of the patient. OMM takes into account the physical and mental health of a patient, and how either aspect...
.
Upon graduation from medical school, many DOs attend the same internship and residency
Residency (medicine)
Residency is a stage of graduate medical training. A resident physician or resident is a person who has received a medical degree , Podiatric degree , Dental Degree and who practices...
training programs as their MD counterparts and then take MD specialty board exams. In addition, the osteopathic medical profession has its own specialty training programs and specialty board examinations for DO graduates.
Licensing and board certification
To obtain a license to practice medicine in the United States, medical students must pass one of two licensing boards at the conclusion of their medical training: USMLE (United States Medical Licensing Exam) or COMLEX (Comprehensive Osteopathic Medical Licensing Exam). Those that have received or are in the process of earning a MD or DO are both eligible to sit for the USMLE. Because of their additional training, only holders of the DO are eligible to sit for the COMLEX.Upon completion of internship and residency requirements for their chosen medical specialty, and depending on whether the program attended as ACGME or AOA accredited, holders of the DO may elect to be board certified by either an allopathic specialty board (through the American Medical Association
American Medical Association
The American Medical Association , founded in 1847 and incorporated in 1897, is the largest association of medical doctors and medical students in the United States.-Scope and operations:...
's American Board of Medical Specialties
American Board of Medical Specialties
The American Board of Medical Specialties is a non-profit physician-led umbrella organization for 24 of the 26 approved medical specialty boards in the United States...
) or an osteopathic specialty board (through the American Osteopathic Association Bureau of Osteopathic Specialists
American Osteopathic Association Bureau of Osteopathic Specialists
The American Osteopathic Association Bureau of Osteopathic Specialists is a non-profit umbrella organization for 18 medical specialty boards in the United States. It is one of three leading entities overseeing physician certification in the United States...
certifying boards).
International variations
There are currently no osteopathic programs located outside of the United States that qualify an individual to practice as an osteopathic physician in the United States. Foreign osteopathic degrees are not recognized by any state in the U.S. as being equivalent to American D.O. degrees.International practice rights
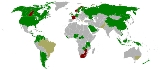
Every country has different requirements and a different way of licensing or registering osteopathic physicians and osteopaths. Osteopaths who have trained outside the United States are not eligible for medical licensure in the United States; however, U.S.-trained DOs are currently able to practice in over 55 countries with full medical rights and in several others with limited rights.The following is an International Licensure Summary for US-trained Doctors of Osteopathic Medicine, as listed by the American Osteopathic Association
American Osteopathic Association
The American Osteopathic Association is the representative member organization for the over 78,000 osteopathic medical physicians in the United States...
:
| Country | Year of Latest Policy | Medical Practice Rights | Requirements for Licensure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Argentina | 2006 | Unlimited | Foreign physicians must submit credentials to various agencies and then appear before any of the National Universities in order to have their diploma recognized. | |
| Australia | 2009 | Varies by state | A US educated DO was recruited to head up an ER in Sydney. Through the hospital’s efforts and the endorsement of the Australian College of Emergency Medicine, he secured an unlimited medical license through the New South Wales Medical Board. | |
| Austria | 2009 | Unlimited | Hospital must have position unable to be filled by Austrian physician. | |
| Bahamas | 2004 | Unlimited | US license recognized. | |
| Bahrain | 2010 | Unlimited | US license recognized. | |
| Barbados | 1995 | Limited | Osteopathic manipulative medicine Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine is the application of the distinct osteopathic philosophy, structural diagnosis and use of Osteopathic Manipulative Technique in the diagnosis and management of the patient. OMM takes into account the physical and mental health of a patient, and how either aspect... only. |
|
| Bermuda | 1997 | Unlimited | Required at least 2 years of GME and examination or interview by the Council’s Examination Committee. Non-Bermudans must have approval from the Ministry of Labour & Home Affairs to work on the island. | |
| Brazil | 2007 | Unlimited | Completion of Brazilian board exam, establishing residency & some training in Brazilian hospital is required. | |
| Canada (varies by province) | Alberta | Unlimited | Requires at least 2 years of GME accredited by the ACGME or AOA and must have passed the Universities Coordinating Council Exam, a basic sciences exam, and have passed all three parts of the LMCC Licentiate of the Medical Council of Canada Licentiate of the Medical Council of Canada, commonly abbreviated as LMCC, is a physician that has either:* Before 1 January 1992: Passed Medical Council of Canada Qualifying Examination Part 1 and has completed successfully one year of postgraduate training or the MCCQE Part 2* After 1 January... . |
|
| British Columbia | Unlimited | Requires at least 1 year of GME approved by the AOA or the ACGME, completed at least 1 year of GME in Canada, passed all three parts of the LMCC. | ||
| Manitoba | Unlimited | US license recognized. | ||
| New Brunswick | Unlimited | Requires at least 2 years of GME approved by the AOA or the ACGME and have passed all 3 parts of the LMCC. Reciprocity pathway for DOs with a Maine license. | ||
| Newfoundland | Unlimited | The Medical Act 2011 allows full licensure of osteopathic physicians, both for the country’s full registry & its educational registry. | ||
| NW Territories | Unlimited | US license recognized. | ||
| Nova Scotia | Unlimited | Requires a Canadian or ACGME residency. | ||
| Ontario | Unlimited | Requires a Canadian or ACGME residency. | ||
| Prince Edward Island | Restricted | No provision for licensing US-trained DOs. | ||
| Quebec | Unlimited | Requires 1 year of GME approved by the AOA or ACGME, 1 year of GME in Quebec passed the written, oral and clinical board examination of the College of Family Physicians of Canada and must speak French fluently. | ||
| Saskatchewan | Limited | Osteopathic manipulative medicine Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine is the application of the distinct osteopathic philosophy, structural diagnosis and use of Osteopathic Manipulative Technique in the diagnosis and management of the patient. OMM takes into account the physical and mental health of a patient, and how either aspect... only. |
||
| Yukon Territory | Unlimited | US license recognized. | ||
| Cayman Islands (UK) | 1983 | Unlimited | US license recognized. | |
| Central African Republic | 1990 | Unlimited | US licensure and annual attendance at the National Congress for Physicians. | |
| Chile | 1993 | Unlimited | A written exam in Spanish is required, besides a series of practical tests involving common procedures (CPR, intubation, lumbar puncture, etc.). | |
| China | 2009 | Unlimited | US-DOs are permitted to apply for "Short Term Medical Practice." | |
| Colombia | 1996 | Unlimited | Same requirements as other foreign physicians. | |
| Costa Rica | 1993 | Unlimited | Same requirements as other foreign physicians. | |
| Dominican Republic | 2000 | Unlimited | US license & board certification recognized. | |
| Ecuador | 1990 | Unlimited | Same requirements as other foreign physicians. Reciprocity exists with most Latin American countries. | |
| Finland | 1996 | Unlimited | Same requirements as other foreign physicians. | |
| France | 2009 | Limited | Osteopathic manipulative medicine Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine is the application of the distinct osteopathic philosophy, structural diagnosis and use of Osteopathic Manipulative Technique in the diagnosis and management of the patient. OMM takes into account the physical and mental health of a patient, and how either aspect... only. French government does not recognize full scope of practice osteopathic medicine. |
|
| Germany | 2008 | Unlimited | Same requirements as other foreign physicians. Depends on need. Decisions made on individual basis. | |
| Greece | 2009 | Unlimited | Greek citizenship required, unless in rare instances, there exists a crucial need for certain types of specialist physicians. Further, a work permit must be obtained, a difficult task, and speaking Greek is an unwritten requirement. These are the same requirements as other foreign physicians. | |
| Grenada | 2007 | Unlimited | US license recognized. | |
| Guyana | 1996 | Unlimited | Case-by case basis. | |
| Honduras | 2009 | Unlimited | National Autonomous University must accredit all foreign titles. After accreditation is completed, the applicant must seek registration with the Medical College of Honduras (MCH). | |
| Hong Kong | 1998 | Unlimited | Written examination. Personal interview. Training approval. | |
| Indonesia | 1992 | Unlimited & Restricted | Foreign physicians affiliated with a university project or a mission have unlimited practice rights. No private practice allowed. | |
| Israel | 2007 | Unlimited | Same requirements as other foreign physicians. Hebrew required. | |
| Italy | 2009 | Unlimited | Physicians are discouraged from seeking employment in Italy without firm contracts and work permits. If there is a U.S. state law outlining reciprocity with Italy, a statement to this effect from the Italian Consulate will warrant better chances. | |
| Jamaica | 1994 | Limited & Restricted | DOs were permitted to supply some services while participating in a specific mission project. | |
| Kenya | 2007 | Unlimited | ||
| Lebanon | 2004 | Unlimited | AOA letter required. Examination required. | |
| Lesotho | 1990s | Unlimited | Applicants must appear before the Medical, Dental and Pharmacy Council to answer some medical questions and present their credentials. The Council will also make a recommendation about where the applicant’s skills would be most helpful in the country. | |
| Liberia | 1990s | Unlimited | Same requirements as other foreign physicians. | |
| Luxembourg | 1987 | Unlimited | The practice of medicine in Luxembourg by a doctor who is not an EU national is very rare. | |
| Malta | 2010 | Unlimited | Accepted on a case by case basis, if training meets the minimum educational requirements for physicians in the EU (Article 24 of Directive 2005/36/EC). Examination required. | |
| Malawi | 1991 | Unlimited | ||
| Mexico | 2011 | Unlimited & Restricted | Health Secretary Quijano of the Yucatán State of Mexico signed a Proclamation recognizing US-trained osteopathic physicians in that state; DOs can now obtain short-term & long-term licensure through the Health Secretary’s office. All other Mexican states require work permits - only available in conjunction with the association of a short-term medical mission project. | |
| Micronesia | 1993 | Unlimited | Statutes specifically include DOs | |
| Nepal | 2008 | Unlimited | Approval by the Nepal Medical Council & a visa from the Immigration Department. | |
| Netherlands | 2009 | Unlimited | Same requirements as other foreign physicians. | |
| New Zealand | 2008 | Unlimited | Hearing required. Case-by-case basis. | |
| Nigeria | 2010 | Unlimited | US Licensure and completion of specialty training required. | |
| Norway | 2009 | Limited | Osteopathic manipulative medicine Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine is the application of the distinct osteopathic philosophy, structural diagnosis and use of Osteopathic Manipulative Technique in the diagnosis and management of the patient. OMM takes into account the physical and mental health of a patient, and how either aspect... only. |
|
| Panama | 2009 | Unlimited | Panamanian citizenship required. | |
| Papua New Guinea | 2010 | Unlimited | Work permit required. Short-term or a long-term volunteer service license also available. | |
| Poland | 2009 | Unlimited | Examination & Polish required. | |
| Russia | 2006 | Unlimited | Foreign physicians make arrangements to practice through Russian sponsors, such as hospitals or businesses. | |
| Saint Lucia | 2000 | Unlimited | US credentials recognized. | |
| Saudi Arabia | 2009 | Unlimited | Foreign physician must be recruited by a government agency, a corporation or a private health care entity, such as a hospital. | |
| Sierra Leone | 1993 | Unlimited | Notarized US credentials. | |
| South Africa | 2009 | Limited | Osteopathic manipulative medicine Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine is the application of the distinct osteopathic philosophy, structural diagnosis and use of Osteopathic Manipulative Technique in the diagnosis and management of the patient. OMM takes into account the physical and mental health of a patient, and how either aspect... only |
|
| Sweden | 2005 | Unlimited | US license recognized. | |
| Taiwan | 2008 | Unlimited | The ROC Republic of China The Republic of China , commonly known as Taiwan , is a unitary sovereign state located in East Asia. Originally based in mainland China, the Republic of China currently governs the island of Taiwan , which forms over 99% of its current territory, as well as Penghu, Kinmen, Matsu and other minor... government recognizes US DO degree. Applicants must take Taiwan Examination Yuan to obtain Taiwanese license. |
|
| United Kingdom | 2005 | Unlimited. | US-trained DOs eligible for full medical practice rights. Applicants must pass the PLAB Professional and Linguistic Assessment Board test The Professional and Linguistic Assessment Board test is the assessment procedure conducted by the General Medical Council of the United Kingdom that is required for overseas doctors outside the European Union before they can practice medicine in the UK.... examination and work for one year in the National Health Service National Health Service The National Health Service is the shared name of three of the four publicly funded healthcare systems in the United Kingdom. They provide a comprehensive range of health services, the vast majority of which are free at the point of use to residents of the United Kingdom... . Following that year, the applicants will be able to apply for a license to practice privately. |
|
| Tanzania | 1985 | Unlimited | US license & GME recognized. Temporary work permits are available | |
| Uganda | 2008 | Unlimited | ||
| United Arab Emirates | 2009 | Unlimited | Examination required. | |
| United Kingdom | 2005 | Unlimited | For GMC registration as a specialist, postgraduate training will need to be separately recognized by the Postgraduate Medical Education and Training Board (PMETB). GOsC registration is also required. | |
| Venezuela | 2007 | Unlimited | Recognized legal status under the “law of the practice of medical.” | |
| Vietnam | 1995 | Unlimited | Foreign physicians can fill vacancies in hospitals that are in need of certain specialists. | |
| Zambia | 2009 | Unlimited | US licensure required. | |
| Zimbabwe | 2009 | Limited | Osteopathic manipulative medicine Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine is the application of the distinct osteopathic philosophy, structural diagnosis and use of Osteopathic Manipulative Technique in the diagnosis and management of the patient. OMM takes into account the physical and mental health of a patient, and how either aspect... only. |
|
| Table data from AOA International Licensure Summary (updated February 2011). | ||||
| OMM:Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine is the application of the distinct osteopathic philosophy, structural diagnosis and use of Osteopathic Manipulative Technique in the diagnosis and management of the patient. OMM takes into account the physical and mental health of a patient, and how either aspect... |
||||

