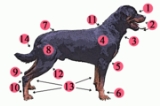
Dog anatomy
Encyclopedia
Dog anatomy includes the same internal structures that are in humans. Details of structures vary tremendously from breed
to breed, more than in any other animal species, wild or domesticated, as dogs vary from the tiny Chihuahua
to the giant Irish Wolfhound
.


The dog's ancestral skeleton provided the ability to jump and leap. Their legs are designed to propel them forward rapidly, leaping as necessary, to chase and overcome prey. Consequently, they have small, tight feet, walking on their toes; their rear legs are fairly rigid and sturdy; the front legs are loose and flexible, with only muscle attaching them to the torso.
Although selective breeding has changed the appearance of many breeds, all dogs retain the basic ingredients from their distant ancestors. Dogs have disconnected shoulder bones (lacking the collar bone of the human skeleton) that allow a greater stride length for running and leaping. They walk on four toes, front and back, and have vestigial dewclaw
s on their front legs and sometimes on their rear legs.When a dog has extra dewclaws in addition to the usual one on each front leg, the dog is said to be "double dewclawed".
There is some debate about whether a dewclaw helps dogs to gain traction when they run because, in some dogs, the dewclaw makes contact when they are running and the nail on the dewclaw often wears down in the same way that the nails on their other toes do, from contact with the ground. However, in many dogs the dewclaws never make contact with the ground; in this case, the dewclaw's nail never wears away, and it is then often trimmed to keep it to a safe length.
The dewclaws are not dead appendages. They can be used to lightly grip bones and other items that dogs hold with the paws. However, in some dogs these claws may not appear to be connected to the leg at all except by a flap of skin; in such dogs the claws do not have a use for gripping as the claw can easily fold or turn. [2]
There is also some debate as to whether dewclaws should be surgically removed.The argument for removal states that dewclaws are a weak digit, barely attached to the leg, so that they can rip partway off or easily catch on something and break, which can be extremely painful and prone to infection. Others say the pain of removing a dewclaw is far greater than any other risk. For this reason, removal of dewclaws is illegal in many countries. There is, perhaps, an exception for hunting dogs, who can sometimes tear the dewclaw while running in overgrown vegetation. [3] If a dewclaw is to be removed, this should be done when the dog is a puppy, sometimes as young as 3 days old, though it can also be performed on older dogs if necessary (though the surgery may be more difficult then). The surgery is fairly straight-forward and may even be done with only local anesthetics if the digit is not well connected to the leg. Unfortunately many dogs can't resist licking at their sore paws following the surgery, so owners need to remain vigilant.
In addition, for those dogs whose dewclaws make contact with the ground when they run, it is possible that removing them could be a disadvantage for a dog's speed in running and changing of direction, particularly in performance dog sports such as dog agility.
The dog's ancestor was about the size of a Dingo
, and its skeleton took about 10 months to mature. Today's toy
breeds have skeletons that mature in only a few months, while giant breeds such as the Mastiff
s take 16 to 18 months for the skeleton to mature. Dwarfism
has affected the proportions of some breeds' skeletons, as in the Basset Hound
.
Knowledge of basic anatomy also helps when competing in dog shows or contests.
and, in turn, is probably responsible for making them tiny. The study, published in 2007, found a regulatory sequence
(not a gene) next to the gene IGF1
; together the gene and regulatory sequence together are known as a haplotype
that "is a major contributor to body size in all small dogs." Medium and large size dogs do not usually have the regulatory sequence, although the small-size sequence was found in the Rottweiler
breed. The study included 3,241 dogs from 143 breeds. The researchers concluded the genetic instructions to make dogs small must be at least 12,000 years old, and it is not found in wolves. Another study has shown that lap dog
s (small dogs) are among the oldest dog type
s.
Modern dog breed
s show more variation in size, appearance, and behavior than any other domestic animal. Within the range of extremes, dogs generally share attributes with their wild ancestors, the wolves
. Dogs are predators and scavenger
s, possessing sharp teeth and strong jaws for attacking, holding, and tearing their food. Although selective breeding has changed the appearance of many breeds, all dogs retain basic traits from their distant ancestors. Like many other predatory mammals, the dog has powerful muscles, fused wristbones, a cardiovascular system that supports both sprinting and endurance, and teeth for catching and tearing.
s and have color vision equivalent to red-green color blindness
in humans. Different breeds of dogs have different eye shapes and dimensions, and they also have different retina
configurations. Dogs with long noses have a "visual streak" which runs across the width of the retina and gives them a very wide field of excellent vision, while those with short noses have an "area centralis" — a central patch with up to three times the density of nerve endings as the visual streak — giving them detailed sight much more like a human's.
Some breeds, particularly the sighthound
s, have a field of vision up to 270° (compared to 180° for humans), although broad-headed breeds with short noses have a much narrower field of vision, as low as 180°.
....
frequency range (compared to 20 to 70 Hz for humans) and above 45 kHz (compared to 13 to 20 kHz for humans),and in addition have a degree of ear mobility that helps them to rapidly pinpoint the exact location of a sound. Eighteen or more muscles can tilt, rotate and raise or lower a dog's ear. Additionally, a dog can identify a sound's location much faster than a human can, as well as hear sounds up to four times the distance that humans are able to. Those with more natural ear shapes, like those of wild canids like the fox, generally hear better than those with the floppier ears of many domesticated species.
 Dogs have nearly 220 million smell-sensitive cells over an area about the size of a pocket handkerchief
Dogs have nearly 220 million smell-sensitive cells over an area about the size of a pocket handkerchief
(compared to 5 million over an area the size of a postage stamp
for humans). According to nhm.org, dogs can sense odours at concentrations nearly 100 million times lower than humans can. According to Dummies.com, the percentage of the dog's brain that is devoted to analyzing smells is actually 40 times larger than that of a human. Some dog breeds have been selectively bred for excellence in detecting scents, even compared to their canine brethren.

Dogs diverged from a now-extinct Asian wolf between 12,000 and 15,000 years ago, according to recent DNA studies. In that time, the long nose and heavy grey-colored double coat of the wolf has changed into the wide variety of dog shapes and coats and colors seen today. The change was due at first to genetic changes that occurred as the original dogs learned to tolerate the presence of humans, as shown in the research on foxes by Dmitri Belyaev in his Farm-Fox Experiment. The research found that a genetic change to tameness brought along other unexpected changes as well; one notable change was in the coats, changed from a typical fox coat to a spotted coat resembling a dog's coat. As ancient dogs learned to live near humans and became less like wolves, their appearance changed as well, long before any selective breeding was done by people.
A Stanford University School of Medicine
study published in Science in October, 2007 found the genetics that explain coat colors in other mammals such as in horse coats
and in cat coats
, did not apply to dogs. The project took samples from 38 different breeds to find the gene (a beta defensin
gene) responsible for dog coat color. One version produces yellow dogs, and a mutation produces black. All dog coat colors are modifications of black or yellow. For example, the white in white miniature schnauzer
s is a cream color, not albinism
(a genotype of e/e at MC1R.)
Modern dog breeds exhibit a diverse array of fur coats, including dogs without fur, such as the Mexican Hairless Dog
. Dog coats vary in texture, color, and markings, and a specialized vocabulary has evolved to describe each characteristic.
 Puppies often have characteristics that do not last beyond early puppyhood. Eye color often changes from blue to its adult color as the puppy matures. The coat color may change: Kerry Blue Terrier
Puppies often have characteristics that do not last beyond early puppyhood. Eye color often changes from blue to its adult color as the puppy matures. The coat color may change: Kerry Blue Terrier
puppies have black coats at birth and change to blue with maturity, and Dalmatians
are white and gain their spots with age. The ear shape will also often change, especially with erect-eared breeds such as the German Shepherd Dog
which have soft ears at birth, but the cartilage strengthens with age. Labrador Retrievers and other swimming dogs start off with a very fluffy puppy coat, and over time the water proof layer grows.
Puppies that are going to grow into larger dogs will often have over sized paws to begin with, and then the rest of them grow to fit.
Dogs possess a rete mirabile
, a complex of intermingled small arteries and veins, in the carotid sinus
at the base of their neck. This acts to thermally isolate the head
, which contains the brain
, the most temperature-sensitive organ, from the body
, which contains the muscle
s, where most of the heat is generated. The result is that dogs can sustain intense physical exertion over a prolonged time in a hot environment, compared to animals which lack this apparatus; thus, a dog chasing a jackrabbit
through the desert
may not be able to outrun the rabbit, but it can continue the chase until the rabbit slows due to overheating.
Dog breed
Dog breeds are groups of closely related and visibly similar domestic dogs, which are all of the subspecies Canis lupus familiaris, having characteristic traits that are selected and maintained by humans, bred from a known foundation stock....
to breed, more than in any other animal species, wild or domesticated, as dogs vary from the tiny Chihuahua
Chihuahua (dog)
The ' is the smallest breed of dog and is so named for the state of Chihuahua in Mexico. Chihuahuas come in a wide variety of sizes, head shapes, colors and coat lengths.-History:...
to the giant Irish Wolfhound
Irish Wolfhound
The Irish wolfhound is a breed of domestic dog , specifically a sighthound. The name originates from its purpose rather than from its appearance...
.



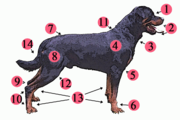
Physical characteristics
Like most predatory mammals, the dog has powerful muscles, a cardiovascular system that supports both sprinting and endurance, and teeth for catching, holding, and tearing.The dog's ancestral skeleton provided the ability to jump and leap. Their legs are designed to propel them forward rapidly, leaping as necessary, to chase and overcome prey. Consequently, they have small, tight feet, walking on their toes; their rear legs are fairly rigid and sturdy; the front legs are loose and flexible, with only muscle attaching them to the torso.
Although selective breeding has changed the appearance of many breeds, all dogs retain the basic ingredients from their distant ancestors. Dogs have disconnected shoulder bones (lacking the collar bone of the human skeleton) that allow a greater stride length for running and leaping. They walk on four toes, front and back, and have vestigial dewclaw
Dewclaw
A dewclaw is a vestigial digit on the foot of many mammals, birds, and reptiles . It commonly grows high on the leg so that in digitigrade species, when the animal is standing, it does not make contact with the ground...
s on their front legs and sometimes on their rear legs.When a dog has extra dewclaws in addition to the usual one on each front leg, the dog is said to be "double dewclawed".
There is some debate about whether a dewclaw helps dogs to gain traction when they run because, in some dogs, the dewclaw makes contact when they are running and the nail on the dewclaw often wears down in the same way that the nails on their other toes do, from contact with the ground. However, in many dogs the dewclaws never make contact with the ground; in this case, the dewclaw's nail never wears away, and it is then often trimmed to keep it to a safe length.
The dewclaws are not dead appendages. They can be used to lightly grip bones and other items that dogs hold with the paws. However, in some dogs these claws may not appear to be connected to the leg at all except by a flap of skin; in such dogs the claws do not have a use for gripping as the claw can easily fold or turn. [2]
There is also some debate as to whether dewclaws should be surgically removed.The argument for removal states that dewclaws are a weak digit, barely attached to the leg, so that they can rip partway off or easily catch on something and break, which can be extremely painful and prone to infection. Others say the pain of removing a dewclaw is far greater than any other risk. For this reason, removal of dewclaws is illegal in many countries. There is, perhaps, an exception for hunting dogs, who can sometimes tear the dewclaw while running in overgrown vegetation. [3] If a dewclaw is to be removed, this should be done when the dog is a puppy, sometimes as young as 3 days old, though it can also be performed on older dogs if necessary (though the surgery may be more difficult then). The surgery is fairly straight-forward and may even be done with only local anesthetics if the digit is not well connected to the leg. Unfortunately many dogs can't resist licking at their sore paws following the surgery, so owners need to remain vigilant.
In addition, for those dogs whose dewclaws make contact with the ground when they run, it is possible that removing them could be a disadvantage for a dog's speed in running and changing of direction, particularly in performance dog sports such as dog agility.
The dog's ancestor was about the size of a Dingo
Dingo
The Australian Dingo or Warrigal is a free-roaming wild dog unique to the continent of Australia, mainly found in the outback. Its original ancestors are thought to have arrived with humans from southeast Asia thousands of years ago, when dogs were still relatively undomesticated and closer to...
, and its skeleton took about 10 months to mature. Today's toy
Toy dog
Toy dog traditionally refers to a very small dog or a grouping of small and very small breeds of dog. A toy dog may be of any of various dog types. Types of dogs referred to as toy dogs may include Spaniels, Pinschers and Terriers that have been bred down in size. Not all toy dogs are lapdogs,...
breeds have skeletons that mature in only a few months, while giant breeds such as the Mastiff
English Mastiff
The English Mastiff, referred to by virtually all Kennel Clubs simply as the Mastiff, is a breed of large dog perhaps descended from the ancient Alaunt through the Pugnaces Britanniae. Distinguishable by enormous size, massive head, and a limited range of colors, but always displaying a black mask,...
s take 16 to 18 months for the skeleton to mature. Dwarfism
Dwarfism
Dwarfism is short stature resulting from a medical condition. It is sometimes defined as an adult height of less than 4 feet 10 inches , although this definition is problematic because short stature in itself is not a disorder....
has affected the proportions of some breeds' skeletons, as in the Basset Hound
Basset Hound
The Basset Hound is a short-legged breed of dog of the hound family. They are scent hounds, bred to hunt rabbits and hare by scent. Their sense of smell for tracking is second only to that of the Bloodhound....
.
Knowledge of basic anatomy also helps when competing in dog shows or contests.
Size
Researchers have identified a particular piece of genetic material that is common to every small-dog breedToy Group
Toy Group is the name of a breed Group of the smallest kinds of dogs, used by kennel clubs to classify a defined collection of dog breeds. Toy Group does not necessarily refer to one particular type of dog. Most major English-language kennel clubs include a Toy Group although different kennel clubs...
and, in turn, is probably responsible for making them tiny. The study, published in 2007, found a regulatory sequence
Regulatory sequence
A regulatory sequence is a segment of DNA where regulatory proteins such as transcription factors bind preferentially. These regulatory proteins bind to short stretches of DNA called regulatory regions, which are appropriately positioned in the genome, usually a short distance 'upstream' of the...
(not a gene) next to the gene IGF1
Insulin-like growth factor 1
Insulin-like growth factor 1 also known as somatomedin C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IGF1 gene. IGF-1 has also been referred to as a "sulfation factor" and its effects were termed "nonsuppressible insulin-like activity" in the 1970s.IGF-1 is a hormone similar in molecular...
; together the gene and regulatory sequence together are known as a haplotype
Haplotype
A haplotype in genetics is a combination of alleles at adjacent locations on the chromosome that are transmitted together...
that "is a major contributor to body size in all small dogs." Medium and large size dogs do not usually have the regulatory sequence, although the small-size sequence was found in the Rottweiler
Rottweiler
The Rottweiler is a medium to large size breed of domestic dog that originated in Rottweil, Germany. The dogs were known as "Rottweil butchers' dogs" because they were used to herd livestock and pull carts laden with butchered meat and other products to market...
breed. The study included 3,241 dogs from 143 breeds. The researchers concluded the genetic instructions to make dogs small must be at least 12,000 years old, and it is not found in wolves. Another study has shown that lap dog
Lap dog
A lapdog or lap dog is a dog that is small enough to be held in the arms or lie comfortably on a person's lap. Lapdogs are not a specific breed, but is a generic term for a type of dog of small size and friendly disposition....
s (small dogs) are among the oldest dog type
Dog type
Dog types are broad categories of dogs based on function, with dogs identified primarily by specific function or style of work rather than by lineage or appearance....
s.
Modern dog breed
Dog breed
Dog breeds are groups of closely related and visibly similar domestic dogs, which are all of the subspecies Canis lupus familiaris, having characteristic traits that are selected and maintained by humans, bred from a known foundation stock....
s show more variation in size, appearance, and behavior than any other domestic animal. Within the range of extremes, dogs generally share attributes with their wild ancestors, the wolves
Gray Wolf
The gray wolf , also known as the wolf, is the largest extant wild member of the Canidae family...
. Dogs are predators and scavenger
Scavenger
Scavenging is both a carnivorous and herbivorous feeding behavior in which individual scavengers search out dead animal and dead plant biomass on which to feed. The eating of carrion from the same species is referred to as cannibalism. Scavengers play an important role in the ecosystem by...
s, possessing sharp teeth and strong jaws for attacking, holding, and tearing their food. Although selective breeding has changed the appearance of many breeds, all dogs retain basic traits from their distant ancestors. Like many other predatory mammals, the dog has powerful muscles, fused wristbones, a cardiovascular system that supports both sprinting and endurance, and teeth for catching and tearing.
Sight
Like most mammals, dogs are dichromatDichromat
Dichromacy is the state of having two types of functioning color receptors, called cone cells, in the eyes. Organisms with dichromacy are called dichromats. Dichromats can match any color they see with a mixture of no more than two pure spectral lights...
s and have color vision equivalent to red-green color blindness
Color blindness
Color blindness or color vision deficiency is the inability or decreased ability to see color, or perceive color differences, under lighting conditions when color vision is not normally impaired...
in humans. Different breeds of dogs have different eye shapes and dimensions, and they also have different retina
Retina
The vertebrate retina is a light-sensitive tissue lining the inner surface of the eye. The optics of the eye create an image of the visual world on the retina, which serves much the same function as the film in a camera. Light striking the retina initiates a cascade of chemical and electrical...
configurations. Dogs with long noses have a "visual streak" which runs across the width of the retina and gives them a very wide field of excellent vision, while those with short noses have an "area centralis" — a central patch with up to three times the density of nerve endings as the visual streak — giving them detailed sight much more like a human's.
Some breeds, particularly the sighthound
Sighthound
Sighthounds, also called gazehounds, are hounds that primarily hunt by speed and sight, instead of by scent and endurance as scent hounds do.-Appearance:...
s, have a field of vision up to 270° (compared to 180° for humans), although broad-headed breeds with short noses have a much narrower field of vision, as low as 180°.
....
Hearing
Dogs detect sounds as low as the 16 to 20 HzHertz
The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
frequency range (compared to 20 to 70 Hz for humans) and above 45 kHz (compared to 13 to 20 kHz for humans),and in addition have a degree of ear mobility that helps them to rapidly pinpoint the exact location of a sound. Eighteen or more muscles can tilt, rotate and raise or lower a dog's ear. Additionally, a dog can identify a sound's location much faster than a human can, as well as hear sounds up to four times the distance that humans are able to. Those with more natural ear shapes, like those of wild canids like the fox, generally hear better than those with the floppier ears of many domesticated species.
Smell

Handkerchief
A handkerchief , also called a handkercher or hanky, is a form of a kerchief, typically a hemmed square of thin fabric that can be carried in the pocket or purse, and which is intended for personal hygiene purposes such as wiping one's hands or face, or blowing one's nose...
(compared to 5 million over an area the size of a postage stamp
Postage stamp
A postage stamp is a small piece of paper that is purchased and displayed on an item of mail as evidence of payment of postage. Typically, stamps are made from special paper, with a national designation and denomination on the face, and a gum adhesive on the reverse side...
for humans). According to nhm.org, dogs can sense odours at concentrations nearly 100 million times lower than humans can. According to Dummies.com, the percentage of the dog's brain that is devoted to analyzing smells is actually 40 times larger than that of a human. Some dog breeds have been selectively bred for excellence in detecting scents, even compared to their canine brethren.

Coat
Domestic dogs often display the remnants of counter-shading, a common natural camouflage pattern. The general theory of countershading is that an animal that is lit from above will appear lighter on its upper half and darker on its lower half where it will usually be in its own shade. This is a pattern that predators can learn to watch for. A countershaded animal will have dark coloring on its upper surfaces and light coloring below. This reduces the general visibility of the animal. One reminder of this pattern is that many breeds will have the occasional "blaze", stripe, or "star" of white fur on their chest or undersides.Dogs diverged from a now-extinct Asian wolf between 12,000 and 15,000 years ago, according to recent DNA studies. In that time, the long nose and heavy grey-colored double coat of the wolf has changed into the wide variety of dog shapes and coats and colors seen today. The change was due at first to genetic changes that occurred as the original dogs learned to tolerate the presence of humans, as shown in the research on foxes by Dmitri Belyaev in his Farm-Fox Experiment. The research found that a genetic change to tameness brought along other unexpected changes as well; one notable change was in the coats, changed from a typical fox coat to a spotted coat resembling a dog's coat. As ancient dogs learned to live near humans and became less like wolves, their appearance changed as well, long before any selective breeding was done by people.
A Stanford University School of Medicine
Stanford University School of Medicine
Stanford University School of Medicine is a leading medical school located at Stanford University Medical Center in Stanford, California. Originally based in San Francisco, California as Cooper Medical College, it is the oldest continuously running medical school in the western United States...
study published in Science in October, 2007 found the genetics that explain coat colors in other mammals such as in horse coats
Equine coat color genetics
Equine coat color genetics determine a horse's coat color. There are many different coat colors possible, but all colors are produced by the action of only a few different genes. The simplest genetic default color of all domesticated horses can be described as either "red" or "non-red", depending...
and in cat coats
Cat coat genetics
The genetics of cat coat coloration, pattern, length, and texture is a complex subject, and many different genes are involved.- Genes involved in albinism, dominant white, and white spotting :...
, did not apply to dogs. The project took samples from 38 different breeds to find the gene (a beta defensin
Beta defensin
Beta defensins are a family of mammalian defensins. The beta defensins are antimicrobial peptides implicated in theresistance of epithelial surfaces to microbial colonization....
gene) responsible for dog coat color. One version produces yellow dogs, and a mutation produces black. All dog coat colors are modifications of black or yellow. For example, the white in white miniature schnauzer
Miniature Schnauzer
The Miniature Schnauzer is a breed of small dog of the Schnauzer type that originated in Germany in the mid-to-late 19th century. Miniature Schnauzers developed from crosses between the Standard Schnauzer and one or more smaller breeds such as the Poodle and Affenpinscher.The breed remains one of...
s is a cream color, not albinism
Albinism
Albinism is a congenital disorder characterized by the complete or partial absence of pigment in the skin, hair and eyes due to absence or defect of an enzyme involved in the production of melanin...
(a genotype of e/e at MC1R.)
Modern dog breeds exhibit a diverse array of fur coats, including dogs without fur, such as the Mexican Hairless Dog
Mexican Hairless Dog
The Mexican Hairless Dog is a rare, hairless breed of dog, the size of which varies greatly. It is also known as Xoloitzcuintle .-History:...
. Dog coats vary in texture, color, and markings, and a specialized vocabulary has evolved to describe each characteristic.
Tail
There are many different shapes for dog tails: straight, straight up, sickle, curled, cork-screw. In some breeds, the tail is traditionally docked to avoid injuries (especially for hunting dogs). It can happen that some puppies are born with a short tail or no tail in some breeds.Puppy characteristics

Kerry Blue Terrier
The Kerry Blue Terrier is a breed of dog. Mistakenly thought to be from County Kerry in South West Ireland, it's actually from Tipperary in South Central Ireland. In Ireland it is often called the Irish Blue Terrier...
puppies have black coats at birth and change to blue with maturity, and Dalmatians
Dalmatian (dog)
The Dalmatian is a breed of dog whose roots are often said to trace back to Dalmatia, a region of Croatia where the first illustrations of the dog have been found. The Dalmatian is noted for its unique black- or brown-spotted coat and was mainly used as a carriage dog in its early days...
are white and gain their spots with age. The ear shape will also often change, especially with erect-eared breeds such as the German Shepherd Dog
German Shepherd Dog
The German Shepherd Dog , also known as an Alsatian or just the German Shepherd, is a breed of large-sized dog that originated in Germany. The German Shepherd is a relatively new breed of dog, with its origin dating to 1899. As part of the Herding Group, the German Shepherd is a working dog...
which have soft ears at birth, but the cartilage strengthens with age. Labrador Retrievers and other swimming dogs start off with a very fluffy puppy coat, and over time the water proof layer grows.
Puppies that are going to grow into larger dogs will often have over sized paws to begin with, and then the rest of them grow to fit.
Temperature regulation
It is a common misconception that dogs do not sweat. They do sweat, mainly through the footpads, but only a small fraction of a dog's excess heat is lost this way. Primarily, dogs regulate their body temperature through panting. Panting moves cooling air over the moist surfaces of the tongue and lungs, rejecting heat to the atmosphere.Dogs possess a rete mirabile
Rete mirabile
A rete mirabile is a complex of arteries and veins lying very close to each other, found in some vertebrates. The rete mirabile utilizes countercurrent blood flow within the net...
, a complex of intermingled small arteries and veins, in the carotid sinus
Carotid sinus
In human anatomy, the carotid sinus is a localized dilation of the internal carotid artery at its origin, the common carotid artery.-Functions:...
at the base of their neck. This acts to thermally isolate the head
Head
In anatomy, the head of an animal is the rostral part that usually comprises the brain, eyes, ears, nose and mouth . Some very simple animals may not have a head, but many bilaterally symmetric forms do....
, which contains the brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
, the most temperature-sensitive organ, from the body
Body
With regard to living things, a body is the physical body of an individual. "Body" often is used in connection with appearance, health issues and death...
, which contains the muscle
Muscle
Muscle is a contractile tissue of animals and is derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells. Muscle cells contain contractile filaments that move past each other and change the size of the cell. They are classified as skeletal, cardiac, or smooth muscles. Their function is to...
s, where most of the heat is generated. The result is that dogs can sustain intense physical exertion over a prolonged time in a hot environment, compared to animals which lack this apparatus; thus, a dog chasing a jackrabbit
Hare
Hares and jackrabbits are leporids belonging to the genus Lepus. Hares less than one year old are called leverets. Four species commonly known as types of hare are classified outside of Lepus: the hispid hare , and three species known as red rock hares .Hares are very fast-moving...
through the desert
Desert
A desert is a landscape or region that receives an extremely low amount of precipitation, less than enough to support growth of most plants. Most deserts have an average annual precipitation of less than...
may not be able to outrun the rabbit, but it can continue the chase until the rabbit slows due to overheating.
See also
- Canine terminology
- Conformation (dog)Conformation (dog)Conformation in dogs refers solely to the externally visible details of a dog's structure and appearance, as defined in detail by each dog breed's written breed standard. A dog that conforms to most of the items of description in its individual breed standard is said to have good conformation...
- TemperamentTemperamentIn psychology, temperament refers to those aspects of an individual's personality, such as introversion or extroversion, that are often regarded as innate rather than learned...
- GroomingDog groomingDog grooming refers to both the hygienic care and cleaning of a dog, as well as a process by which a dog's physical appearance is enhanced for showing or other types of competition. A dog groomer is a person who earns their living grooming dogs.-Reasons for grooming:Grooming is an important part...
- Junior ShowmanshipJunior ShowmanshipJunior Showmanship , also called Junior Handling, is a sport for young people in which they exhibit their dog handling skills in an event similar to a conformation dog show.- History :...

