
Doppler cooling limit
Encyclopedia
Doppler temperature is the minimum temperature achievable with Doppler cooling
, one of the methods of laser cooling
.
When a photon
is absorbed by an atom moving in the opposite direction, its velocity is decreased according to the laws of momentum conservation. Accordingly, when a photon is emitted by this excited
atom, there is an extra momentum added to the atom. But since emission is non-directional, this effect "averages" out, and on a time average, there is just a little increase in the atom's momentum due to emission. At the temperature, T, when this effect exactly balances out the cooling effect of the laser
, no further cooling is possible. It turns out that it is equal to:
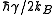
where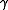 is the natural linewidth of the atomic transition,
is the natural linewidth of the atomic transition, 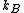 is the Boltzmann's constant and
is the Boltzmann's constant and 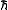 is the reduced Planck constant.
is the reduced Planck constant.
The term Doppler arises from the fact that the Doppler effect
, which provides a velocity dependence of the absorption rate and thus the light force, is an essential ingredient of the Doppler cooling mechanism.
Temperatures well below the Doppler limit have been achieved with various laser cooling methods, including Sisyphus cooling
, which allows to approach the lower so-called recoil limit.
Doppler cooling
Doppler cooling is a mechanism that can be used to trap and cool atoms. The term is sometimes used synonymously with laser cooling, though laser cooling includes other techniques.-History:...
, one of the methods of laser cooling
Laser cooling
Laser cooling refers to the number of techniques in which atomic and molecular samples are cooled through the interaction with one or more laser light fields...
.
When a photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
is absorbed by an atom moving in the opposite direction, its velocity is decreased according to the laws of momentum conservation. Accordingly, when a photon is emitted by this excited
Excited state
Excitation is an elevation in energy level above an arbitrary baseline energy state. In physics there is a specific technical definition for energy level which is often associated with an atom being excited to an excited state....
atom, there is an extra momentum added to the atom. But since emission is non-directional, this effect "averages" out, and on a time average, there is just a little increase in the atom's momentum due to emission. At the temperature, T, when this effect exactly balances out the cooling effect of the laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
, no further cooling is possible. It turns out that it is equal to:
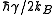
where
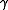 is the natural linewidth of the atomic transition,
is the natural linewidth of the atomic transition, 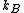 is the Boltzmann's constant and
is the Boltzmann's constant and 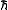 is the reduced Planck constant.
is the reduced Planck constant.The term Doppler arises from the fact that the Doppler effect
Doppler effect
The Doppler effect , named after Austrian physicist Christian Doppler who proposed it in 1842 in Prague, is the change in frequency of a wave for an observer moving relative to the source of the wave. It is commonly heard when a vehicle sounding a siren or horn approaches, passes, and recedes from...
, which provides a velocity dependence of the absorption rate and thus the light force, is an essential ingredient of the Doppler cooling mechanism.
Temperatures well below the Doppler limit have been achieved with various laser cooling methods, including Sisyphus cooling
Sisyphus cooling
Sisyphus cooling is a mechanism through which atoms can be cooled using laser beams below the temperatures expected to be achieved by Doppler cooling. It comes about as a result of a polarization gradient created by two counter-propagating laser beams with orthogonal polarization...
, which allows to approach the lower so-called recoil limit.

