
Double-balloon enteroscopy
Encyclopedia
Double-balloon enteroscopy, also known as push-and-pull enteroscopy
is an endoscopic
technique for visualization of the small bowel. It was developed by Hironori Yamamoto in 2001. It is novel in the field of diagnostic gastroenterology
as it is the first endoscopic technique that allows for the entire gastrointestinal tract
to be visualized in real time.
at the end of a special enteroscope camera and an overtube, which is a tube that fits over the endoscope, and which is also fitted with a balloon. The procedure is usually done under general anesthesia
, but may be done with the use of conscious sedation
. The enteroscope and overtube are inserted through the mouth
and passed in conventional fashion (that is, as with gastroscopy) into the small bowel. Following this, the endoscope is advanced a small distance in front of the overtube and the balloon at the end is inflated. Using the assistance of friction at the interface of the enteroscope and intestinal wall, the small bowel is accordioned back to the overtube. The overtube balloon is then deployed, and the enteroscope balloon is deflated. The process is then continued until the entire small bowel is visualized.
The double-balloon enteroscope can also be passed in retrograde fashion, through the colon
and into the ileum
to visualize the end of the small bowel.
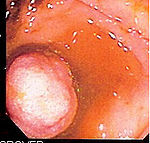 Double-balloon enteroscopy offers a number of advantages to other small bowel image techniques, including barium
Double-balloon enteroscopy offers a number of advantages to other small bowel image techniques, including barium
imaging, wireless capsule endoscopy and push enteroscopy:
The key disadvantage of double-balloon enteroscopy is the time required to visualize the small bowel; this can exceed three hours, and may require that patients be admitted to hospital
for the procedure. There have also been case reports of acute pancreatitis
and intestinal necrosis associated with the technique.
Enteroscopy
Enteroscopy is the procedure of using an enteroscope for the direct visualization of small bowel.*video chip endoscope**Double-balloon enteroscopy**Single-balloon enteroscopy**Spiral enteroscopy*wireless endoscopy system**Capsule endoscopy...
is an endoscopic
Endoscopy
Endoscopy means looking inside and typically refers to looking inside the body for medical reasons using an endoscope , an instrument used to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike most other medical imaging devices, endoscopes are inserted directly into the organ...
technique for visualization of the small bowel. It was developed by Hironori Yamamoto in 2001. It is novel in the field of diagnostic gastroenterology
Gastroenterology
Gastroenterology is the branch of medicine whereby the digestive system and its disorders are studied. The name is a combination of three Ancient Greek words gaster , enteron , and logos...
as it is the first endoscopic technique that allows for the entire gastrointestinal tract
Gastrointestinal tract
The human gastrointestinal tract refers to the stomach and intestine, and sometimes to all the structures from the mouth to the anus. ....
to be visualized in real time.
Technique
The technique involves the use of a balloonBalloon
A balloon is an inflatable flexible bag filled with a gas, such as helium, hydrogen, nitrous oxide, oxygen, or air. Modern balloons can be made from materials such as rubber, latex, polychloroprene, or a nylon fabric, while some early balloons were made of dried animal bladders, such as the pig...
at the end of a special enteroscope camera and an overtube, which is a tube that fits over the endoscope, and which is also fitted with a balloon. The procedure is usually done under general anesthesia
Anesthesia
Anesthesia, or anaesthesia , traditionally meant the condition of having sensation blocked or temporarily taken away...
, but may be done with the use of conscious sedation
Sedation
Sedation is the reduction of irritability or agitation by administration of sedative drugs, generally to facilitate a medical procedure or diagnostic procedure...
. The enteroscope and overtube are inserted through the mouth
Mouth
The mouth is the first portion of the alimentary canal that receives food andsaliva. The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane epithelium lining the inside of the mouth....
and passed in conventional fashion (that is, as with gastroscopy) into the small bowel. Following this, the endoscope is advanced a small distance in front of the overtube and the balloon at the end is inflated. Using the assistance of friction at the interface of the enteroscope and intestinal wall, the small bowel is accordioned back to the overtube. The overtube balloon is then deployed, and the enteroscope balloon is deflated. The process is then continued until the entire small bowel is visualized.
The double-balloon enteroscope can also be passed in retrograde fashion, through the colon
Colon (anatomy)
The colon is the last part of the digestive system in most vertebrates; it extracts water and salt from solid wastes before they are eliminated from the body, and is the site in which flora-aided fermentation of unabsorbed material occurs. Unlike the small intestine, the colon does not play a...
and into the ileum
Ileum
The ileum is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine may be used instead of ileum.The ileum follows the duodenum...
to visualize the end of the small bowel.
Indications
Double-balloon enteroscopy has found a niche application in the following settings:- bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract of obscure cause
- iron deficiency anemiaIron deficiency anemiaIron-deficiency anemia is a common anemia that occurs when iron loss occurs, and/or the dietary intake or absorption of iron is insufficient...
with normal colonoscopyColonoscopyColonoscopy is the endoscopic examination of the large bowel and the distal part of the small bowel with a CCD camera or a fiber optic camera on a flexible tube passed through the anus. It may provide a visual diagnosis and grants the opportunity for biopsy or removal of suspected...
and gastroscopy - visualization and therapeutic intervention on abnormalities seen on traditional small bowel imaging
- ERCP in post-surgical patients with long afferent limbs
Advantages and disadvantages

Barium meal
A barium meal, also known as an upper gastrointestinal series is a procedure in which radiographs of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum are taken after barium sulfate is ingested by a patient...
imaging, wireless capsule endoscopy and push enteroscopy:
- it allows for visualization of the entire small bowel to the terminal ileumTerminal ileumThe terminal ileum is the most distal part of the small intestine. It connects to the cecum, the pouch between the small and the large intestine, via the ileocecal valve.-Pathology of the terminal ileum:...
- it allows for the application of therapeutics
- it allows for the sampling or biopsyBiopsyA biopsy is a medical test involving sampling of cells or tissues for examination. It is the medical removal of tissue from a living subject to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist, and can also be analyzed chemically...
ing of small bowel mucosa, for the resection of polypsPolyp (medicine)A polyp is an abnormal growth of tissue projecting from a mucous membrane. If it is attached to the surface by a narrow elongated stalk, it is said to be pedunculated. If no stalk is present, it is said to be sessile. Polyps are commonly found in the colon, stomach, nose, sinus, urinary bladder...
of the small bowel, and in the placement of stentStentIn the technical vocabulary of medicine, a stent is an artificial 'tube' inserted into a natural passage/conduit in the body to prevent, or counteract, a disease-induced, localized flow constriction. The term may also refer to a tube used to temporarily hold such a natural conduit open to allow...
s or dilatationVasodilationVasodilation refers to the widening of blood vessels resulting from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, particularly in the large arteries, smaller arterioles and large veins. The process is essentially the opposite of vasoconstriction, or the narrowing of blood vessels. When...
of strictureStenosisA stenosis is an abnormal narrowing in a blood vessel or other tubular organ or structure.It is also sometimes called a stricture ....
s of the small bowel. - it allows for access to the papilla in patients with long afferent limbs after Billroth II antrectomy.
The key disadvantage of double-balloon enteroscopy is the time required to visualize the small bowel; this can exceed three hours, and may require that patients be admitted to hospital
Hospital
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment by specialized staff and equipment. Hospitals often, but not always, provide for inpatient care or longer-term patient stays....
for the procedure. There have also been case reports of acute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis or acute pancreatic necrosis is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas. It can have severe complications and high mortality despite treatment...
and intestinal necrosis associated with the technique.

