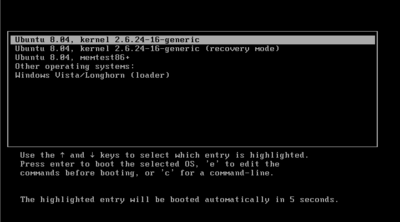
Dual boot
Encyclopedia
Operating system
An operating system is a set of programs that manage computer hardware resources and provide common services for application software. The operating system is the most important type of system software in a computer system...
s on a computer
Computer
A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
, and being able to choose which one to boot
Booting
In computing, booting is a process that begins when a user turns on a computer system and prepares the computer to perform its normal operations. On modern computers, this typically involves loading and starting an operating system. The boot sequence is the initial set of operations that the...
when starting the computer. The term dual-booting refers to the common configuration of exactly two operating systems. Multi-booting requires a program called a boot loader.
Usage
Multi-booting is useful in many situations such as those where several pieces of softwareComputer software
Computer software, or just software, is a collection of computer programs and related data that provide the instructions for telling a computer what to do and how to do it....
require different operating systems and cannot be run on a single system. A multi-boot configuration will allow a user to use all of this software on one computer. Another reason for setting up a multi-boot system can be to investigate or test a new operating system without switching completely. Multi-booting allows one to get to know the new system, configure all applications needed, and migrate data before making the final step and removing the old operating system. This is often accomplished by using a boot loader such as NTLDR
NTLDR
NTLDR is the boot loader for all releases of Windows NT operating system up to and including Windows XP and Windows Server 2003. NTLDR is typically run from the primary hard disk drive, but it can also run from portable storage devices such as a CD-ROM, USB flash drive, or floppy disk...
, LILO
LILO (boot loader)
LILO is a generic boot loader for Linux.-Overview:LILO does not depend on a specific file system, and can boot an operating system from floppy disks and hard disks. One of up to sixteen different images can be selected at boot time. Various parameters, such as the root device, can be set...
, or GRUB
GNU GRUB
GNU GRUB is a boot loader package from the GNU Project. GRUB is the reference implementation of the Multiboot Specification, which provides a user the choice to boot one of multiple operating systems installed on a computer or select a specific kernel configuration available on a particular...
which can boot more than one operating system.
Multi-booting can also aid software developer
Software developer
A software developer is a person concerned with facets of the software development process. Their work includes researching, designing, developing, and testing software. A software developer may take part in design, computer programming, or software project management...
s where multiple operating systems are required for development or testing purposes. Having these systems on one machine can greatly reduce hardware costs. However, hardware costs are counterbalanced by system management costs, and the costs of the unavailability of the software that cannot be run at any given moment.
An alternative to multi-booting is to use virtual machine
Virtual machine
A virtual machine is a "completely isolated guest operating system installation within a normal host operating system". Modern virtual machines are implemented with either software emulation or hardware virtualization or both together.-VM Definitions:A virtual machine is a software...
software to emulate another computer from within the operating system of choice.
Number of Operating Systems per Storage Device
In a multi-boot computer each of the multiple operating systems can reside on its own storage device, or some storage devices might contain more than one operating system.An example of a computer with one operating system per storage device is a dual-booting computer that stores Windows on one disk drive and Linux on another disk drive. In this case a multi-booting boot loader is not strictly necessary because the user can choose to enter BIOS configuration immediately after power-up and make the desired drive first in the boot-order list. However, it is more convenient to have a multi-booting boot loader on one of the drives, set BIOS once to always start booting from (i.e., load the boot loader from) that drive, and then allow the user to choose an operating system from that boot loader's menu. No special disk partitioning is necessary when each operating system has its own dedicated disk drive.
An example of a computer with multiple operating systems per storage device is a dual-booting computer that stores both Windows and Linux on the same disk drive. In this case a multi-booting boot loader is necessary. Also, the disk must be partitioned to give each operating system its own partition of the disk drive.
Partitioning
The basic concept involves partitioning a disk to accommodate each planned installation, optionally including separate partitions for data storage or backups.Windows XP/2000
Note that Vista's partitioners may not be compatible withXP/2000 (see Logical disk manager#Compatibility problems). If you use Windows 2000/XP, probably the safest approach (for disks under 2 TiB
TIB
TIB may mean:* Therapy Interfering Behavior* Forbundet Træ-Industri-Byg i Danmark, the Danish Timber Industry and Construction Workers' Union* Tibet* The Win32 Thread Information Block, an element in Microsoft Windows computer programming....
) is to use a CHS partition table alignment that is chosen by Windows XP/2000 (not Vista or Windows 7). If starting with a disk with nothing important on it, delete all partitions, unplug the disk or reboot, create at least one partition with Windows XP/2000 Disk Management or the XP/2000 installer, and format all FAT partitions (only so that Ranish Partition Manager will not show them in red). The alignment can be checked with Ranish Partition Manager
Ranish Partition Manager
Ranish Partition Manager is a freeware hard disk partition editor, disk cloning tool, and boot manager, that gives a high level of control for creating multi-boot systems. It is available on the freeware live cd SystemRescueCD and the Ultimate Boot CD...
: All partitions (including EBR
EBR
EBR may refer to:* Experimental Breeder Reactor I, a nuclear research reactor* Experimental Breeder Reactor II, another nuclear research reactor* Mk 14 Mod 0 Enhanced Battle Rifle, an M14 battle rifle variant...
extended partitions—type 05) should start at the beginning of a head, and end at the end of a cylinder. If nothing is shown in red (with error messages when you highlight them) you probably have a disk with a standard CHS partition table alignment. If you wish to edit the partition table with Linux, first run sfdisk with "--show-geometry" and "--show-pt-geometry"http://linux.die.net/man/8/sfdisk. If these return the same geometry, it should be safe to use Gparted
GParted
GParted is a GTK+ front-end to GNU Parted and the official GNOME Partition Editor application.It is used for creating, deleting, resizing, moving, checking and copying partitions, and the file systems on them...
, so long as it is set to round to cylinders, and you only add partitions to the end of the partition table. If you add a partition to the middle of the extended partition table, Gparted will not put them in the order they are on the disk (so that hda7 will follow hda9 instead of hda6). The order can be fixed with a Linux fdisk advanced function. Most Linux partitioners that don't use parted, may not end EBR extended partitions (type 05) on the same sector as their logical drives. When Gparted or parted edit these "nonstandard" partition tables, they will "fix" all these EBRs, so that the extended partitions end on the same sector as their logical drives. Ranish PM then shows these partitions as having no "errors". This can also be checked using (for example) sfdisk -l -x -us /dev/hda http://linux.die.net/man/8/sfdisk.
Windows and GNU/Linux
One popular multi-boot configuration is to dual-boot GNU/Linux and Windows operating systems, each contained within its own partition. Windows does not facilitate or support multi-boot systems, other than allowing for partition-specific installations, and no choice of boot loader is offered. However, most current Linux installers accommodate dual-booting (although some knowledge of partitions is desirable).There are some advantages to installing a Linux boot manager/loader (usually GRUB) as the primary bootloader pointed to by the master boot record
Master boot record
A master boot record is a type of boot sector popularized by the IBM Personal Computer. It consists of a sequence of 512 bytes located at the first sector of a data storage device such as a hard disk...
. All Windows installations will be found by Linux bootloaders, but Windows boot managers do not recognize Linux installations (nor does Windows deal natively with Linux file systems).
However, in Vista, in order to install services packs (or other Windows updates) it may be necessary to restore the Vista boot loader first. SP2 may fail to install if it does not find certain files from the Vista boot loader, in the MBR
MBR
MBR may refer to:* Minerações Brasileiras Reunidas, a division of Caemi* Malaysian Book of Records* Master boot record, the first sector of a partitioned data storage device, used for booting* Membrane bioreactor* Memory buffer register...
. Similar problems may occur with SP1 http://blogs.sun.com/pomah/entry/installing_windows_vista_service_pack or when there are cloned disks or partitions http://news.softpedia.com/news/Vista-SP2-Fails-to-Install-on-PCs-with-Cloned-Disks-or-Partitions-111761.shtml. The MBR boot code can be backed up and restored with dd (unix)
Dd (Unix)
In computing, dd is a common Unix program whose primary purpose is the low-level copying and conversion of raw data. According to the manual page for Version 7 Unix, it will "convert and copy a file". It is used to copy a specified number of bytes or blocks, performing on-the-fly byte order...
, available on System Rescue CD.
It is often recommended that Windows be installed to the first primary partition. The boot loaders of both Windows and GNU/Linux identify partitions with a number derived by counting the partitions. (Note, both Windows and Linux count the partitions according to the ordering of the partitions in the partition table, which may be different than the order of the partitions on the disk.) Adding or deleting a partition at the end of a hard drive will have no effect on any partitions prior to it. However, if a partition is added or deleted at the beginning or middle of a hard drive, the numbering of subsequent partitions may change. If the number of the system partition changes, it requires boot loader reconfiguration in order for an operating system to boot and function properly.
Windows must be installed into a primary partition (and in older systems this must be the first partition). Linux can be installed into a partition in any position on the hard drive and can also be installed into logical partitions (within the extended partition). If Linux is installed into a logical partition within the extended partition, it is unaffected by changes in the primary partitions.
Installing multiple Windows systems
Further difficulties can arise when installing Windows, when Windows is already installed on another visible partition (as opposed to a partition that is on the disk but deleted from the partition table). Other (bootable) partitions (such as a recovery partition) may have similar problems with the Windows XP installer.Windows 2000/XP
If installing Windows XP/2000 when a Windows XP/2000 system is already installed on another partition, the installer may configure the boot loader (NTLDR
NTLDR
NTLDR is the boot loader for all releases of Windows NT operating system up to and including Windows XP and Windows Server 2003. NTLDR is typically run from the primary hard disk drive, but it can also run from portable storage devices such as a CD-ROM, USB flash drive, or floppy disk...
) on the older installation, to boot both the newer installation and the old installation, and not install another NTLDR on the partition of the new installation. (See system and boot partitions
System partition and boot partition
In Microsoft Windows, the system partition and boot partition refer to:*The system partition is a disk partition that contains the boot sector and files such as NTLDR that are needed for booting Windows XP and earlier...
.) This can create problems as the new partition will be dependent on the old partition, and will not be able to boot unless both partitions are properly configured. For example, if the partition with the old system is deleted, the new system can not be booted by activating it, or using another boot loader (such as GRUB or XOSL
XOSL
xOSL is the name of a bootloader, which is a program product class that launches operating systems from a bootable device such as a hard disk or floppy drive. The letters are an acronym that stand for eXtended Operating System Loader...
) because Windows 2000/XP requires NTLDR to boot. It may also name the system partition of the second installation, some letter other than "C:" (usually "D:"). It is not desirable to have a system partition named "D:" because if the disk signature is changed, this may cause the system drive to be renamed as "C:", and fixing this may require editing the registry of a non-bootable system (not an easy task).
To make the Windows installer put NTLDR on the partition of the system being installed, and to make this system name its partition C:, it may be necessary to hide other partitions. It is safest to hide certain other (bootable) partitions (such as a Dell
Dell
Dell, Inc. is an American multinational information technology corporation based in 1 Dell Way, Round Rock, Texas, United States, that develops, sells and supports computers and related products and services. Bearing the name of its founder, Michael Dell, the company is one of the largest...
recovery partition) because these might cause similar problems with a Windows XP installer. These partitions must be hidden before attempting the second Windows installation. It is safest to leave these partitions hidden until after the new installation is booted for the first time, so that it will give its partition the letter "C:". The hiding can be done with MBRWizard
MBRwizard
MBRWizard is a Master Boot Record management application for x86 and x86-64 based computers. As the use of disk imaging applications for backup and operating system deployment began to increase, as well as many users beginning to experiment with dual-booting Linux on existing Windows machines,...
or the partition(s) can be deleted from the partition table (and later recreated) with a sector-precise partitioner such as Ranish Partition Manager
Ranish Partition Manager
Ranish Partition Manager is a freeware hard disk partition editor, disk cloning tool, and boot manager, that gives a high level of control for creating multi-boot systems. It is available on the freeware live cd SystemRescueCD and the Ultimate Boot CD...
http://www.trombettworks.com/multi-boot.htm#key.
However, using this method will not automatically set up a dual-boot configuration. In order to boot the initial Windows installation you must either, activate that partition, configure boot.ini of the new system to dual-boot the old system, or install a third party boot loader such as GRUB or XOSL
XOSL
xOSL is the name of a bootloader, which is a program product class that launches operating systems from a bootable device such as a hard disk or floppy drive. The letters are an acronym that stand for eXtended Operating System Loader...
.
XP/2003 deletes Vista's System Restore points
On a computer with both Windows VistaWindows Vista
Windows Vista is an operating system released in several variations developed by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops, tablet PCs, and media center PCs...
and either Windows XP
Windows XP
Windows XP is an operating system produced by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops and media centers. First released to computer manufacturers on August 24, 2001, it is the second most popular version of Windows, based on installed user base...
or Windows Server 2003
Windows Server 2003
Windows Server 2003 is a server operating system produced by Microsoft, introduced on 24 April 2003. An updated version, Windows Server 2003 R2, was released to manufacturing on 6 December 2005...
installed, Windows XP or Windows Server 2003 deletes any existing System Restore
System Restore
System Restore is a component of Microsoft's Windows Me, Windows XP, Windows Vista and Windows 7, but not Windows 2000, operating systems that allows for the rolling back of system files, registry keys, installed programs, etc., to a previous state in the event of system malfunction or failure.The...
points belonging to Windows Vista during boot. Microsoft confirms this problem but maintains that it is a fundamental function of the way XP works and cannot be changed. According to Microsoft, the solution is to install Windows Vista on a separate partition invisible to XP.
Apple Boot Camp
Boot Camp allows owners of Intel-based Apple Macintosh computers to install Windows XP, Vista and Windows 7 on their Macs. The software comes bundled with Mac OS XMac OS X
Mac OS X is a series of Unix-based operating systems and graphical user interfaces developed, marketed, and sold by Apple Inc. Since 2002, has been included with all new Macintosh computer systems...
10.5 Leopard, 10.6 Snow Leopard and Mac OS X 10.7 Lion, Apple's latest version of the Operating System included on their computers. Previously the application was available in beta version as a download from Apple's website.
Boot Camp allows non-destructive disk partitioning and resizing of HFS+ filesystems, boot menu options, and an option to burn a CD with necessary device drivers. Since Windows XP
Windows XP
Windows XP is an operating system produced by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops and media centers. First released to computer manufacturers on August 24, 2001, it is the second most popular version of Windows, based on installed user base...
is incompatible with Extensible Firmware Interface
Extensible Firmware Interface
The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface is a specification that defines a software interface between an operating system and platform firmware...
(the successor to legacy BIOS
BIOS
In IBM PC compatible computers, the basic input/output system , also known as the System BIOS or ROM BIOS , is a de facto standard defining a firmware interface....
), the firmware on early Intel Macs need to be updated to support BIOS emulation first. BIOS emulation is achieved with a compatibility support module (CSM). Apple does not support non-Windows partition formats or drivers so therefore configuring other operating systems is not directly possible through Boot Camp itself. However, any operating system which can utilize the BIOS emulation of Intel Macintosh can be made to work, including non-XP versions of Windows
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
. The Ubuntu
Ubuntu (operating system)
Ubuntu is a computer operating system based on the Debian Linux distribution and distributed as free and open source software. It is named after the Southern African philosophy of Ubuntu...
Linux distribution is particularly popular for this purpose because they provide an option to use proprietary
Proprietary software
Proprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...
device drivers along with open source drivers.
See also
- Comparison of boot loadersComparison of boot loadersThe following tables compare general and technical information for a number of available boot loaders.-Features:- External links :* * Let you boot legacy PCs from CD-ROM and USB without BIOS support...
- GNU GRUBGNU GRUBGNU GRUB is a boot loader package from the GNU Project. GRUB is the reference implementation of the Multiboot Specification, which provides a user the choice to boot one of multiple operating systems installed on a computer or select a specific kernel configuration available on a particular...
- Multiboot SpecificationMultiboot SpecificationThe Multiboot Specification is an open standard originally created in 1995 and developed by the Free Software Foundation. The specification describes a method of loading various multiboot kernels using a single compliant boot loader. GNU Hurd, VMware ESXi, Xen, and L4 microkernels all need to be...
- Windows To GoWindows To GoWindows To Go is a feature in Windows 8 that allows the entire system to run from USB mass storage devices such as flash drives and external hard drives....
- NeoSmart Technologies' EasyBCDEasyBCDEasyBCD is a free program developed by NeoSmart Technologies to configure and tweak the Boot Configuration Data , a boot database first introduced in Windows Vista...
, a free program to configure Multi-booting on Windows - XOSLXOSLxOSL is the name of a bootloader, which is a program product class that launches operating systems from a bootable device such as a hard disk or floppy drive. The letters are an acronym that stand for eXtended Operating System Loader...
, a free, graphical, open source boot loader
External links
- Dual, Triple, Quad Boot a Macbook with Mac OS X, Ubuntu Linux, Windows XP, and Windows Vista
- The definitive dual-booting guide: Windows 7, Linux, Vista, XP: with screenshots.
- Installing Windows XP:Dual-Booting Versus Single Booting
- Instructions on how to make your Playstation 3 dual boot applicable
- Tutorial on multi-booting and solutions to issues that arise
- Information on Vista specific multi-booting issues
- https://help.ubuntu.com/community/WindowsDualBoot

