
Dual currency deposit
Encyclopedia
In finance
, a dual currency deposit (DCD) is a derivative instrument
which combines a money market
deposit with a currency option to provide a higher yield
than that available for a standard deposit. There is a higher risk than with the latter - you can receive less funds than originally deposited and in a different currency. So one could do a USD/JPY DCD depositing USD and receive JPY.
If an investor has a view on the initial investment currency a Dual Currency strategy allows the investor to benefit from higher returns.
The returns are higher than the returns on normal deposits in compensation for the higher risks that are associated with DCDs due to being exposed foreign exchange,
At maturity,
if the local currency is weaker than the strike rate funds will be redeemed in the local currency.
If the local currency is stronger than the strike, the principal is repaid in the alternative currency, converted at the strike rate
The distance from current exchange rate to “strike” is determined by investor risk appetite: If the client is comfortable with risk the conversion level will be closer to the current level, the interest payable will be higher as the risk of conversion
DCDs are also known as Dual Currency Instruments.
The Sales person is eager to provide the customer with all the investment opportunities possible and generally earns higher fees on more complicated / new products.
or spot date
, however in the case of the DCD the client is paid at the end of the deposit period. For this reason some banks offer their clients a product commonly called a DCD+ which includes an interest element to account for this.
Adding this to the deposit redemption-amount means that the amount of currency that will need converting if the option strike is passed at expiry has now increased. So the option face amount needs to be altered to take the extra interest into account. This affects the premium again, and so on.
To avoid having to compute this to infinity one can use a geometric series with
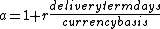
and
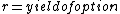
where yield is the forward value (FV) of the option premium giving a multiplier to change a DCD's option premium to a DCD+ of:
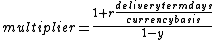
• Currency Pair: INR/USD
• Base Currency: Indian National Rupee(INR)
• Alternate Currency: US dollars (USD)
• Strike Rate: Strike Rate = 0.7300
• Investment Amount: INR100,000
• Term: 1 month (30 days)
Other investment parameters determined by product offering institution
• Spot Rate: The Spot Rate at the time of investment is 0.7200
• Applicable yield : 6% per annum
Let’s assume - On the Expiry Date, the Reference Rate is 0.723
Currency of repayment
Since the Reference Rate on the Expiry Date (0.7230) is less than the Strike Rate selected by Investor (0.7300), Proceeds will be paid in the Base Currency (Indian Rupee) to Investor on the Maturity Date. Here, the Base Currency (INR) has appreciated no greater than the Strike Rate selected by Investor.
Finance
"Finance" is often defined simply as the management of money or “funds” management Modern finance, however, is a family of business activity that includes the origination, marketing, and management of cash and money surrogates through a variety of capital accounts, instruments, and markets created...
, a dual currency deposit (DCD) is a derivative instrument
Derivative (finance)
A derivative instrument is a contract between two parties that specifies conditions—in particular, dates and the resulting values of the underlying variables—under which payments, or payoffs, are to be made between the parties.Under U.S...
which combines a money market
Money market
The money market is a component of the financial markets for assets involved in short-term borrowing and lending with original maturities of one year or shorter time frames. Trading in the money markets involves Treasury bills, commercial paper, bankers' acceptances, certificates of deposit,...
deposit with a currency option to provide a higher yield
Yield (finance)
In finance, the term yield describes the amount in cash that returns to the owners of a security. Normally it does not include the price variations, at the difference of the total return...
than that available for a standard deposit. There is a higher risk than with the latter - you can receive less funds than originally deposited and in a different currency. So one could do a USD/JPY DCD depositing USD and receive JPY.
Formal Definition
A Dual Currency Deposit (“DCD”) is a foreign exchange linked deposit in which the principal can be repaid after being converted into the alternative currency at the Strike rate at maturity depending on the spot foreign exchange rate.If an investor has a view on the initial investment currency a Dual Currency strategy allows the investor to benefit from higher returns.
The returns are higher than the returns on normal deposits in compensation for the higher risks that are associated with DCDs due to being exposed foreign exchange,
At maturity,
if the local currency is weaker than the strike rate funds will be redeemed in the local currency.
If the local currency is stronger than the strike, the principal is repaid in the alternative currency, converted at the strike rate
The distance from current exchange rate to “strike” is determined by investor risk appetite: If the client is comfortable with risk the conversion level will be closer to the current level, the interest payable will be higher as the risk of conversion
DCDs are also known as Dual Currency Instruments.
Customer
The customer wants to receive a higher return than the deposit rate for their investment currency in return for the risk of receiving the returns in a different currency, converted at a disadvantageous rate.Bank
The FX Options Desk of the bank is best able to price and manage the risk for these sorts of products, and also benefits from the extra liquidity (more options!) in their book, making it easier for them to cancel out the risk of different buy/sell positions.The Sales person is eager to provide the customer with all the investment opportunities possible and generally earns higher fees on more complicated / new products.
DCD+
The DCD is actually composed of a normal deposit and an option. Normally in the options market the seller of an option is paid before the premium value dateValue date
Value date in finance is the date when the value of an asset that fluctuates in price is determined. The value date is used when there is a possibility for discrepancies due to differences in the timing of asset valuation...
or spot date
Spot date
In finance, the spot date of a transaction is the normal settlement day when the transaction is done today. This kind of transaction is referred to as a spot transaction or simply spot....
, however in the case of the DCD the client is paid at the end of the deposit period. For this reason some banks offer their clients a product commonly called a DCD+ which includes an interest element to account for this.
Adding this to the deposit redemption-amount means that the amount of currency that will need converting if the option strike is passed at expiry has now increased. So the option face amount needs to be altered to take the extra interest into account. This affects the premium again, and so on.
To avoid having to compute this to infinity one can use a geometric series with
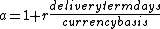
and
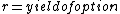
where yield is the forward value (FV) of the option premium giving a multiplier to change a DCD's option premium to a DCD+ of:
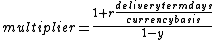
Example of DCI/DCD
Lets say parameters selected by an Investor• Currency Pair: INR/USD
• Base Currency: Indian National Rupee(INR)
• Alternate Currency: US dollars (USD)
• Strike Rate: Strike Rate = 0.7300
• Investment Amount: INR100,000
• Term: 1 month (30 days)
Other investment parameters determined by product offering institution
• Spot Rate: The Spot Rate at the time of investment is 0.7200
• Applicable yield : 6% per annum
Let’s assume - On the Expiry Date, the Reference Rate is 0.723
Currency of repayment
Since the Reference Rate on the Expiry Date (0.7230) is less than the Strike Rate selected by Investor (0.7300), Proceeds will be paid in the Base Currency (Indian Rupee) to Investor on the Maturity Date. Here, the Base Currency (INR) has appreciated no greater than the Strike Rate selected by Investor.

