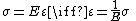Duality (mechanical engineering)
Encyclopedia
In mechanical engineering
, many terms are associated into pairs called duals. A dual of a relationship is formed by interchanging force (stress) and deformation (strain) in an expression.
Here is a partial list of mechanical dualities:
Mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is a discipline of engineering that applies the principles of physics and materials science for analysis, design, manufacturing, and maintenance of mechanical systems. It is the branch of engineering that involves the production and usage of heat and mechanical power for the...
, many terms are associated into pairs called duals. A dual of a relationship is formed by interchanging force (stress) and deformation (strain) in an expression.
Here is a partial list of mechanical dualities:
- forceForceIn physics, a force is any influence that causes an object to undergo a change in speed, a change in direction, or a change in shape. In other words, a force is that which can cause an object with mass to change its velocity , i.e., to accelerate, or which can cause a flexible object to deform...
— deformation - stressStress (physics)In continuum mechanics, stress is a measure of the internal forces acting within a deformable body. Quantitatively, it is a measure of the average force per unit area of a surface within the body on which internal forces act. These internal forces are a reaction to external forces applied on the body...
— strainStrain (materials science)In continuum mechanics, the infinitesimal strain theory, sometimes called small deformation theory, small displacement theory, or small displacement-gradient theory, deals with infinitesimal deformations of a continuum body... - stiffness method — flexibility methodFlexibility methodIn structural engineering, the flexibility method is the classical consistent deformation method for computing member forces and displacements in structural systems...
Constitutive relation
- stress and strain (Hooke's lawHooke's lawIn mechanics, and physics, Hooke's law of elasticity is an approximation that states that the extension of a spring is in direct proportion with the load applied to it. Many materials obey this law as long as the load does not exceed the material's elastic limit. Materials for which Hooke's law...
.)