
Dust (relativity)
Encyclopedia
In special
and general relativity
, dust is the name conventionally given to a configuration of matter which can be interpreted as small bodies ("dust particles") which interact only gravitationally.
The number density
 of dust is defined as the number of particles per unit volume in the (unique) inertial frame in which the particles are at rest.
of dust is defined as the number of particles per unit volume in the (unique) inertial frame in which the particles are at rest.
Dust possesses a number flux four vector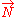 which defines the
which defines the
fluxes across coordinate planes defined by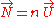
where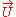 is the four velocity of the particles.
is the four velocity of the particles.
Special relativity
Special relativity is the physical theory of measurement in an inertial frame of reference proposed in 1905 by Albert Einstein in the paper "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies".It generalizes Galileo's...
and general relativity
General relativity
General relativity or the general theory of relativity is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1916. It is the current description of gravitation in modern physics...
, dust is the name conventionally given to a configuration of matter which can be interpreted as small bodies ("dust particles") which interact only gravitationally.
The number density
Number density
In physics, astronomy, and chemistry, number density is an intensive quantity used to describe the degree of concentration of countable objects in the three-dimensional physical space...
 of dust is defined as the number of particles per unit volume in the (unique) inertial frame in which the particles are at rest.
of dust is defined as the number of particles per unit volume in the (unique) inertial frame in which the particles are at rest.Dust possesses a number flux four vector
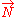 which defines the
which defines thefluxes across coordinate planes defined by
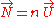
where
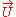 is the four velocity of the particles.
is the four velocity of the particles.

