
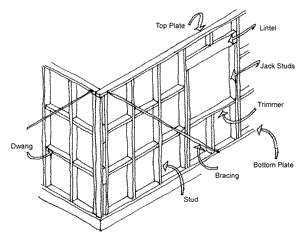
Dwang
Encyclopedia
Construction
In the fields of architecture and civil engineering, construction is a process that consists of the building or assembling of infrastructure. Far from being a single activity, large scale construction is a feat of human multitasking...
, a dwang (Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
, New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
), nogging (England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
, Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
) or blocking (North America) is a horizontal bracing piece used between wall stud
Wall stud
A wall stud is a vertical member in the light frame construction techniques called balloon framing and platform framing of a building's wall.-Purpose:...
s or floor joists
Joist
A joist, in architecture and engineering, is one of the horizontal supporting members that run from wall to wall, wall to beam, or beam to beam to support a ceiling, roof, or floor. It may be made of wood, steel, or concrete. Typically, a beam is bigger than, and is thus distinguished from, a joist...
to give rigidity to the wall or floor frames of a building. Noggings may be made of timber, steel or aluminium. If made of timber they are cut slightly longer than the space they fit into, and are driven into place so they fit tightly or are rebated into the stud.
The interval between noggings is dictated by local building codes and by the type of timber used; a typical timber-framed house in a non-cyclonic area will have two or three noggings per storey between each pair of neighbouring studs. Additional noggings may be added as grounds for later fixings.
Noggings between vertical studs generally brace the studs against buckling
Buckling
In science, buckling is a mathematical instability, leading to a failure mode.Theoretically, buckling is caused by a bifurcation in the solution to the equations of static equilibrium...
under load; noggings on floor joists prevent the joists from twisting or rotating under load (lateral-torsional buckling), and are often fixed at intervals, in pairs diagonally for that reason. In floors this type of bracing is also called herringbone strutting.
Noggings provide no bracing effect in shear
Shear stress
A shear stress, denoted \tau\, , is defined as the component of stress coplanar with a material cross section. Shear stress arises from the force vector component parallel to the cross section...
and are generally supplemented by diagonal bracing to prevent the frame from racking.

