Dynamic compaction
Encyclopedia
Soil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
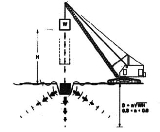
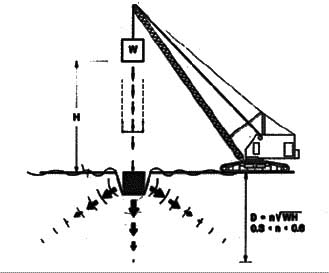
when certain subsurface constraints make other methods inappropriate. It is a method that is used to increase the density of soil deposits. The process involves of dropping a heavy weight repeatedly on the ground at regularly spaced intervals. The weight and the height determine the amount of compaction
Compaction
Compaction may refer to:* Soil compaction, for mechanically induced compaction near the ground surface* Compaction , part of the process of lithification involving mechanical dewatering of a sediment by progressive loading under several km of geomaterial* Waste compaction, related to garbage* Cold...
that would occur. The weight that is used, depends on the degree of compaction desired and is between 8 tonne to 36 tonne. The height varies from 1m to 30m.
The impact of the free fall
Free fall
Free fall is any motion of a body where gravity is the only force acting upon it, at least initially. These conditions produce an inertial trajectory so long as gravity remains the only force. Since this definition does not specify velocity, it also applies to objects initially moving upward...
creates stress waves that help in the densification of the soil. These stress waves can penetrate up to 10m. In cohesionless soils, these waves create liquefaction that is followed by the compaction of the soil, and in cohesive soils, they create an increased amount of pore water pressure that is followed by the compaction of the soil. Pore water pressure is the pressure of water that is trapped within the particles of rocks and soils.
The degree of compaction depends on the weight of the hammer, the height from which the hammer
Hammer
A hammer is a tool meant to deliver an impact to an object. The most common uses are for driving nails, fitting parts, forging metal and breaking up objects. Hammers are often designed for a specific purpose, and vary widely in their shape and structure. The usual features are a handle and a head,...
is dropped, and the spacing of the locations at which the hammer is dropped. The initial weight dropping has the most impact, and penetrates up to a greater depth. The following drops, if spaced closer to one another, compact the shallower layers and the process is completed by compacting the soil at the surface.
Most soil types can be improved with dynamic compaction. Old fills and granular soils are most often treated. The soils that are below the water table have to be treated carefully to permit emission of the excess pore water pressure that is created when the weight is dropped onto the surface.
To watch a video of dynamic compaction, navigate here: http://ww2.bcradesign.com/civil/30Tons.html

