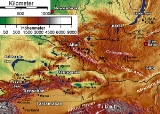
Dzungaria
Encyclopedia
Dzungaria, also called Zungaria, is a geographical region in northwest China
corresponding to the northern half of Xinjiang
. It covers approximately 777000 km² (300,001.4 sq mi), lying mostly within Xinjiang, and extending into western Mongolia
and eastern Kazakhstan
. Formerly the term could cover a wider area, depending on temporary political boundaries.
term "Züün Gar" or "Jüün Gar" depending on the dialect of Mongolian used. "Züün"/"Jüün" means "left" and "Gar" means "hand". The name originates from the notion that the Western Mongols are on the left hand side when the Mongol Empire began its division into East and West Mongols. After this fragmentation, the western Mongolian nation was called "Zuun Gar". Today, the cradle of this former nation retains its name: Zungaria.
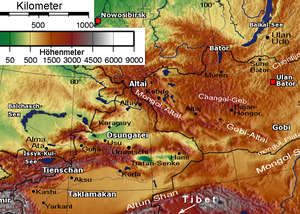 The core of Dzungaria is the triangular Dzungarian Basin (also Junggar Basin) with its central Gurbantunggut Desert
The core of Dzungaria is the triangular Dzungarian Basin (also Junggar Basin) with its central Gurbantunggut Desert
. It is bounded by the Tien Shan to the south, the Altai Mountains to the northeast and the Tarbagatai Mountains
to the northwest. The three corners are relatively open. The northern corner is the valley of the upper Irtysh River. The western corner is the Dzungarian Gate
with its railroad (opened in 1990). The eastern corner leads to Gansu
and the rest of China. In the south an easy pass leads from Ürümqi
to the Turfan Depression
. In the southwest the Borohoro Mountains branch of the Tian Shan
separates the basin from the upper Ili River
.
The extensive Dzungarian Basin is in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in northwestern China. It is surrounded by mountains. The basin is located between the Mongolian Altai Mountains and Tian Shan to the south. The basin is similar to the larger Tarim Basin
on the southern side of the Tian Shan Range. Only a gap in the mountains to the north allows moist air masses to provide the basin lands with enough moisture to remain semi-desert rather than becoming a true desert like most of the Tarim Basin, and allows a thin layer of vegetation to grow. This is enough to sustain populations of wild camel
s, jerboa
s, and other wild species.
The Dzungarian Basin is a structural basin with thick sequences of Paleozoic-Pleistocene rocks with large estimated oil reserves. The Gurbantunggut Desert
, China’s second largest, is in the center of the basin. Aibi Lake is the basin's catchment
center.
The cold climate of nearby Siberia influences the climate of the Dzungarian Basin, making the temperature colder—as low as -4 °F—and providing more precipitation, ranging from 3 to 10 in (7.6 to 25.4 ), compared to the warmer, drier basins to the south. Runoff from the surrounding mountains into the basin supplies several lakes. The ecologically rich habitats traditionally included meadows, marshlands, and rivers. However most of the land is now used for agriculture.
It is a largely steppe
and semi-desert basin surrounded by high mountains: the Tian Shan
(ancient Mount Imeon
) in the south and the Altai in the north. Geologically it is an extension of the Paleozoic Kazakhstan Block and was once part of an independent continent before the Altai mountains formed in the late Paleozoic. It does not contain the abundant minerals of Kazakhstan and may have been a pre-existing continental block before the Kazakhstan Block was formed.
Ürümqi
, Yining and Karamai are the main cities; other smaller oasis
towns dot the piedmont areas.
A recent notable find, in February 2006, is the oldest tyrannosaur fossil unearthed by a team of scientists from George Washington University
who were conducting a study in the Dzungarian Basin. The species, named Guanlong
, lived 160 million years ago, more than 90 million years before the famed Tyrannosaurus rex
.
ecoregion
known as the Dzungarian Basin semi-desert. The vegetation consists mostly of low scrub of Anabasis brevifolia. Taller shrublands of saxaul
bush (Haloxylon ammodendron) and Ephedra przewalskii
can be found near the margins of the basin. Streams descending from the Tian Shan and Altai ranges support stands of poplar
(Populus diversifolia) together with Nitraria roborovsky, N. sibirica, Achnatherum splendens, tamarisk (Tamarix sibirimosissima), and willow
(Salix ledebouriana).
The northeastern portion of the Dzungarian Basin semi-desert lies within Great Gobi National Park, and is home to herds of Asian wild ass (Equus hemionus) and goitered gazelle
(Gazella subgutturosa), and wild Bactrian camel
s (Camelus ferus).
The basin was one of the last habitat
s of Przewalski's Horse
(Equus przewalskii), which is now extinct in the wild.
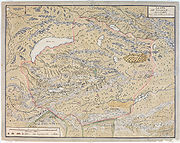 One of the earliest mentions of the Dzungaria region occurs when the Han Dynasty
One of the earliest mentions of the Dzungaria region occurs when the Han Dynasty
dispatched an explorer to investigate lands to the west, using the northernmost Silk Road
trackway
of about 2600 kilometres (1,615.6 mi) in length, which connected the ancient Chinese capital of Xi'an
to the west over the Wushao Ling Pass to Wuwei and emerged in Kashgar
.
Istämi
of the Göktürks
received the lands of Dzungaria as an inheritance after the death of his father in the latter half of the sixth century AD.
Dzungaria is named after a Mongolian
kingdom which existed in Central Asia
during the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. It derived its name from the Dzungars, who were so called because they formed the left wing (züün, left; gar, hand) of the Mongolian army, self-named Oirats
. Dzungar power reached its height in the second half of the 17th century, when Kaldan (also known as Galdan Boshigtu Khan), repeatedly intervened in the affairs of the Kazakhs
to the west, but it was completely destroyed by the Qing
government about 1757–1759. It has played an important part in the history of Mongolia
and the great migrations of Mongolian stems westward.
Since 1761, its territory fell mostly to the Qing dynasty
(Xinjiang
and north-western Mongolia) and partly to Russian Turkestan
(earlier Kazakh state provinces of Semirechye- Jetysu and Irtysh river).
Its widest limit included Kashgar
, Yarkand, Khotan
, the whole region of the Tian Shan
, and in short the greater proportion of that part of Central Asia which extends from 35º to 50º N and from 72º to 97º E.
As a political or geographical term Dzungaria has practically disappeared from the map; but the range of mountains stretching north-east along the southern frontier of the Jeti-su, as the district to the south-east of Lake Balkhash
preserves the name of Dzungarian Alatau
. It also gave name to Dzungarian Hamsters.
, Kyrgyz, Mongols
, Uyghurs
and Han Chinese
. Since 1953 there has been a massive influx of Han Chinese to work on water conservation and industrial projects, especially the Karamay
oil fields.
, barley
, oat
s, and sugar beet
s are grown, and cattle
, sheep, and horse
s are raised. The fields are irrigated with melted snow from the permanently white-capped mountains.
Dzungaria has deposits of coal
, iron
, and gold
, as well as large oil field
s.
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
corresponding to the northern half of Xinjiang
Xinjiang
Xinjiang is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. It is the largest Chinese administrative division and spans over 1.6 million km2...
. It covers approximately 777000 km² (300,001.4 sq mi), lying mostly within Xinjiang, and extending into western Mongolia
Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East and Central Asia. It is bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east and west. Although Mongolia does not share a border with Kazakhstan, its western-most point is only from Kazakhstan's eastern tip. Ulan Bator, the capital and largest...
and eastern Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan , officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country in Central Asia and Eastern Europe. Ranked as the ninth largest country in the world, it is also the world's largest landlocked country; its territory of is greater than Western Europe...
. Formerly the term could cover a wider area, depending on temporary political boundaries.
Etymology
The name Dzungaria is a corruption of the MongolianMongolian language
The Mongolian language is the official language of Mongolia and the best-known member of the Mongolic language family. The number of speakers across all its dialects may be 5.2 million, including the vast majority of the residents of Mongolia and many of the Mongolian residents of the Inner...
term "Züün Gar" or "Jüün Gar" depending on the dialect of Mongolian used. "Züün"/"Jüün" means "left" and "Gar" means "hand". The name originates from the notion that the Western Mongols are on the left hand side when the Mongol Empire began its division into East and West Mongols. After this fragmentation, the western Mongolian nation was called "Zuun Gar". Today, the cradle of this former nation retains its name: Zungaria.
Dzungarian Basin

Gurbantunggut Desert
Gurbantünggüt Desert that occupies a large part of the Dzungarian Basin in northern Xinjiang, in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is approximately 50,000 square kilometers , and located around 300 to 600 meters above sea level...
. It is bounded by the Tien Shan to the south, the Altai Mountains to the northeast and the Tarbagatai Mountains
Tarbagatai Mountains
Tarbagatai Mountains is a range of mountains located in the north-western parts of Xinjiang, China and East Kazakhstan....
to the northwest. The three corners are relatively open. The northern corner is the valley of the upper Irtysh River. The western corner is the Dzungarian Gate
Dzungarian Gate
The Dzungarian Gate is a geographically and historically significant mountain pass between China and Central Asia. It has been described as the "one and only gateway in the mountain-wall which stretches from Manchuria to Afghanistan, over a distance of three thousand miles." Given its association...
with its railroad (opened in 1990). The eastern corner leads to Gansu
Gansu
' is a province located in the northwest of the People's Republic of China.It lies between the Tibetan and Huangtu plateaus, and borders Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Ningxia to the north, Xinjiang and Qinghai to the west, Sichuan to the south, and Shaanxi to the east...
and the rest of China. In the south an easy pass leads from Ürümqi
Ürümqi
Ürümqi , formerly Tihwa , is the capital of Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China, in the northwest of the country....
to the Turfan Depression
Turfan Depression
The Turpan Depression or Turfan Depression is a fault-bounded trough located around and south of the city-oasis of Turpan, in the Xinjiang Autonomous Region in far western China, about 150 km southeast of the provincial capital Ürümqi. It includes the third lowest exposed point on the Earth's...
. In the southwest the Borohoro Mountains branch of the Tian Shan
Tian Shan
The Tian Shan , also spelled Tien Shan, is a large mountain system located in Central Asia. The highest peak in the Tian Shan is Victory Peak , ....
separates the basin from the upper Ili River
Ili River
thumb|right|300px|Map of the Lake Balkhash drainage basin showing the Ili River and its tributariesThe Ili River is a river in northwestern China and southeastern Kazakhstan .It is long, of which is in Kazakhstan...
.
The extensive Dzungarian Basin is in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in northwestern China. It is surrounded by mountains. The basin is located between the Mongolian Altai Mountains and Tian Shan to the south. The basin is similar to the larger Tarim Basin
Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is a large endorheic basin occupying an area of about . It is located in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in China's far west. Its northern boundary is the Tian Shan mountain range and its southern is the Kunlun Mountains on the northern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. The...
on the southern side of the Tian Shan Range. Only a gap in the mountains to the north allows moist air masses to provide the basin lands with enough moisture to remain semi-desert rather than becoming a true desert like most of the Tarim Basin, and allows a thin layer of vegetation to grow. This is enough to sustain populations of wild camel
Camel
A camel is an even-toed ungulate within the genus Camelus, bearing distinctive fatty deposits known as humps on its back. There are two species of camels: the dromedary or Arabian camel has a single hump, and the bactrian has two humps. Dromedaries are native to the dry desert areas of West Asia,...
s, jerboa
Jerboa
The jerboa form the bulk of the membership of the family Dipodidae. Jerboas are hopping desert rodents found throughout Asia and Northern Africa. They tend to be found in hot deserts....
s, and other wild species.
The Dzungarian Basin is a structural basin with thick sequences of Paleozoic-Pleistocene rocks with large estimated oil reserves. The Gurbantunggut Desert
Gurbantunggut Desert
Gurbantünggüt Desert that occupies a large part of the Dzungarian Basin in northern Xinjiang, in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is approximately 50,000 square kilometers , and located around 300 to 600 meters above sea level...
, China’s second largest, is in the center of the basin. Aibi Lake is the basin's catchment
Drainage basin
A drainage basin is an extent or an area of land where surface water from rain and melting snow or ice converges to a single point, usually the exit of the basin, where the waters join another waterbody, such as a river, lake, reservoir, estuary, wetland, sea, or ocean...
center.
The cold climate of nearby Siberia influences the climate of the Dzungarian Basin, making the temperature colder—as low as -4 °F—and providing more precipitation, ranging from 3 to 10 in (7.6 to 25.4 ), compared to the warmer, drier basins to the south. Runoff from the surrounding mountains into the basin supplies several lakes. The ecologically rich habitats traditionally included meadows, marshlands, and rivers. However most of the land is now used for agriculture.
It is a largely steppe
Steppe
In physical geography, steppe is an ecoregion, in the montane grasslands and shrublands and temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biomes, characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes...
and semi-desert basin surrounded by high mountains: the Tian Shan
Tian Shan
The Tian Shan , also spelled Tien Shan, is a large mountain system located in Central Asia. The highest peak in the Tian Shan is Victory Peak , ....
(ancient Mount Imeon
Mount Imeon
Mount Imeon is an ancient name for the Central Asian complex of mountain ranges comprising the present Hindu Kush, Pamir and Tian Shan, extending from the Zagros Mountains in the southwest to the Altay Mountains in the northeast, and linked to the Kunlun, Karakoram and Himalayas to the southeast...
) in the south and the Altai in the north. Geologically it is an extension of the Paleozoic Kazakhstan Block and was once part of an independent continent before the Altai mountains formed in the late Paleozoic. It does not contain the abundant minerals of Kazakhstan and may have been a pre-existing continental block before the Kazakhstan Block was formed.
Ürümqi
Ürümqi
Ürümqi , formerly Tihwa , is the capital of Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China, in the northwest of the country....
, Yining and Karamai are the main cities; other smaller oasis
Oasis
In geography, an oasis or cienega is an isolated area of vegetation in a desert, typically surrounding a spring or similar water source...
towns dot the piedmont areas.
Prehistory
Dzungaria and its derivatives are used to name a number of pre-historic animals hailing from the rocky outcrops located in an eponymous sedimentary basin of that region, the Junggar Basin.- DsungaripterusDsungaripterusDsungaripterus was a genus of pterosaur, with an average wingspan of . It lived during the Early Cretaceous, in China, where the first fossil was found in the Junggar Basin.-Discovery and species:...
weii (pterosaurPterosaurPterosaurs were flying reptiles of the clade or order Pterosauria. They existed from the late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous Period . Pterosaurs are the earliest vertebrates known to have evolved powered flight...
) - JunggarsuchusJunggarsuchusJunggarsuchus is an extinct genus of sphenosuchian crocodylomorph from the Middle Jurassic of China. The type species is J. sloani.-Anatomy:...
sloani (crocodylomorph)
A recent notable find, in February 2006, is the oldest tyrannosaur fossil unearthed by a team of scientists from George Washington University
George Washington University
The George Washington University is a private, coeducational comprehensive university located in Washington, D.C. in the United States...
who were conducting a study in the Dzungarian Basin. The species, named Guanlong
Guanlong
Guanlong was a genus of proceratosaurid tyrannosauroid dinosaur, one of the earliest known examples of the lineage.-Description and discovery:...
, lived 160 million years ago, more than 90 million years before the famed Tyrannosaurus rex
Tyrannosaurus
Tyrannosaurus meaning "tyrant," and sauros meaning "lizard") is a genus of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaur. The species Tyrannosaurus rex , commonly abbreviated to T. rex, is a fixture in popular culture. It lived throughout what is now western North America, with a much wider range than other...
.
Ecology
Dzungaria is home to a semi-desert steppeSteppe
In physical geography, steppe is an ecoregion, in the montane grasslands and shrublands and temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biomes, characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes...
ecoregion
Ecoregion
An ecoregion , sometimes called a bioregion, is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than an ecozone and larger than an ecosystem. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and contain characteristic, geographically distinct assemblages of natural...
known as the Dzungarian Basin semi-desert. The vegetation consists mostly of low scrub of Anabasis brevifolia. Taller shrublands of saxaul
Haloxylon ammodendron
The saxaul, black saxaul, sometimes sacsaoul or saksaul , is a plant belonging to the Amaranthaceae.-Description:The saxaul ranges in size from a large shrub to a small tree, 2-8 m tall. It has a brown trunk 4-10 cm in diameter. The wood is heavy and coarse and the bark is spongy and water-soaked...
bush (Haloxylon ammodendron) and Ephedra przewalskii
Ephedra przewalskii
Ephedra przewalskii is a species of Ephedra that is native to northwestern China and Mongolia. It was originally described by Otto Stapf in 1889 and placed in section Alatae, tribe Tropidolepides. In 1996 Robert A. Price left E. przewalskii in section Alatae without recognizing a tribe....
can be found near the margins of the basin. Streams descending from the Tian Shan and Altai ranges support stands of poplar
Poplar
Populus is a genus of 25–35 species of deciduous flowering plants in the family Salicaceae, native to most of the Northern Hemisphere. English names variously applied to different species include poplar , aspen, and cottonwood....
(Populus diversifolia) together with Nitraria roborovsky, N. sibirica, Achnatherum splendens, tamarisk (Tamarix sibirimosissima), and willow
Willow
Willows, sallows, and osiers form the genus Salix, around 400 species of deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist soils in cold and temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere...
(Salix ledebouriana).
The northeastern portion of the Dzungarian Basin semi-desert lies within Great Gobi National Park, and is home to herds of Asian wild ass (Equus hemionus) and goitered gazelle
Goitered Gazelle
The Goitered, Black-tailed or Persian gazelle is a gazelle found in the north part of Azerbaijan, in a large area of central Asia, including part of Iran and southern west Pakistan in the western end of the range, as well as the Gobi desert...
(Gazella subgutturosa), and wild Bactrian camel
Bactrian camel
The Bactrian camel is a large, even-toed ungulate native to the steppes of central Asia. It is presently restricted in the wild to remote regions of the Gobi and Taklamakan Deserts of Mongolia and Xinjiang. A small number of wild Bactrian camels still roam the Mangystau Province of southwest...
s (Camelus ferus).
The basin was one of the last habitat
Habitat
* Habitat , a place where a species lives and grows*Human habitat, a place where humans live, work or play** Space habitat, a space station intended as a permanent settlement...
s of Przewalski's Horse
Przewalski's Horse
Przewalski's Horse or Dzungarian Horse, is a rare and endangered subspecies of wild horse native to the steppes of central Asia, specifically China and Mongolia.At one time extinct in the wild, it has been reintroduced to its native habitat in Mongolia at the Khustain Nuruu...
(Equus przewalskii), which is now extinct in the wild.
History

Han Dynasty
The Han Dynasty was the second imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Qin Dynasty and succeeded by the Three Kingdoms . It was founded by the rebel leader Liu Bang, known posthumously as Emperor Gaozu of Han. It was briefly interrupted by the Xin Dynasty of the former regent Wang Mang...
dispatched an explorer to investigate lands to the west, using the northernmost Silk Road
Silk Road
The Silk Road or Silk Route refers to a historical network of interlinking trade routes across the Afro-Eurasian landmass that connected East, South, and Western Asia with the Mediterranean and European world, as well as parts of North and East Africa...
trackway
Trackway
A trackway is an ancient route of travel for people or animals. In biology, a trackway can be a set of impressions in the soft earth, usually a set of footprints, left by an animal. A fossil trackway is the fossilized imprint of a trackway. Trackways have been found all over the world...
of about 2600 kilometres (1,615.6 mi) in length, which connected the ancient Chinese capital of Xi'an
Xi'an
Xi'an is the capital of the Shaanxi province, and a sub-provincial city in the People's Republic of China. One of the oldest cities in China, with more than 3,100 years of history, the city was known as Chang'an before the Ming Dynasty...
to the west over the Wushao Ling Pass to Wuwei and emerged in Kashgar
Kashgar
Kashgar or Kashi is an oasis city with approximately 350,000 residents in the western part of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China. Kashgar is the administrative centre of Kashgar Prefecture which has an area of 162,000 km² and a population of approximately...
.
Istämi
Istämi
Istämi was the ruler of the western part of the Göktürks, the Western Turkic Khaganate and dominated the Sogdians. He was the yabgu of his brother Bumin Qaghan in 553 AD...
of the Göktürks
Göktürks
The Göktürks or Kök Türks, were a nomadic confederation of peoples in medieval Inner Asia. Known in Chinese sources as 突厥 , the Göktürks under the leadership of Bumin Qaghan The Göktürks or Kök Türks, (Old Turkic: Türük or Kök Türük or Türük; Celestial Turks) were a nomadic confederation of...
received the lands of Dzungaria as an inheritance after the death of his father in the latter half of the sixth century AD.
Dzungaria is named after a Mongolian
Mongols
Mongols ) are a Central-East Asian ethnic group that lives mainly in the countries of Mongolia, China, and Russia. In China, ethnic Mongols can be found mainly in the central north region of China such as Inner Mongolia...
kingdom which existed in Central Asia
Central Asia
Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north...
during the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. It derived its name from the Dzungars, who were so called because they formed the left wing (züün, left; gar, hand) of the Mongolian army, self-named Oirats
Oirats
Oirats are the westernmost group of the Mongols who unified several tribes origin whose ancestral home is in the Altai region of western Mongolia. Although the Oirats originated in the eastern parts of Central Asia, the most prominent group today is located in the Republic of Kalmykia, a federal...
. Dzungar power reached its height in the second half of the 17th century, when Kaldan (also known as Galdan Boshigtu Khan), repeatedly intervened in the affairs of the Kazakhs
Kazakhs
The Kazakhs are a Turkic people of the northern parts of Central Asia ....
to the west, but it was completely destroyed by the Qing
Qing Dynasty
The Qing Dynasty was the last dynasty of China, ruling from 1644 to 1912 with a brief, abortive restoration in 1917. It was preceded by the Ming Dynasty and followed by the Republic of China....
government about 1757–1759. It has played an important part in the history of Mongolia
Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East and Central Asia. It is bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east and west. Although Mongolia does not share a border with Kazakhstan, its western-most point is only from Kazakhstan's eastern tip. Ulan Bator, the capital and largest...
and the great migrations of Mongolian stems westward.
Since 1761, its territory fell mostly to the Qing dynasty
Qing Dynasty
The Qing Dynasty was the last dynasty of China, ruling from 1644 to 1912 with a brief, abortive restoration in 1917. It was preceded by the Ming Dynasty and followed by the Republic of China....
(Xinjiang
Xinjiang
Xinjiang is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. It is the largest Chinese administrative division and spans over 1.6 million km2...
and north-western Mongolia) and partly to Russian Turkestan
Russian Turkestan
Russian Turkestan was the western part of Turkestan within the Russian Empire , comprising the oasis region to the south of the Kazakh steppes, but not the protectorates of the Emirate of Bukhara and the Khanate of Khiva.-History:-Establishment:Although Russia had been pushing south into the...
(earlier Kazakh state provinces of Semirechye- Jetysu and Irtysh river).
Its widest limit included Kashgar
Kashgar
Kashgar or Kashi is an oasis city with approximately 350,000 residents in the western part of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China. Kashgar is the administrative centre of Kashgar Prefecture which has an area of 162,000 km² and a population of approximately...
, Yarkand, Khotan
Khotan
Hotan , or Hetian , also spelled Khotan, is the seat of the Hotan Prefecture in Xinjiang, China. It was previously known in Chinese as 于窴/於窴 and to 19th-century European explorers as Ilchi....
, the whole region of the Tian Shan
Tian Shan
The Tian Shan , also spelled Tien Shan, is a large mountain system located in Central Asia. The highest peak in the Tian Shan is Victory Peak , ....
, and in short the greater proportion of that part of Central Asia which extends from 35º to 50º N and from 72º to 97º E.
As a political or geographical term Dzungaria has practically disappeared from the map; but the range of mountains stretching north-east along the southern frontier of the Jeti-su, as the district to the south-east of Lake Balkhash
Lake Balkhash
Lake Balkhash is one of the largest lakes in Asia and 12th largest continental lake in the world. It is located in southeastern Kazakhstan, in Central Asia, and belongs to an endorheic basin shared by Kazakhstan and China, with a small part in Kyrgyzstan. The basin drains into the lake via seven...
preserves the name of Dzungarian Alatau
Dzungarian Alatau
The Dzungarian Alatau is a mountain range that lies on the boundary of Xinjiang region of China and Kazakhstan. The range is named after Dzungaria. Length: cca...
. It also gave name to Dzungarian Hamsters.
Dzungaria and the Silk Road
A traveler going west from China must go either north of the Tien Shan through Dzungaria or south of the Tien Shan through the Tarim Basin. Trade usually took the south side and migrations the north. This is most likely because the Tarim leads to the Ferghana Valley and Iran, while Dzungaria leads only to the open steppe. The difficulty with south side was the high mountains between the Tarim and Ferghana. There is also another reason. The Taklamakan is too dry to support much grass, and therefore nomads when they are not robbing caravans. Its inhabitants live mostly in oases formed where rivers run out of the mountains into the desert. These are inhabited by peasants who are unwarlike and merchants who have an interest in keeping trade running smoothly. Dzungaria has a fair amount of grass, few towns to base soldiers in and no significant mountain barriers to the west. Therefore trade went south and migrations north.People
The population consists of KazakhsKazakhs
The Kazakhs are a Turkic people of the northern parts of Central Asia ....
, Kyrgyz, Mongols
Mongols
Mongols ) are a Central-East Asian ethnic group that lives mainly in the countries of Mongolia, China, and Russia. In China, ethnic Mongols can be found mainly in the central north region of China such as Inner Mongolia...
, Uyghurs
Uyghur people
The Uyghur are a Turkic ethnic group living in Eastern and Central Asia. Today, Uyghurs live primarily in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in the People's Republic of China...
and Han Chinese
Han Chinese
Han Chinese are an ethnic group native to China and are the largest single ethnic group in the world.Han Chinese constitute about 92% of the population of the People's Republic of China , 98% of the population of the Republic of China , 78% of the population of Singapore, and about 20% of the...
. Since 1953 there has been a massive influx of Han Chinese to work on water conservation and industrial projects, especially the Karamay
Karamay
Karamay, Qaramay or Kelamayi is a prefecture-level city in the north of the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, in northwestern China...
oil fields.
Economy
WheatWheat
Wheat is a cereal grain, originally from the Levant region of the Near East, but now cultivated worldwide. In 2007 world production of wheat was 607 million tons, making it the third most-produced cereal after maize and rice...
, barley
Barley
Barley is a major cereal grain, a member of the grass family. It serves as a major animal fodder, as a base malt for beer and certain distilled beverages, and as a component of various health foods...
, oat
Oat
The common oat is a species of cereal grain grown for its seed, which is known by the same name . While oats are suitable for human consumption as oatmeal and rolled oats, one of the most common uses is as livestock feed...
s, and sugar beet
Sugar beet
Sugar beet, a cultivated plant of Beta vulgaris, is a plant whose tuber contains a high concentration of sucrose. It is grown commercially for sugar production. Sugar beets and other B...
s are grown, and cattle
Cattle
Cattle are the most common type of large domesticated ungulates. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae, are the most widespread species of the genus Bos, and are most commonly classified collectively as Bos primigenius...
, sheep, and horse
Horse
The horse is one of two extant subspecies of Equus ferus, or the wild horse. It is a single-hooved mammal belonging to the taxonomic family Equidae. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million years from a small multi-toed creature into the large, single-toed animal of today...
s are raised. The fields are irrigated with melted snow from the permanently white-capped mountains.
Dzungaria has deposits of coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
, iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
, and gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
, as well as large oil field
Oil field
An oil field is a region with an abundance of oil wells extracting petroleum from below ground. Because the oil reservoirs typically extend over a large area, possibly several hundred kilometres across, full exploitation entails multiple wells scattered across the area...
s.

