
E-Z notation
Encyclopedia
E-Z notation, or the E-Z convention, is the IUPAC preferred method
of describing the stereochemistry
of double bond
s in organic chemistry
. It is an extension of cis/trans notation that can be used to describe double bonds having three or four substituent
s.
Following a set of defined rules (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority rules), each substituent on a double bond
is assigned a priority.
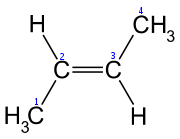
If the two groups of higher priority are on opposite sides of the double bond, the bond is assigned the configuration E (from entgegen, ɛntˈɡeːɡən, the German word for "opposite").
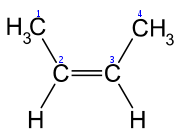
If the two groups of higher priority are on the same side of the double bond, the bond is assigned the configuration Z (from zusammen, tsuˈzamən, the German word for "together").
The letters E and Z are conventionally printed in italic type
, within parentheses, and separated from the rest of the name with a hyphen
. They are always printed as full capitals (not lower case or small capitals), but do not constitute the first letter of the name for English capitalization rules (as in the example above).
IUPAC nomenclature
A chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry ....
of describing the stereochemistry
Stereochemistry
Stereochemistry, a subdiscipline of chemistry, involves the study of the relative spatial arrangement of atoms within molecules. An important branch of stereochemistry is the study of chiral molecules....
of double bond
Double bond
A double bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two chemical elements involving four bonding electrons instead of the usual two. The most common double bond, that between two carbon atoms, can be found in alkenes. Many types of double bonds between two different elements exist, for example in...
s in organic chemistry
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
. It is an extension of cis/trans notation that can be used to describe double bonds having three or four substituent
Substituent
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a substituent is an atom or group of atoms substituted in place of a hydrogen atom on the parent chain of a hydrocarbon...
s.
Following a set of defined rules (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority rules), each substituent on a double bond
Double bond
A double bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two chemical elements involving four bonding electrons instead of the usual two. The most common double bond, that between two carbon atoms, can be found in alkenes. Many types of double bonds between two different elements exist, for example in...
is assigned a priority.
If the two groups of higher priority are on opposite sides of the double bond, the bond is assigned the configuration E (from entgegen, ɛntˈɡeːɡən, the German word for "opposite").
If the two groups of higher priority are on the same side of the double bond, the bond is assigned the configuration Z (from zusammen, tsuˈzamən, the German word for "together").
 |
 |
|
| (E)-But-2-ene | (Z)-But-2-ene |
The letters E and Z are conventionally printed in italic type
Italic type
In typography, italic type is a cursive typeface based on a stylized form of calligraphic handwriting. Owing to the influence from calligraphy, such typefaces often slant slightly to the right. Different glyph shapes from roman type are also usually used—another influence from calligraphy...
, within parentheses, and separated from the rest of the name with a hyphen
Hyphen
The hyphen is a punctuation mark used to join words and to separate syllables of a single word. The use of hyphens is called hyphenation. The hyphen should not be confused with dashes , which are longer and have different uses, or with the minus sign which is also longer...
. They are always printed as full capitals (not lower case or small capitals), but do not constitute the first letter of the name for English capitalization rules (as in the example above).

