
Earplug
Encyclopedia
Ear canal
The ear canal , is a tube running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The human ear canal extends from the pinna to the eardrum and is about 35 mm in length and 5 to 10 mm in diameter....
to protect the wearer's ears from loud noises or the intrusion of water, foreign bodies, dust or excessive wind.
Protection from water
Some earplugs are primarily designed to keep water out of the ear canal, especially during swimming and watersports. These may be made of waxWax
thumb|right|[[Cetyl palmitate]], a typical wax ester.Wax refers to a class of chemical compounds that are plastic near ambient temperatures. Characteristically, they melt above 45 °C to give a low viscosity liquid. Waxes are insoluble in water but soluble in organic, nonpolar solvents...
or moldable silicone
Silicone
Silicones are inert, synthetic compounds with a variety of forms and uses. Typically heat-resistant and rubber-like, they are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medical applications , cookware, and insulation....
which is custom-fitted to the ear canal by the wearer.
Exostosis, or Surfer's ear
Surfer's Ear
Surfer's ear is the common name for an exostosis or abnormal bone growth within the ear canal. Surfer's ear is not the same as swimmer's ear, although infection can result as a side effect....
, is common among those who spend large amounts of time in water in areas with cold climates. In addition, wind may increase the prevalence of the amount of exostosis seen in one ear versus the other dependent on the direction it originates from and the orientation of the individual to the wind. Custom-fitted surfer's earplugs help reduce the amount of cold water and wind that is allowed to enter the external ear canal and, thus, would help slow the progression of exostosis.
A 2003 study published in Clinical Otolaryngology found that a cotton ball saturated with petroleum jelly was more effective at keeping water out of the ear, easier to use, and more comfortable than wax plugs, foam plugs, EarGuard, or Aquafit.
As many have advised, including Jacques-Yves Cousteau
Jacques-Yves Cousteau
Jacques-Yves Cousteau was a French naval officer, explorer, ecologist, filmmaker, innovator, scientist, photographer, author and researcher who studied the sea and all forms of life in water...
, ear plugs are actually harmful to divers, especially scuba divers
Scuba diving
Scuba diving is a form of underwater diving in which a diver uses a scuba set to breathe underwater....
. Scuba divers breathe compressed air or other gas mixtures, at a pressure matching the water pressure. This pressure is also inside the ear, but not between the eardrum and the earplug, so the pressure behind the eardrum will often burst the eardrum. Skin divers have less pressure inside the ears, but they also have only atmospheric pressure in the outer ear canal. Vented earplugs are the only type of earplug which can be used by divers safely.
Hearing protection
There are mainly three types of earplugs for hearing protection:- Foam earplugs, mainly made of memory foamMemory foamMemory foam is polyurethane with additional chemicals increasing its viscosity and density. It is often referred to as "visco-elastic" polyurethane foam, or low-resilience polyurethane foam . Higher-density memory foam softens in reaction to body heat, allowing it to mold to a warm body in a few...
, which are compressed and put into the ear canal, where they expand to plug it. - Silicone earplugs, which are rolled into a ball and carefully molded to fit over the external portion of the ear canal, providing a snug custom fit for the wearer.
- Flanged earplugs, including most types of musicians' or 'Hi-Fi' earplugs, as well as custom molds once they are molded.
NIOSH Mining Safety and Health Research recommends using the roll, pull, and hold method when using memory foam earplugs. The process involves the user rolling the earplug into a thin rod, pulling back on the ear, and holding the earplug deep in the canal
Ear canal
The ear canal , is a tube running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The human ear canal extends from the pinna to the eardrum and is about 35 mm in length and 5 to 10 mm in diameter....
with the finger. To get a complete seal, the user must wait about 20 seconds for the earplug to expand inside the canal.
Furthermore, they may be either disposable or nondisposable, with foam and silicone ones generally being disposable or for use a relatively limited number of times, while solid ones generally may be regarded as nondisposable. A variation of the traditional foam earplug is the no-roll foam earplug that uses a built-in central stem to push the foam plugs into the ears. These earplugs achieve a seal due to their tapered shape, rather than expansion after being rolled.
Ear plugs are especially useful to people exposed to excessively noisy devices or environments (80 dB or more).
| Level of noise in dB(A) | Maximum daily exposure time |
|---|---|
| 85 | 8 Hours |
| 91 | 2 Hours |
| 97 | 30 Minutes |
| 103 | 7 Minutes |
History
The first recorded use of wax earplugs is in the OdysseyOdyssey
The Odyssey is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is, in part, a sequel to the Iliad, the other work ascribed to Homer. The poem is fundamental to the modern Western canon, and is the second—the Iliad being the first—extant work of Western literature...
, wherein Odysseus
Odysseus
Odysseus or Ulysses was a legendary Greek king of Ithaca and the hero of Homer's epic poem the Odyssey. Odysseus also plays a key role in Homer's Iliad and other works in the Epic Cycle....
's crew used wax earplugs to avoid being distracted by the Siren
Siren
In Greek mythology, the Sirens were three dangerous mermaid like creatures, portrayed as seductresses who lured nearby sailors with their enchanting music and voices to shipwreck on the rocky coast of their island. Roman poets placed them on an island called Sirenum scopuli...
s' songs.
In 1907, the German company Ohropax, which produced earplugs, was started by German inventor Max Negwer.
Current earplug material was discovered in 1967, at National Research in the USA by Ross Gardner and his team. As part of a project on sealing joints, they developed a resin with energy absorption properties. This E-A-R material was later developed into commercial memory foam
Memory foam
Memory foam is polyurethane with additional chemicals increasing its viscosity and density. It is often referred to as "visco-elastic" polyurethane foam, or low-resilience polyurethane foam . Higher-density memory foam softens in reaction to body heat, allowing it to mold to a warm body in a few...
earplugs.
'Basic' type plugs
Industrial noise
Industrial noise is usually considered mainly from the point of view of environmental health and safety, rather than nuisance, as sustained exposure can cause permanent hearing damage. Traditionally, occupational noise has been a hazard linked to heavy industries such as ship-building and...
for long periods, and is used by the British Ministry of Defense (MoD) for soldier
Soldier
A soldier is a member of the land component of national armed forces; whereas a soldier hired for service in a foreign army would be termed a mercenary...
s to use when firing weapons. Earplugs are rated for their ability to reduce noise. In the United States, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency mandates that hearing protection be tested to provide a Noise Reduction Rating (NRR) where a panel of ten subjects are tested in a laboratory to determine the attenuation over a range of frequencies. In the European Union, hearing protectors are required to be tested according to the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) acoustical testing standard, ISO 4869 Part 1 and the Single Number Rating (SNR) or High/Middle/Low (HML) ratings are calculated according to ISO 4869 Part 2. In Brazil, hearing protectors are tested according to the American National Standards Institute ANSI S12.6-1997 and are rated using the Noise Reduction Rating Subject Fit NRR(SF). Australia and New Zealand have different standards for protector ratings yielding a quantity SLC80 (Sound Level Class for the 80th percentile). Canada implements a class system for rating the performance of protectors. Gauger and Berger have reviewed the merits of several different rating methods and developed a rating system that is the basis of a new American National Standard, ANSI S12.68-2007
The various methods have slightly different interpretations, however, each method has an effective percentile associated with the rating for which that percent of the users should be able to achieve the rated attenuation. For instance the NRR is determined by the mean attenuation minus two standard deviations, thus it translates to a 98% statistic. That is at least 98 percent of users should be able to achieve that level of attenuation. The SNR and HML are a mean minus one standard deviation statistic. Therefore, approximately 86% of the users should be able to achieve that level of protection. Similarly, the NRR(SF) is a mean minus one standard deviation and represents an 86% of users should achieve that level of protection. The difference between the ratings lies in how the protectors are tested. NRR is tested with an experimenter-fit protocol. SNR/HML are tested with an experienced subject-fit protocol. NRR(SF) is tested with a naive subject-fit protocol. According to Murphy et al. (2004), these three protocols will yield different amounts of attenuation with the NRR being the greatest and NRR(SF) being the least.
The experimenter-fit NRR should be adjusted per the guidelines of the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health as the required NRR ratings differ greatly from lab tests to field tests.
The NRR(SF) used in Brazil does not require derating as it resembles the manner in which the typical user will wear hearing protection.
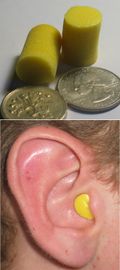
Most earplugs are elastic ones made of memory foam
Memory foam
Memory foam is polyurethane with additional chemicals increasing its viscosity and density. It is often referred to as "visco-elastic" polyurethane foam, or low-resilience polyurethane foam . Higher-density memory foam softens in reaction to body heat, allowing it to mold to a warm body in a few...
, that is typically rolled into a tightly compressed cylinder (without creases) by the wearer's fingers and then inserted in the ear canal. Once released, the earplug expands until it seals the canal, blocking the sound vibrations that could reach the eardrum
Eardrum
The eardrum, or tympanic membrane, is a thin membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear in humans and other tetrapods. Its function is to transmit sound from the air to the ossicles inside the middle ear. The malleus bone bridges the gap between the eardrum and the other ossicles...
. Other plugs simply push into the ear canal without being rolled first. Sometimes earplugs are connected with a cord to keep them together when not in use. Other common material bases for earplugs are viscous wax
Wax
thumb|right|[[Cetyl palmitate]], a typical wax ester.Wax refers to a class of chemical compounds that are plastic near ambient temperatures. Characteristically, they melt above 45 °C to give a low viscosity liquid. Waxes are insoluble in water but soluble in organic, nonpolar solvents...
or silicone
Silicone
Silicones are inert, synthetic compounds with a variety of forms and uses. Typically heat-resistant and rubber-like, they are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medical applications , cookware, and insulation....
.
Other devices that provide hearing protection include electronic devices worn around and/or in the ear, designed to cancel out the loud noise of a gunshot, while possibly amplifying quieter sounds to normal levels. While rich in features, these electronic devices carry a price over one hundred times that of their foam counterparts.
Since they reduce the sound volume, earplugs are often used to help prevent hearing loss and tinnitus
Tinnitus
Tinnitus |ringing]]") is the perception of sound within the human ear in the absence of corresponding external sound.Tinnitus is not a disease, but a symptom that can result from a wide range of underlying causes: abnormally loud sounds in the ear canal for even the briefest period , ear...
(ringing of the ears), amongst other ailments.
Noise reduction ratings
Hearing protectors sold in the U.S. are required by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to have a noise reduction rating (NRR), which is an estimate of the reduction of noise at the ear when protectors are worn properly. However, due to the discrepancy between how protectors are fit in the testing laboratory and how users wear protectors in the real world, the Occupational Safety and Health AdministrationOccupational Safety and Health Administration
The United States Occupational Safety and Health Administration is an agency of the United States Department of Labor. It was created by Congress of the United States under the Occupational Safety and Health Act, signed by President Richard M. Nixon, on December 29, 1970...
(OSHA) and the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health is the United States’ federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related injury and illness. NIOSH is part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention within the U.S...
(NIOSH) have developed derating formulas to reduce the effective NRR.
While the NRR and the SNR (Single Number Rating) are designed to be used with C-weighted
A-weighting
A Weighting curve is a graph of a set of factors, that are used to 'weight' measured values of a variable according to their importance in relation to some outcome. The most commonly known example is frequency weighting in sound level measurement where a specific set of weighting curves known as A,...
noise, which means that the lower frequencies are not de-emphasized, other ratings (NRR(SF) and NRSA) are determined for use with A-weighted
A-weighting
A Weighting curve is a graph of a set of factors, that are used to 'weight' measured values of a variable according to their importance in relation to some outcome. The most commonly known example is frequency weighting in sound level measurement where a specific set of weighting curves known as A,...
noise levels, which have lower frequencies de-emphasized. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health recommended and the U.S. EPA mandated that 7-dB compensation between C and A weighting be applied when the NRR is used with A-weighted noise levels.
OSHA has defined in their training manual for inspectors that the adequacy of hearing protection for use in a hazardous noise environment should be derated to account for how workers typically wear protection relative to how manufacturers test the protector's attenuation in the laboratory. For all types of hearing protection, OSHA’s derating factor is 50%. If used with C-weighted noise, the derated NRR will become NRR/2. If used with A-weighted noise, OSHA applies the 7-dB adjustment for C-A weighting first then derates the remainder. For example, a protector with 33-dB attenuation would have this derating:
- Derated NRR = (33 – 7)/2
NIOSH has proposed a different method for derating based upon the type of protector. For earmuffs
Earmuffs
Earmuffs are objects designed to cover a person's ears for protection. They consist of a thermoplastic or metal head-band, that fits over the top of the head, and a pad at each end, to cover the external ears....
, the NRR should be derated by 25%, for slow-recovery foam earplugs the derating is 50% for all other protection, the derating is 70%. NIOSH applies the C-A spectral compensation differently than OSHA. Where OSHA subtracts the 7-dB factor first and derates the result, NIOSH derates the NRR first and then compensates for the C-A difference. For example, to find the derated NRR for an earmuff by using the NIOSH derating system, the following equation would be used:
- Derated NRR = (Original NRR x (1-.25)) – 7
Expected updates
In 2007, the American National Standards InstituteAmerican National Standards Institute
The American National Standards Institute is a private non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organization also coordinates U.S. standards with international...
published a new standard for noise reduction ratings for hearing protectors, ANSI S12.68-2007. Using the real ear attenuation at threshold data collected by a laboratory test prescribed in ANSI S12.6-2008, the noise reduction statistic for A-weighted noise (NRSA) is computed using a set of 100 noises listed in the standard. The noise reduction rating, rather than be computed for a single noise spectrum the NRSA incorporates variability of both subject and spectral effects. ANSI S12.68 also defines a method to estimate the performance of a protector in an atypical noise environment. Building upon work from the U.S. Air Force and the ISO 4869-2 standard, the protector's attenuation as a function of the difference in C and A-weighted noise level is used to predict typical performance in that noise environment. The derating may be quite severe (10 to 15 decibels) for protectors that have significant differences between low and high frequency attenuation. For "flat" attenuation protectors, the effect of C-A is less. This new system eliminates the need for calculators, relies on graphs and databases of empirical data, and is believed to be a more accurate system for determining NRRs.
Musicians' or 'Hi-Fi' earplugs

Musician
A musician is an artist who plays a musical instrument. It may or may not be the person's profession. Musicians can be classified by their roles in performing music and writing music.Also....* A person who makes music a profession....
s who perform music styles noted for their loud nature, especially rock music
Rock music
Rock music is a genre of popular music that developed during and after the 1960s, particularly in the United Kingdom and the United States. It has its roots in 1940s and 1950s rock and roll, itself heavily influenced by rhythm and blues and country music...
, often wear earplugs to prevent their own performances from damaging their hearing. Musicians' earplugs are designed to attenuate sounds evenly across the audio
Audio frequency
An audio frequency or audible frequency is characterized as a periodic vibration whose frequency is audible to the average human...
band and thus minimise their effect on the user's perception of bass and treble
Treble (sound)
Treble refers to tones of high frequency or range. In music this corresponds to high notes, and for this reason the treble clef is often used for instruments with higher pitch. Examples of treble sounds are guitar tones, female voice , young boy voice, etc. They have frequencies above 9 KHz. Treble...
levels. These are commonly used by musicians and technicians, both in the studio and in concert, to avoid overexposure to high volume levels.

Diaphragm (acoustics)
In the field of acoustics, a diaphragm is a transducer intended to faithfully inter-convert mechanical motion and sound. It is commonly constructed of a thin membrane or sheet of various materials. The varying air pressure of the sound waves imparts vibrations onto the diaphragm which can then be...
to reduce low frequencies, together with absorbent or damping material for high frequencies. This means they can be quite costly, being intended for constant re-use unlike simple earplugs which are disposable. These earplugs usually give an attenuation of only about 20dB and are not intended for protection from very high noise levels (beyond 105 dB).
_er-25_-_musician_earplug_worn.jpg)
In other activities, hobby motorcyclists and skiers may also choose to use decibel reduction earplugs, to compensate for the ongoing noise of the wind against their head or helmet.
Flight ear protection
Earplugs are available which help to protect ears from the pain caused by airplane cabin pressure changes. Some products contain a porous ceramic insert which reportedly aids equalization of air pressure between the middle and outer ear thereby preventing pain during landings and take-offs.Sleep
Earplugs for sleeping are made to be as comfortable as possible while blocking external sounds that may prevent or disrupt sleep. Specialized earplugs for such noises as a partner's snoringSnoring
Snoring is the vibration of respiratory structures and the resulting sound, due to obstructed air movement during breathing while sleeping. In some cases the sound may be soft, but in other cases, it can be loud and unpleasant...
may have sound-dampening enhancements that enable the user to still hear other noises, such as an alarm clock.
To determine the comfort of earplugs used for sleeping, it is important to try them on while actually lying down. The pressure on the ear between the head and pillow may cause significant discomfort. Furthermore, just tilting the head back or to the side causes significant anatomical changes in the ear canal, mostly a reduction of the ear canal diameter, which may reduce comfort if the earplug is too large.
Health risks
Earplugs are generally safe, but precautions may be needed against a number of possible health risks, with additional ones appearing with long term use:- Pushing in earplugs into the external ear canal may cause the air pressure to rise in it, in effect pushing against the eardrum and causing pain. This may be caused by pressure on the ear while lying down on the side, and is also the case when completely expanded foam earplugs are pushed further into the ear. To bypass the latter risk, such earplugs are instead removed, compressed and inserted to the desired depth. Vice versa, when pulled out, the resultant negative pressure pulls the eardrum. Therefore, some earplugs are better carefully screwed or jiggled out rather than yanked out. Yawning does not help equalizing this air pressure difference, since it equalizes the pressures between the middle ear and the environment, while this overpressure rather is located in the outer ear, between the eardrum and the earplug.
- If pushed too far into the ear canal, they may push ear wax and debris into the canal and possibly against the ear drum. As a precaution, ear plugs should not be pushed further into the ear canal than they may be grabbed and rotated. Ear wax impacted by earplugs can be removed by irrigation or other remedies, as described there.
- There is a possibility for allergic reactions, but this is likely rare, as earplugs generally are made of immunologically inert materials.
Long-term use
Custom molded plugs are recommended for long-term use, since they are more comfortable and gentle to the skin and won't go too far into the ear canal.Nevertheless, prolonged or frequently repeated use of ear plugs have the following health risks, in addition to the short term health risks:
- They may cause earwaxEarwaxEarwax, also known by the medical term cerumen, is a yellowish waxy substance secreted in the ear canal of humans and other mammals. It protects the skin of the human ear canal, assists in cleaning and lubrication, and also provides some protection from bacteria, fungi, insects and water...
to build up and plug the outer earOuter earThe outer ear is the external portion of the ear, which consists of the pinna, concha, and external auditory meatus. It gathers sound energy and focuses it on the eardrum . One consequence of the configuration of the external ear is to selectively boost the sound pressure 30- to 100-fold for...
, since it blocks the normal flow of earwax outwards. This can result in tinnitusTinnitusTinnitus |ringing]]") is the perception of sound within the human ear in the absence of corresponding external sound.Tinnitus is not a disease, but a symptom that can result from a wide range of underlying causes: abnormally loud sounds in the ear canal for even the briefest period , ear...
, hearing loss, discharge, pain or infection. Excess earwax should be carefully removed from the ear, and earplugs should be cleaned regularly with water and mild soap. However, foam type ear plugs are usually designed to be disposable, and will expand and lose their memory property upon drying after washing with water and soap. They will become quite spongy, expand very quickly after being compressed, making them quite problematic in proper insertion into the ear canal. They also lose a large proportion of sound attenuating capability after such washing and drying. - They may cause irritation of the temporomandibular jointTemporomandibular jointThe temporomandibular joint is the joint of the jaw and is frequently referred to as TMJ. There are two TMJs, one on either side, working in unison. The name is derived from the two bones which form the joint: the upper temporal bone which is part of the cranium , and the lower jaw bone called the...
, which is located very close to the ear canal, causing pain. Individually fitted non-elastic earplugs may be less likely to cause this irritation compared with foam ones that expand inside the ear canal. - Earplugs are also a possible cause of ear inflammation, otitis externaOtitis externaOtitis externa is an inflammation of the outer ear and ear canal. Along with otitis media, external otitis is one of the two human conditions commonly called "earache". It also occurs in many other species. Inflammation of the skin of the ear canal is the essence of this disorder...
, although the short term use of earplugs when swimming and shampooing hair may actually help prevent it. Still, many pathogenic bacteriaPathogenic bacteriaPathogenic bacteria are bacteria that cause bacterial infection. This article deals with human pathogenic bacteria.Although the vast majority of bacteria are harmless or beneficial, quite a few bacteria are pathogenic...
grow well on warm, moist, foam-type plugs (polyvinylchloride (PVC) or polyurethane). However, there need also be a loss of integrity of the skin for infection to occur. Hard and poorly fitting ear plugs can scratch the skin of the ear canal and set off an episode. When earplugs are used during an acute episode, disposable plugs are recommended, or used plugs must be cleaned and dried properly to avoid contaminating the healing ear canal with infected discharge.
Custom molds
Noise and decibel reduction earplugs can be molded to fit an individual's ear canalEar canal
The ear canal , is a tube running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The human ear canal extends from the pinna to the eardrum and is about 35 mm in length and 5 to 10 mm in diameter....
. This is associated with a higher cost, but can help to reduce the discomfort typically experienced after longer use, or if the level of protection or performance is inadequate.
Pressure and flight earplug molds are less common, as they are typically not used as long as other earplugs, and are therefore less in demand.
For best results they are molded in the ear while in the position that they will be used. For instance, if they are to be used for sleeping then they should be molded in the ear while lying down, as different positioning of the jaws causes significant changes to the form of the ear canal, mostly a reduction of the diameter, risking the sleep earplug to be made too large otherwise. These changes can be felt by feeling with a finger just at the entrance to the ear canal while moving the jaws sideways, up and down or anterior and posterior.
Most moulded earplugs are made from silicon but other materials may be used including thermoplastics
See also
- HeadphonesHeadphonesHeadphones are a pair of small loudspeakers, or less commonly a single speaker, held close to a user's ears and connected to a signal source such as an audio amplifier, radio, CD player or portable Media Player. They are also known as stereophones, headsets or, colloquially, cans. The in-ear...
- EarmuffsEarmuffsEarmuffs are objects designed to cover a person's ears for protection. They consist of a thermoplastic or metal head-band, that fits over the top of the head, and a pad at each end, to cover the external ears....
- Noise-induced hearing loss
- Plug (jewellery)Plug (jewellery)A plug , in the context of body modification, is a short, cylindrical piece of jewellery commonly worn in larger-gauge body piercings. Because of their size—which is often substantially thicker than a standard wire earring—plugs can be made out of almost any material...
, also called an earplug
External links
- Don't lose the music campaign website
- Royal National Institute for Deaf people
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health - Hearing Protector Device Compendium
- Earplug Reviews
- Earplug Information Center - Learn About Ear Plugs For Hearing Protection and Noise Reduction
- What are the Best Ear Plugs for Musicians?
- Why Swimmers use ear plugs

