Eastern Wu
Encyclopedia
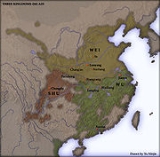
Eastern Wu, also known as Sun Wu, was one the three states competing for control of China
during the Three Kingdoms
period after the fall of the Han Dynasty
. It was based in the Jiangnan
(Yangtze River Delta
) region of China. During its existence, its capital was at Jianye (建業; present-day Nanjing
, Jiangsu
), but at times it was also at Wuchang (武昌; present-day Ezhou
, Hubei
).
, the Wu region
- in the south of the Yangtze River
surrounding present-day Nanjing
- was under the control of the warlord Sun Quan
. Sun Quan succeeded his brother Sun Ce
as the lord over the Wu region paying nominal allegiance to Emperor Xian of Han
(who was, at that point, under the control of Cao Cao
). Unlike his competitors, he did not really have the ambition to be Emperor of China
. However, after Cao Pi
of Cao Wei
and Liu Bei
of Shu Han
each declared themselves emperor, Sun Quan decided to follow suit in 229, claiming to have founded the Wu Dynasty.
Sun Quan's long reign resulted in the stabilizing of the south. Wu and Shu had a military alliance, to defeat Wei in the north. Wu never managed to gain territory north of the Yangtze River, but Wei never managed to take territory south of the river.
Wu was finally conquered
by the Jin Dynasty
in 280, which marked the reunification of China at the end of the Three Kingdoms
period.
region, regarded in early history as a barbaric "jungle" developed into one of the commercial, cultural, and political centers of China. Within five centuries, during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period
, the development of southern China centered around Jiangnan had surpassed that of the north. The achievements of Wu marked the beginning of the cultural and political division between northern and southern China that would repeatedly appear in Chinese history well into modernity.
The island of Taiwan
may have been first reached by the Chinese during the Three Kingdoms period. Contact with the native population and the dispatch of officials to an island named "Yizhou" (夷州) by the Wu navy might have been to Taiwan, but the location of Yizhou is open to dispute; some historians believe it was Taiwan, while others believe it was the Ryukyu Islands
.
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
during the Three Kingdoms
Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms period was a period in Chinese history, part of an era of disunity called the "Six Dynasties" following immediately the loss of de facto power of the Han Dynasty rulers. In a strict academic sense it refers to the period between the foundation of the state of Wei in 220 and the...
period after the fall of the Han Dynasty
Han Dynasty
The Han Dynasty was the second imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Qin Dynasty and succeeded by the Three Kingdoms . It was founded by the rebel leader Liu Bang, known posthumously as Emperor Gaozu of Han. It was briefly interrupted by the Xin Dynasty of the former regent Wang Mang...
. It was based in the Jiangnan
Jiangnan
Jiangnan or Jiang Nan is a geographic area in China referring to lands immediately to the south of the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, including the southern part of the Yangtze Delta...
(Yangtze River Delta
Yangtze River Delta
The Yangtze River Delta, Yangtze Delta or YRD, also called Yangzi, or Chang Jiang Delta, Rive Chang Delta Tai Lake Region or the Golden Triangle of the Yangtze, generally comprises the triangular-shaped territory of Wu-speaking Shanghai, southern Jiangsu province and northern Zhejiang province of...
) region of China. During its existence, its capital was at Jianye (建業; present-day Nanjing
Nanjing
' is the capital of Jiangsu province in China and has a prominent place in Chinese history and culture, having been the capital of China on several occasions...
, Jiangsu
Jiangsu
' is a province of the People's Republic of China, located along the east coast of the country. The name comes from jiang, short for the city of Jiangning , and su, for the city of Suzhou. The abbreviation for this province is "苏" , the second character of its name...
), but at times it was also at Wuchang (武昌; present-day Ezhou
Ezhou
-Geography and climate:Ezhou is located in southeastern Hubei province, on the southern bank of the Yangtze River east of Wuchang , and across the river from the city of Huanggang, to which it is connected by the Ehuang Bridge...
, Hubei
Hubei
' Hupeh) is a province in Central China. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Lake Dongting...
).
History
During the final years of the Han DynastyHan Dynasty
The Han Dynasty was the second imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Qin Dynasty and succeeded by the Three Kingdoms . It was founded by the rebel leader Liu Bang, known posthumously as Emperor Gaozu of Han. It was briefly interrupted by the Xin Dynasty of the former regent Wang Mang...
, the Wu region
Wu (region)
Wu is a region in the Jiangnan area , surrounding Suzhou, in Jiangsu province and Zhejiang province of China. It is also the abbreviation of several kingdoms based in Wu. The two largest cities in the Wu region today are Shanghai and Hangzhou...
- in the south of the Yangtze River
Yangtze River
The Yangtze, Yangzi or Cháng Jiāng is the longest river in Asia, and the third-longest in the world. It flows for from the glaciers on the Tibetan Plateau in Qinghai eastward across southwest, central and eastern China before emptying into the East China Sea at Shanghai. It is also one of the...
surrounding present-day Nanjing
Nanjing
' is the capital of Jiangsu province in China and has a prominent place in Chinese history and culture, having been the capital of China on several occasions...
- was under the control of the warlord Sun Quan
Sun Quan
Sun Quan , son of Sun Jian, formally Emperor Da of Wu, was the founder of Eastern Wu during the Three Kingdoms period of Chinese history. He ruled from 222 to 229 as King of Wu and from 229 to 252 as Emperor of Wu....
. Sun Quan succeeded his brother Sun Ce
Sun Ce
Sun Ce was a military general and warlord during the late Han Dynasty period of Chinese history. He was the oldest of the children of Sun Jian who was killed during the Battle of Xiangyang when Sun Ce was only 16. Sun Ce then broke away from his father's overlord, Yuan Shu, and headed to...
as the lord over the Wu region paying nominal allegiance to Emperor Xian of Han
Emperor Xian of Han
Emperor Xian of Han , personal name Liu Xie, style name Bohe, was the last emperor of the Han Dynasty period of Chinese history...
(who was, at that point, under the control of Cao Cao
Cao Cao
Cao Cao was a warlord and the penultimate chancellor of the Eastern Han Dynasty who rose to great power during the dynasty's final years. As one of the central figures of the Three Kingdoms period, he laid the foundations for what was to become the state of Cao Wei and was posthumously titled...
). Unlike his competitors, he did not really have the ambition to be Emperor of China
Emperor of China
The Emperor of China refers to any sovereign of Imperial China reigning between the founding of Qin Dynasty of China, united by the King of Qin in 221 BCE, and the fall of Yuan Shikai's Empire of China in 1916. When referred to as the Son of Heaven , a title that predates the Qin unification, the...
. However, after Cao Pi
Cao Pi
Cao Pi , formally known as Emperor Wen of Wei, was the first emperor of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of Chinese history. Born in Qiao County, Pei Commandery , he was the second son of the late Han Dynasty warlord Cao Cao.Cao Pi, like his father, was a poet...
of Cao Wei
Cao Wei
Cao Wei was one of the states that competed for control of China during the Three Kingdoms period. With the capital at Luoyang, the state was established by Cao Pi in 220, based upon the foundations that his father Cao Cao laid...
and Liu Bei
Liu Bei
Liu Bei , also known as Liu Xuande, was a warlord, military general and later the founding emperor of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms era of Chinese history...
of Shu Han
Shu Han
Shu Han was one of the three states competing for control of China during the Three Kingdoms period, after the fall of the Han Dynasty. The state was based on areas around Sichuan, which was then known as Shu...
each declared themselves emperor, Sun Quan decided to follow suit in 229, claiming to have founded the Wu Dynasty.
Sun Quan's long reign resulted in the stabilizing of the south. Wu and Shu had a military alliance, to defeat Wei in the north. Wu never managed to gain territory north of the Yangtze River, but Wei never managed to take territory south of the river.
Wu was finally conquered
Conquest of Wu by Jin
The conquest of Wu by Jin was a military campaign launched by the Jin Dynasty against the state of Eastern Wu in 280 towards the end of the Three Kingdoms period of Chinese history...
by the Jin Dynasty
Jìn Dynasty (265-420)
The Jìn Dynasty , was a dynasty in Chinese history, lasting between the years 265 and 420 AD. There are two main divisions in the history of the Dynasty, the first being Western Jin and the second Eastern Jin...
in 280, which marked the reunification of China at the end of the Three Kingdoms
Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms period was a period in Chinese history, part of an era of disunity called the "Six Dynasties" following immediately the loss of de facto power of the Han Dynasty rulers. In a strict academic sense it refers to the period between the foundation of the state of Wei in 220 and the...
period.
Legacy
Under the rule of Wu, the Yangtze River DeltaYangtze River Delta
The Yangtze River Delta, Yangtze Delta or YRD, also called Yangzi, or Chang Jiang Delta, Rive Chang Delta Tai Lake Region or the Golden Triangle of the Yangtze, generally comprises the triangular-shaped territory of Wu-speaking Shanghai, southern Jiangsu province and northern Zhejiang province of...
region, regarded in early history as a barbaric "jungle" developed into one of the commercial, cultural, and political centers of China. Within five centuries, during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period
Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period
Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms was between 907–960/979 AD and an era of political upheaval in China, between the fall of the Tang Dynasty and the founding of the Song Dynasty. During this period, five dynasties quickly succeeded one another in the north, and more than 12 independent states were...
, the development of southern China centered around Jiangnan had surpassed that of the north. The achievements of Wu marked the beginning of the cultural and political division between northern and southern China that would repeatedly appear in Chinese history well into modernity.
The island of Taiwan
Taiwan
Taiwan , also known, especially in the past, as Formosa , is the largest island of the same-named island group of East Asia in the western Pacific Ocean and located off the southeastern coast of mainland China. The island forms over 99% of the current territory of the Republic of China following...
may have been first reached by the Chinese during the Three Kingdoms period. Contact with the native population and the dispatch of officials to an island named "Yizhou" (夷州) by the Wu navy might have been to Taiwan, but the location of Yizhou is open to dispute; some historians believe it was Taiwan, while others believe it was the Ryukyu Islands
Ryukyu Islands
The , also known as the , is a chain of islands in the western Pacific, on the eastern limit of the East China Sea and to the southwest of the island of Kyushu in Japan. From about 1829 until the mid 20th century, they were alternately called Luchu, Loochoo, or Lewchew, akin to the Mandarin...
.
List of territories
| Province | Provincial capital | Commandery | Commandery capital | No. of counties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yang 揚 |
Jianye 建業 |
Danyang 丹陽 |
Jianye 建業 |
16 |
| Wu 吳 |
Wu County 吳縣 |
10 | ||
| Qichun 蘄春 |
Qichun 蘄春 |
2 | ||
| Kuaiji 會稽 |
Shanyin County 山陰縣 |
10 | ||
| Yuzhang 豫章 |
Nanchang 南昌 |
16 | ||
| Lujiang 廬江 |
Wan County 皖縣 |
2 | ||
| Luling 廬陵 |
Gaochang County 高昌縣 |
10 | ||
| Poyang 鄱陽 |
Poyang County 鄱陽縣 |
9 | ||
| Xindu 新都 |
Shixin County 始新縣 |
6 | ||
| Linchuan 臨川 |
Nancheng County 南城縣 |
10 | ||
| Linhai 臨海 |
Zhang'an County 章安縣 |
7 | ||
| Jian'an 建安 |
Jian'an County 建安縣 |
9 | ||
| Wuxing 吳興 |
Wucheng County 烏程縣 |
9 | ||
| Dongyang 東陽 |
Changshan County 長山縣 |
9 | ||
| Piling 毗陵典農校尉 |
Piling County 毗陵縣 |
3 | ||
| South Luling 廬陵南部都尉 |
Yudu County 雩都縣 |
6 | ||
| Jing 荊 |
Jiangling 江陵 |
Nan 南 |
Jiangling 江陵 |
9 |
| Wuling 武陵 |
Linyuan County 臨沅縣 |
11 | ||
| Lingling 零陵 |
Quanling County 泉陵縣 |
10 | ||
| Guiyang 桂陽 |
Chen County 郴縣 |
6 | ||
| Changsha 長沙 |
Linxiang County 臨湘縣 |
10 | ||
| Wuchang 武昌 |
Wuchang County 武昌縣 |
6 | ||
| Ancheng 安成 |
Ancheng County 安成縣 |
6 | ||
| Pengze 彭澤 |
Pengze County 彭澤縣 |
4 | ||
| Yidu 宜都 |
Yidao County 夷道縣 |
3 | ||
| Linhe 臨賀 |
Linhe County 臨賀縣 |
6 | ||
| Hengyang 衡陽 |
Xiangnan County 湘南縣 |
10 | ||
| Xiangdong 湘東 |
Ling County 酃縣 |
6 | ||
| Jianping 建平 |
Wu County 巫縣 |
6 | ||
| Tianmen 天門 |
Lüzhong County 漊中縣 |
3 | ||
| Zhaoling 昭陵 |
Zhaoling County 昭陵縣 |
5 | ||
| Shi'an 始安 |
Shi'an County 始安縣 |
7 | ||
| Shixing 始興 |
Qujiang County 曲江縣 |
7 | ||
| Guang 廣 |
Panyu 番禺 |
Nanhai 南海 |
Panyu County 番禺縣 |
6 |
| Cangwu 蒼梧 |
Guangxin County 廣信縣 |
11 | ||
| Yulin 鬱林 |
Bushan County 布山縣 |
9 | ||
| Gaoliang 高涼 |
Siping County 思平縣 |
3 | ||
| Gaoxing 高興 |
Guanghua County 廣化縣 |
5 | ||
| Guilin 桂林 |
Wu'an County 武安縣 |
6 | ||
| North Hepu 合浦北部尉 |
Anguang County 安廣縣 |
3 | ||
| Jiao 交 |
Longbian 龍編 |
Jiaozhi 交阯 |
Longbian 龍編 |
14 |
| Rinan 日南 |
Zhuwu 朱吾 |
5 | ||
| Jiuzhen 九真 |
Xupu 胥浦 |
6 | ||
| Hepu 合浦 |
Hepu County 合浦縣 |
5 | ||
| Wuping 武平 |
Wuning 武寧 |
7 | ||
| Jiude 九德 |
Jiude 九德 |
6 | ||
| Xinchang 新昌 |
Jianing 嘉寧 |
4 | ||
| Zhuya 朱崖 |
Xuwen County 徐聞縣 |
2 |
List of sovereigns
| Posthumous name Posthumous name A posthumous name is an honorary name given to royalty, nobles, and sometimes others, in East Asia after the person's death, and is used almost exclusively instead of one's personal name or other official titles during his life... s |
Family (in bold) name Chinese surname Chinese family names have been historically used by Han Chinese and Sinicized Chinese ethnic groups in mainland China, Taiwan, Hong Kong, and among overseas Chinese communities. In ancient times two types of surnames, family names and clan names , existed.The colloquial expressions laobaixing... and first names Chinese name Personal names in Chinese culture follow a number of conventions different from those of personal names in Western cultures. Most noticeably, a Chinese name is written with the family name first and the given name next, therefore "John-Paul Smith" as a Chinese name would be "Smith John-Paul"... |
Year(s) of reigns | Era name Chinese era name A Chinese era name is the regnal year, reign period, or regnal title used when traditionally numbering years in an emperor's reign and naming certain Chinese rulers . Some emperors have several era names, one after another, where each beginning of a new era resets the numbering of the year back... s and their range of years |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese convention: family and first names, and less commonly "Wu" + posthumous name + "di" | |||
| Emperor Da of Wu | Sun Quan Sun Quan Sun Quan , son of Sun Jian, formally Emperor Da of Wu, was the founder of Eastern Wu during the Three Kingdoms period of Chinese history. He ruled from 222 to 229 as King of Wu and from 229 to 252 as Emperor of Wu.... |
222-252 | Huangchu 222-229 Huanglong 229-231 Jiahe 232-238 Chiwu 238-251 Taiyuan 251-252 Shenfeng 252 |
| Prince of Kuaiji | Sun Liang Sun Liang Sun Liang was the second emperor of Eastern Wu during the Three Kingdoms period of Chinese history. He was the founding emperor Sun Quan's youngest son and heir... |
252-258 | Jianxing 252-253 Wufeng 254-256 Taiping 256-258 |
| Emperor Jing of Wu | Sun Xiu | 258-264 | Yong'an 258-264 |
| Marquis of Wucheng or Marquis of Guiming | Sun Hao Sun Hao Sun Hao , style name Yuanzong , originally named Sun Pengzu with the style name Yuanzong , was the fourth and last emperor of Eastern Wu during the Three Kingdoms period. He was the son of Sun He, a one-time crown prince of the founding emperor Sun Quan... |
264-280 | Yuanxing 264-265 Ganlu 265-266 Baoding 266-269 Jianheng 269-271 Fenghuang 272-274 Tiance 275-276 Tianxi 276 Tianji 277-280 |
See also
- Shu HanShu HanShu Han was one of the three states competing for control of China during the Three Kingdoms period, after the fall of the Han Dynasty. The state was based on areas around Sichuan, which was then known as Shu...
- Cao WeiCao WeiCao Wei was one of the states that competed for control of China during the Three Kingdoms period. With the capital at Luoyang, the state was established by Cao Pi in 220, based upon the foundations that his father Cao Cao laid...
- Three KingdomsThree KingdomsThe Three Kingdoms period was a period in Chinese history, part of an era of disunity called the "Six Dynasties" following immediately the loss of de facto power of the Han Dynasty rulers. In a strict academic sense it refers to the period between the foundation of the state of Wei in 220 and the...
- List of people of the Three Kingdoms
- Timeline of the Three Kingdoms periodTimeline of the Three Kingdoms periodThis is a timeline of the Three Kingdoms period of Chinese history....
- Romance of the Three KingdomsRomance of the Three KingdomsRomance of the Three Kingdoms, written by Luo Guanzhong in the 14th century, is a Chinese historical novel based on the events in the turbulent years near the end of the Han Dynasty and the Three Kingdoms era of Chinese history, starting in 169 and ending with the reunification of the land in...
- Records of Three KingdomsRecords of Three KingdomsRecords of Three Kingdoms , is regarded as the official and authoritative historical text on the Three Kingdoms period of Chinese history covering the years 184-280 CE. Written by Chen Shou in the 3rd century, the work combines the smaller histories of the rival states of Cao Wei , Shu Han and...

