
Edmund Kirby Smith
Encyclopedia
Edmund Kirby Smith was a career United States Army
officer and educator. He served as a general in the Confederate States Army
during the American Civil War
, notable for his command of the Trans-Mississippi Department
of the Confederacy after the fall of Vicksburg.
After the conflict ended Smith worked in both the telegraph
and railway business, and also served as a college professor
until his death.
, Florida
, to Joseph Lee Smith
and Frances Kirby Smith. Both his parents were natives of Connecticut
, and moved to Florida
in 1821 shortly before the elder Smith was named a U.S. District Judge there. In 1836, his parents sent him to a military boarding school in Virginia, which he attended until his enrollment in the United States Military Academy
at West Point
, New York
.
On July 1, 1841, Smith entered West Point and graduated four years later, standing 25th out of 41 cadets. While there he was nicknamed "Seminole" after his native state, and brevetted
a second lieutenant in the 5th U.S. Infantry
on July 1, 1845. He was promoted to second lieutenant on August 22, 1846, now serving in the 7th U.S. Infantry
.
In the Mexican-American War he served under General Zachary Taylor
at the Battle of Palo Alto
and the Battle of Resaca de la Palma
. He served under General Winfield Scott
later, and received brevet promotions to first lieutenant for Cerro Gordo
and to captain for Contreras
and Churubusco
. His older brother, Ephraim Kirby Smith, a captain in the regular army, served with him in the 5th U.S. Infantry in both the campaign with Taylor and Scott, until he died from wounds suffered at the Battle of Molino del Rey
in 1847.
After that war, he served as a captain in the 2nd U.S. Cavalry, primarily in Texas
, but he also taught mathematics
at West Point and was wounded in his thigh on May 13, 1859, fighting Indians
in the Nescutunga Valley of Texas. When Texas seceded
, Smith, now a major
, refused to surrender his command at Camp Colorado in what is now Coleman, Texas
, to the Texas State forces under Col. Benjamin McCulloch
and expressed his willingness to fight to hold it. On January 31, 1861, Smith was promoted to major
, but resigned his commission in the U.S. Army on April 6 to join the Confederacy.
in the regular
artillery
, and was transferred to the regular cavalry
that same day with the rank of lieutenant colonel
. After serving briefly as Brig. Gen. Joseph E. Johnston
's assistant adjutant general
in the Shenandoah Valley
, Smith was promoted to brigadier general on June 17, 1861, and given command of a brigade
in the Army of the Shenandoah
, which he led at the First Battle of Bull Run
on July 21. Wounded severely in the neck and shoulder, he recuperated while commanding the Department of Middle and East Florida. He returned to duty on October 11 as a major general and division
commander in the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia
, operating in northern Virginia.
In February 1862, Smith was sent west to command the Army of East Tennessee. Cooperating with Gen. Braxton Bragg
in the invasion of Kentucky
, he scored a victory at the Battle of Richmond, Kentucky on August 30, 1862, and was named on October 9 to the newly created grade of lieutenant general, becoming a corps
commander in the Army of Tennessee
. Smith would also receive the Confederate "Thanks of Congress
" on February 17, 1864, for his actions at Richmond.
for the balance of the war, based part of this time in Shreveport
, Louisiana. As forces under Union Maj. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant
tightened their grip on the river, Smith attempted to intervene. However, his department never had more than 30,000 men stationed over an immense area and he was not able to concentrate forces adequately to challenge Grant nor the Union Navy on the river.
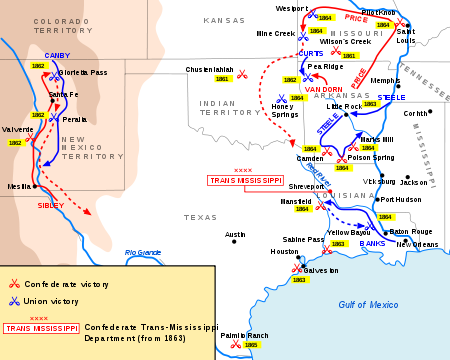 Following the Union capture of the remaining strongholds at Vicksburg and Port Hudson
Following the Union capture of the remaining strongholds at Vicksburg and Port Hudson
and the closing of the Mississippi, he was virtually cut off from the Confederate capital at Richmond
and was confronted with the command of a virtually independent area of the Confederacy, with all of its inherent administrative problems. The area became known in the Confederacy as "Kirby Smithdom".
In the spring of 1864, Lt. Gen. Richard Taylor
, directly under Smith's command, soundly defeated Maj. Gen. Nathaniel P. Banks at the Battle of Mansfield
in the Red River Campaign
on April 8, 1864. After the Battle of Pleasant Hill
on April 9, Smith joined Taylor and dispatched half of Taylor's Army, Walker's Greyhounds
, under the command of Maj. Gen. John George Walker
northward to defeat Union Maj. Gen. Frederick Steele
's incursion into Arkansas
. This decision, strongly opposed by Taylor, caused great enmity between the two men.
With the pressure relieved, Smith attempted to send reinforcements east of the Mississippi but, as in the case of his earlier attempts to relieve Vicksburg, it proved impracticable because of Union naval control of the river. Instead he dispatched Maj. Gen. Sterling Price
, with all available cavalry, on an unsuccessful invasion of Missouri
. Thereafter the war west of the river was principally one of small raids and guerrilla activity
. By now a full general (as of February 19, 1864, one of only seven such men in the Confederacy), he negotiated the surrender of his department—the only significant Confederate field army left—on May 26, 1865, and signed the terms of surrender in Galveston, Texas
, on June 2, whence he fled to Mexico and then to Cuba
to escape potential prosecution for treason
. He returned to take an oath of amnesty at Lynchburg, Virginia
, on November 14, 1865.
. Kirby Smith was recovering from being wounded at the First Battle of Manassas, but still found time for wooing - they were married on September 24. Cassie wrote on October 10, 1862 from Lynchburg, Virginia asking what to name their first child. Cassie suggested "something uncommon as I consider her an uncommon baby." The new baby was later named Frances.
The couple briefly reunited when Cassie followed her husband to Shreveport February 1863. In the spring of 1864 she moved to Hempstead, Texas
where she was to remain for the duration of the war. After the war's end, Cassie traveled to Washington to secure permission for her husband's return to the United States.
In Sewanee, Tennessee
, the Kirby Smiths lived happily. They had five sons and six daughters. Cassie died in 1905.
. In 1870, he combined efforts with former Confederate general officer Bushrod Johnson
and became president of the University of Nashville
. In 1875, he left that post to become professor of mathematics at the University of the South
at Sewanee
from 1875 to 1893. At the time of his death in Sewanee, he was the last surviving man who had been a full general in the war. He is buried in the University Cemetery at Sewanee.
building on the campus of LSU
in Baton Rouge is named Kirby-Smith Hall
. The state of Florida erected a statue honoring General Smith in the National Statuary Hall Collection
of the United States Capitol
in Washington, D.C. He is memorialized (as Edmund Kirby-Smith) at Sewanee by the Kirby-Smith Memorial on University Avenue, by Kirby-Smith Point on the edge of the South Cumberland Mountains on the University Domain, and in the naming of the Kirby-Smith Chapter of the United Daughters of the Confederacy at Sewanee, and in the naming of the Kirby-Smith Camp 1209, Sons of Confederate Veterans, Jacksonville, Florida. The Alachua County Public Schools administrative building, which was built in 1903, is named for Kirby-Smith.
He is memorialized with a tablet and in a stained-glass window at the university's All Saints Chapel, and in a painting in the university's Jessie Ball du Pont Library and in a painting in the Chapter Room of the Tennessee Omega Chapter of the Sigma Alpha Epsilon
Fraternity House. During World War II
the 422 feet (129 m) Liberty Ship
SS E. Kirby Smith was built in Panama City, Florida
, in 1943, named in his honor.
(1840 - February 11, 1894) was an African American
born into slavery in the same home as Smith in St. Augustine, Florida. Darnes was the son of Violent Pinkney, a black slave owned by Smith's parents. He served as Smith's personal valet starting from 1855 and continuing throughout the Civil War after which he would go on to medical school and became one of the first black physicians in the state of Florida.
United States Army
The United States Army is the main branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for land-based military operations. It is the largest and oldest established branch of the U.S. military, and is one of seven U.S. uniformed services...
officer and educator. He served as a general in the Confederate States Army
Confederate States Army
The Confederate States Army was the army of the Confederate States of America while the Confederacy existed during the American Civil War. On February 8, 1861, delegates from the seven Deep South states which had already declared their secession from the United States of America adopted the...
during the American Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
, notable for his command of the Trans-Mississippi Department
Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War
The Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War was the major military and naval operations west of the Mississippi River. The area excluded the states and territories bordering the Pacific Ocean, which formed the Pacific Coast Theater of the American Civil War.The campaign classification...
of the Confederacy after the fall of Vicksburg.
After the conflict ended Smith worked in both the telegraph
Telegraphy
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages via some form of signalling technology. Telegraphy requires messages to be converted to a code which is known to both sender and receiver...
and railway business, and also served as a college professor
Professor
A professor is a scholarly teacher; the precise meaning of the term varies by country. Literally, professor derives from Latin as a "person who professes" being usually an expert in arts or sciences; a teacher of high rank...
until his death.
Early life and the U.S. Army
Smith was born in St. AugustineSt. Augustine, Florida
St. Augustine is a city in the northeast section of Florida and the county seat of St. Johns County, Florida, United States. Founded in 1565 by Spanish explorer and admiral Pedro Menéndez de Avilés, it is the oldest continuously occupied European-established city and port in the continental United...
, Florida
Florida
Florida is a state in the southeastern United States, located on the nation's Atlantic and Gulf coasts. It is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the north by Alabama and Georgia and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of 18,801,310 as measured by the 2010 census, it...
, to Joseph Lee Smith
Joseph Lee Smith
Joseph Lee Smith was an American lawyer, soldier, and jurist. He was the father of Confederate States of America General Edmund Kirby Smith....
and Frances Kirby Smith. Both his parents were natives of Connecticut
Connecticut
Connecticut is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, and the state of New York to the west and the south .Connecticut is named for the Connecticut River, the major U.S. river that approximately...
, and moved to Florida
Florida
Florida is a state in the southeastern United States, located on the nation's Atlantic and Gulf coasts. It is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the north by Alabama and Georgia and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of 18,801,310 as measured by the 2010 census, it...
in 1821 shortly before the elder Smith was named a U.S. District Judge there. In 1836, his parents sent him to a military boarding school in Virginia, which he attended until his enrollment in the United States Military Academy
United States Military Academy
The United States Military Academy at West Point is a four-year coeducational federal service academy located at West Point, New York. The academy sits on scenic high ground overlooking the Hudson River, north of New York City...
at West Point
West Point, New York
West Point is a federal military reservation established by President of the United States Thomas Jefferson in 1802. It is a census-designated place located in Town of Highlands in Orange County, New York, United States. The population was 7,138 at the 2000 census...
, New York
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
.
On July 1, 1841, Smith entered West Point and graduated four years later, standing 25th out of 41 cadets. While there he was nicknamed "Seminole" after his native state, and brevetted
Brevet (military)
In many of the world's military establishments, brevet referred to a warrant authorizing a commissioned officer to hold a higher rank temporarily, but usually without receiving the pay of that higher rank except when actually serving in that role. An officer so promoted may be referred to as being...
a second lieutenant in the 5th U.S. Infantry
5th Infantry Regiment (United States)
The 5th Infantry Regiment is the third-oldest infantry regiment of the United States Army, tracing its origins to 1808...
on July 1, 1845. He was promoted to second lieutenant on August 22, 1846, now serving in the 7th U.S. Infantry
7th Infantry Regiment (United States)
The United States Army's 7th Infantry Regiment, known as "The Cottenbalers" from an incident that occurred during the Battle of New Orleans, while under the command of Andrew Jackson, when soldiers of the 7th Infantry Regiment held positions behind a breastwork of bales of cotton during the...
.
In the Mexican-American War he served under General Zachary Taylor
Zachary Taylor
Zachary Taylor was the 12th President of the United States and an American military leader. Initially uninterested in politics, Taylor nonetheless ran as a Whig in the 1848 presidential election, defeating Lewis Cass...
at the Battle of Palo Alto
Battle of Palo Alto
The Battle of Palo Alto was the first major battle of the Mexican-American War and was fought on May 8, 1846, on disputed ground five miles from the modern-day city of Brownsville, Texas...
and the Battle of Resaca de la Palma
Battle of Resaca de la Palma
At the Battle of Resaca de la Palma, one of the early engagements of the Mexican-American War,United States General Zachary Taylor engaged the retreating forces of the Mexican Ejército del Norte under General Mariano Arista on May 9, 1846.-Background:During the night of May 8, following...
. He served under General Winfield Scott
Winfield Scott
Winfield Scott was a United States Army general, and unsuccessful presidential candidate of the Whig Party in 1852....
later, and received brevet promotions to first lieutenant for Cerro Gordo
Battle of Cerro Gordo
The Battle of Cerro Gordo, or Battle of Sierra Gordo, in the Mexican-American War saw Winfield Scott's United States troops flank and drive Santa Anna's larger Mexican army from a strong defensive position.-Battle:...
and to captain for Contreras
Battle of Contreras
The Battle of Contreras, also known as the Battle of Padierna, took place during August 19–20, 1847, in the final encounters of the Mexican-American War. In the Battle of Churubusco, fighting continued the following day.-Background:...
and Churubusco
Battle of Churubusco
The Battle of Churubusco took place on August 20, 1847, in the immediate aftermath of the Battle of Contreras during the Mexican-American War. After defeating the Mexican army at Churubusco, the U.S. Army was only 5 miles away from Mexico City, the capital of the nation...
. His older brother, Ephraim Kirby Smith, a captain in the regular army, served with him in the 5th U.S. Infantry in both the campaign with Taylor and Scott, until he died from wounds suffered at the Battle of Molino del Rey
Battle of Molino del Rey
The Battle of Molino del Rey was one of the bloodiest engagements of the Mexican-American War. It was fought in September 1847 between Mexican forces under General Antonio Léon against an American force under General Winfield Scott at a hill called El Molino del Rey near Mexico City.-Background:On...
in 1847.
After that war, he served as a captain in the 2nd U.S. Cavalry, primarily in Texas
Texas
Texas is the second largest U.S. state by both area and population, and the largest state by area in the contiguous United States.The name, based on the Caddo word "Tejas" meaning "friends" or "allies", was applied by the Spanish to the Caddo themselves and to the region of their settlement in...
, but he also taught mathematics
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
at West Point and was wounded in his thigh on May 13, 1859, fighting Indians
Native Americans in the United States
Native Americans in the United States are the indigenous peoples in North America within the boundaries of the present-day continental United States, parts of Alaska, and the island state of Hawaii. They are composed of numerous, distinct tribes, states, and ethnic groups, many of which survive as...
in the Nescutunga Valley of Texas. When Texas seceded
Secession in the United States
Secession in the United States can refer to secession of a state from the United States, secession of part of a state from that state to form a new state, or secession of an area from a city or county....
, Smith, now a major
Major (United States)
In the United States Army, Air Force, and Marine Corps, major is a field grade military officer rank just above the rank of captain and just below the rank of lieutenant colonel...
, refused to surrender his command at Camp Colorado in what is now Coleman, Texas
Coleman, Texas
Coleman is a city in Coleman County, Texas, United States. The population was 5,127 at the 2000 census. It is the county seat of Coleman County.-Geography:Coleman is located at ....
, to the Texas State forces under Col. Benjamin McCulloch
Benjamin McCulloch
Benjamin McCulloch was a soldier in the Texas Revolution, a Texas Ranger, a U.S. marshal, and a brigadier general in the army of the Confederate States during the American Civil War.-Early life:...
and expressed his willingness to fight to hold it. On January 31, 1861, Smith was promoted to major
Major (United States)
In the United States Army, Air Force, and Marine Corps, major is a field grade military officer rank just above the rank of captain and just below the rank of lieutenant colonel...
, but resigned his commission in the U.S. Army on April 6 to join the Confederacy.
Civil War service
On March 16, 1861, Smith entered the Confederate forces as a majorMajor
Major is a rank of commissioned officer, with corresponding ranks existing in almost every military in the world.When used unhyphenated, in conjunction with no other indicator of rank, the term refers to the rank just senior to that of an Army captain and just below the rank of lieutenant colonel. ...
in the regular
Regular Army
The Regular Army of the United States was and is the successor to the Continental Army as the country's permanent, professional military establishment. Even in modern times the professional core of the United States Army continues to be called the Regular Army...
artillery
Field artillery in the American Civil War
Field artillery in the American Civil War refers to the important artillery weapons, equipment, and practices used by the Artillery branch to support the infantry and cavalry forces in the field. It does not include siege artillery, use of artillery in fixed fortifications, or coastal or naval...
, and was transferred to the regular cavalry
Cavalry in the American Civil War
Cavalry in the American Civil War was a branch of army service in a process of transition. It suffered from emerging technology threats, difficult logistics, and sometimes misguided or inept commanders...
that same day with the rank of lieutenant colonel
Lieutenant colonel
Lieutenant colonel is a rank of commissioned officer in the armies and most marine forces and some air forces of the world, typically ranking above a major and below a colonel. The rank of lieutenant colonel is often shortened to simply "colonel" in conversation and in unofficial correspondence...
. After serving briefly as Brig. Gen. Joseph E. Johnston
Joseph E. Johnston
Joseph Eggleston Johnston was a career U.S. Army officer, serving with distinction in the Mexican-American War and Seminole Wars, and was also one of the most senior general officers in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War...
's assistant adjutant general
Adjutant general
An Adjutant General is a military chief administrative officer.-Imperial Russia:In Imperial Russia, the General-Adjutant was a Court officer, who was usually an army general. He served as a personal aide to the Tsar and hence was a member of the H. I. M. Retinue...
in the Shenandoah Valley
Shenandoah Valley
The Shenandoah Valley is both a geographic valley and cultural region of western Virginia and West Virginia in the United States. The valley is bounded to the east by the Blue Ridge Mountains, to the west by the eastern front of the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians , to the north by the Potomac River...
, Smith was promoted to brigadier general on June 17, 1861, and given command of a brigade
Brigade
A brigade is a major tactical military formation that is typically composed of two to five battalions, plus supporting elements depending on the era and nationality of a given army and could be perceived as an enlarged/reinforced regiment...
in the Army of the Shenandoah
Army of the Shenandoah
Army of the Shenandoah refers to two armies in the American Civil War:* Confederate Army of the Shenandoah* Union Army of the Shenandoah...
, which he led at the First Battle of Bull Run
First Battle of Bull Run
First Battle of Bull Run, also known as First Manassas , was fought on July 21, 1861, in Prince William County, Virginia, near the City of Manassas...
on July 21. Wounded severely in the neck and shoulder, he recuperated while commanding the Department of Middle and East Florida. He returned to duty on October 11 as a major general and division
Division (military)
A division is a large military unit or formation usually consisting of between 10,000 and 20,000 soldiers. In most armies, a division is composed of several regiments or brigades, and in turn several divisions typically make up a corps...
commander in the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia
Army of Northern Virginia
The Army of Northern Virginia was the primary military force of the Confederate States of America in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War, as well as the primary command structure of the Department of Northern Virginia. It was most often arrayed against the Union Army of the Potomac...
, operating in northern Virginia.
In February 1862, Smith was sent west to command the Army of East Tennessee. Cooperating with Gen. Braxton Bragg
Braxton Bragg
Braxton Bragg was a career United States Army officer, and then a general in the Confederate States Army—a principal commander in the Western Theater of the American Civil War and later the military adviser to Confederate President Jefferson Davis.Bragg, a native of North Carolina, was...
in the invasion of Kentucky
Confederate Heartland Offensive
The Confederate Heartland Offensive or Kentucky Campaign was a series of maneuvers and battles in East Tennessee and Kentucky in 1862 during the American Civil War...
, he scored a victory at the Battle of Richmond, Kentucky on August 30, 1862, and was named on October 9 to the newly created grade of lieutenant general, becoming a corps
Corps
A corps is either a large formation, or an administrative grouping of troops within an armed force with a common function such as Artillery or Signals representing an arm of service...
commander in the Army of Tennessee
Army of Tennessee
The Army of Tennessee was the principal Confederate army operating between the Appalachian Mountains and the Mississippi River during the American Civil War. It was formed in late 1862 and fought until the end of the war in 1865, participating in most of the significant battles in the Western Theater...
. Smith would also receive the Confederate "Thanks of Congress
Thanks of Congress
The Thanks of Congress are a series of formal resolutions passed by the United States Congress originally to extend the government's formal thanks for significant victories or impressive actions by American military commanders and their troops. Although it began during the American Revolutionary...
" on February 17, 1864, for his actions at Richmond.
Trans-Mississippi Department
On January 14, 1863, Smith was transferred to command the Trans-Mississippi Department (primarily Arkansas, Western Louisiana, and Texas) and he remained west of the Mississippi RiverMississippi River
The Mississippi River is the largest river system in North America. Flowing entirely in the United States, this river rises in western Minnesota and meanders slowly southwards for to the Mississippi River Delta at the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains...
for the balance of the war, based part of this time in Shreveport
Shreveport, Louisiana
Shreveport is the third largest city in Louisiana. It is the principal city of the fourth largest metropolitan area in the state of Louisiana and is the 109th-largest city in the United States....
, Louisiana. As forces under Union Maj. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant was the 18th President of the United States as well as military commander during the Civil War and post-war Reconstruction periods. Under Grant's command, the Union Army defeated the Confederate military and ended the Confederate States of America...
tightened their grip on the river, Smith attempted to intervene. However, his department never had more than 30,000 men stationed over an immense area and he was not able to concentrate forces adequately to challenge Grant nor the Union Navy on the river.

Siege of Port Hudson
The Siege of Port Hudson occurred from May 22 to July 9, 1863, when Union Army troops assaulted and then surrounded the Mississippi River town of Port Hudson, Louisiana, during the American Civil War....
and the closing of the Mississippi, he was virtually cut off from the Confederate capital at Richmond
Richmond, Virginia
Richmond is the capital of the Commonwealth of Virginia, in the United States. It is an independent city and not part of any county. Richmond is the center of the Richmond Metropolitan Statistical Area and the Greater Richmond area...
and was confronted with the command of a virtually independent area of the Confederacy, with all of its inherent administrative problems. The area became known in the Confederacy as "Kirby Smithdom".
In the spring of 1864, Lt. Gen. Richard Taylor
Richard Taylor (general)
Richard Taylor was a Confederate general in the American Civil War. He was the son of United States President Zachary Taylor and First Lady Margaret Taylor.-Early life:...
, directly under Smith's command, soundly defeated Maj. Gen. Nathaniel P. Banks at the Battle of Mansfield
Battle of Mansfield
The Battle of Mansfield, also known as the Battle of Sabine Crossroads, occurred on April 8, 1864, in De Soto Parish, Louisiana. Confederate forces commanded by Richard Taylor attacked a Union army commanded by Nathaniel Banks a few miles outside the town of Mansfield, near Sabine Crossroads...
in the Red River Campaign
Red River Campaign
The Red River Campaign or Red River Expedition consisted of a series of battles fought along the Red River in Louisiana during the American Civil War from March 10 to May 22, 1864. The campaign was a Union initiative, fought between approximately 30,000 Union troops under the command of Maj. Gen....
on April 8, 1864. After the Battle of Pleasant Hill
Battle of Pleasant Hill
The Battle of Pleasant Hill was fought on April 9, 1864, during the Red River Campaign of the American Civil War, near Pleasant Hill, Louisiana, between Union forces led by Maj. Gen. Nathaniel P. Banks and Confederate forces, led by Maj. Gen...
on April 9, Smith joined Taylor and dispatched half of Taylor's Army, Walker's Greyhounds
Walker's Greyhounds
Walker's Greyhounds was the name given to a division of the Confederate States Army composed exclusively of regiments from Texas. It fought exclusively in the Western Theater and gained a reputation as a solid fighting force.-Organization:...
, under the command of Maj. Gen. John George Walker
John George Walker
John George Walker was a Confederate general in the American Civil War.-Early life and military career:Walker was born in Jefferson City, Missouri...
northward to defeat Union Maj. Gen. Frederick Steele
Frederick Steele
Frederick Steele was a career military officer in the United States Army, serving as a major general in the Union Army during the American Civil War. He was most noted for his successful campaign to retake much of secessionist Arkansas for the Union cause.-Early life:Steele was born in Delhi, New...
's incursion into Arkansas
Arkansas
Arkansas is a state located in the southern region of the United States. Its name is an Algonquian name of the Quapaw Indians. Arkansas shares borders with six states , and its eastern border is largely defined by the Mississippi River...
. This decision, strongly opposed by Taylor, caused great enmity between the two men.
With the pressure relieved, Smith attempted to send reinforcements east of the Mississippi but, as in the case of his earlier attempts to relieve Vicksburg, it proved impracticable because of Union naval control of the river. Instead he dispatched Maj. Gen. Sterling Price
Sterling Price
Sterling Price was a lawyer, planter, and politician from the U.S. state of Missouri, who served as the 11th Governor of the state from 1853 to 1857. He also served as a United States Army brigadier general during the Mexican-American War, and a Confederate Army major general in the American Civil...
, with all available cavalry, on an unsuccessful invasion of Missouri
Price's Raid
Price's Missouri Expedition, also known as Price's Raid, was an 1864 Confederate cavalry raid through the states of Missouri and Kansas during the American Civil War. While Confederate Major General Sterling Price enjoyed some successes during this campaign, he was decisively beaten at the Battle...
. Thereafter the war west of the river was principally one of small raids and guerrilla activity
Guerrilla warfare
Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare and refers to conflicts in which a small group of combatants including, but not limited to, armed civilians use military tactics, such as ambushes, sabotage, raids, the element of surprise, and extraordinary mobility to harass a larger and...
. By now a full general (as of February 19, 1864, one of only seven such men in the Confederacy), he negotiated the surrender of his department—the only significant Confederate field army left—on May 26, 1865, and signed the terms of surrender in Galveston, Texas
Galveston, Texas
Galveston is a coastal city located on Galveston Island in the U.S. state of Texas. , the city had a total population of 47,743 within an area of...
, on June 2, whence he fled to Mexico and then to Cuba
Cuba
The Republic of Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean. The nation of Cuba consists of the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud, and several archipelagos. Havana is the largest city in Cuba and the country's capital. Santiago de Cuba is the second largest city...
to escape potential prosecution for treason
Treason
In law, treason is the crime that covers some of the more extreme acts against one's sovereign or nation. Historically, treason also covered the murder of specific social superiors, such as the murder of a husband by his wife. Treason against the king was known as high treason and treason against a...
. He returned to take an oath of amnesty at Lynchburg, Virginia
Lynchburg, Virginia
Lynchburg is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia. The population was 75,568 as of 2010. Located in the foothills of the Blue Ridge Mountains along the banks of the James River, Lynchburg is known as the "City of Seven Hills" or "The Hill City." Lynchburg was the only major city in...
, on November 14, 1865.
Marriage and Family Life
In August 1861, Kirby Smith met Cassie Selden, the daughter of Samuel S. Selden of Lynchburg, VirginiaLynchburg, Virginia
Lynchburg is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia. The population was 75,568 as of 2010. Located in the foothills of the Blue Ridge Mountains along the banks of the James River, Lynchburg is known as the "City of Seven Hills" or "The Hill City." Lynchburg was the only major city in...
. Kirby Smith was recovering from being wounded at the First Battle of Manassas, but still found time for wooing - they were married on September 24. Cassie wrote on October 10, 1862 from Lynchburg, Virginia asking what to name their first child. Cassie suggested "something uncommon as I consider her an uncommon baby." The new baby was later named Frances.
The couple briefly reunited when Cassie followed her husband to Shreveport February 1863. In the spring of 1864 she moved to Hempstead, Texas
Hempstead, Texas
Hempstead is a city in Waller County, Texas, United States. The community, located at the junctions of U.S. Highway 290, Texas State Highway 6, and Texas State Highway 159, is around fifty miles northwest of Downtown Houston. The population was 4,691 at the 2000 census. It is the county seat of...
where she was to remain for the duration of the war. After the war's end, Cassie traveled to Washington to secure permission for her husband's return to the United States.
In Sewanee, Tennessee
Sewanee, Tennessee
Sewanee is an unincorporated locality in Franklin County, Tennessee, United States, treated by the U.S. Census as a census-designated place . The population was 2,361 at the 2000 census...
, the Kirby Smiths lived happily. They had five sons and six daughters. Cassie died in 1905.
Postwar Career
After the war, Kirby Smith was active in the telegraph business and education. From 1866 to 1868, he was president of the Atlantic and Pacific Telegraph Company. When that effort ended in failure, he started a preparatory school in New Castle, KentuckyNew Castle, Kentucky
New Castle is a city in Henry County, Kentucky, in the United States. As of the 2000 census, the city population was 919. It is the county seat of Henry County. It is located on U.S. Route 421 30 miles northeast of Louisville.- History :...
. In 1870, he combined efforts with former Confederate general officer Bushrod Johnson
Bushrod Johnson
Bushrod Rust Johnson was a teacher, university chancellor, and Confederate general in the American Civil War. He was one of a handful of Confederate generals who were born and raised in the North.-Early life:...
and became president of the University of Nashville
University of Nashville
The University of Nashville was an educational institution that existed as a distinct entity from 1826 until 1909. During its history, it operated at various times a medical school, a four-year military college, a literary arts college, and a boys preparatory school...
. In 1875, he left that post to become professor of mathematics at the University of the South
Sewanee, The University of the South
The University of the South is a private, coeducational liberal arts college located in Sewanee, Tennessee. It is owned by twenty-eight southern dioceses of the Episcopal Church and its School of Theology is an official seminary of the church. The university's School of Letters offers graduate...
at Sewanee
Sewanee, Tennessee
Sewanee is an unincorporated locality in Franklin County, Tennessee, United States, treated by the U.S. Census as a census-designated place . The population was 2,361 at the 2000 census...
from 1875 to 1893. At the time of his death in Sewanee, he was the last surviving man who had been a full general in the war. He is buried in the University Cemetery at Sewanee.
In memoriam
A men's dormitoryDormitory
A dormitory, often shortened to dorm, in the United States is a residence hall consisting of sleeping quarters or entire buildings primarily providing sleeping and residential quarters for large numbers of people, often boarding school, college or university students...
building on the campus of LSU
Louisiana State University
Louisiana State University and Agricultural and Mechanical College, most often referred to as Louisiana State University, or LSU, is a public coeducational university located in Baton Rouge, Louisiana. The University was founded in 1853 in what is now known as Pineville, Louisiana, under the name...
in Baton Rouge is named Kirby-Smith Hall
Kirby-Smith Hall
Kirby-Smith Hall is an on-campus living option at the Louisiana State University. The building was named after the United States Army officer of the same name...
. The state of Florida erected a statue honoring General Smith in the National Statuary Hall Collection
National Statuary Hall Collection
The National Statuary Hall Collection in the United States Capitol comprises statues donated by individual states to honor persons notable in their history...
of the United States Capitol
United States Capitol
The United States Capitol is the meeting place of the United States Congress, the legislature of the federal government of the United States. Located in Washington, D.C., it sits atop Capitol Hill at the eastern end of the National Mall...
in Washington, D.C. He is memorialized (as Edmund Kirby-Smith) at Sewanee by the Kirby-Smith Memorial on University Avenue, by Kirby-Smith Point on the edge of the South Cumberland Mountains on the University Domain, and in the naming of the Kirby-Smith Chapter of the United Daughters of the Confederacy at Sewanee, and in the naming of the Kirby-Smith Camp 1209, Sons of Confederate Veterans, Jacksonville, Florida. The Alachua County Public Schools administrative building, which was built in 1903, is named for Kirby-Smith.
He is memorialized with a tablet and in a stained-glass window at the university's All Saints Chapel, and in a painting in the university's Jessie Ball du Pont Library and in a painting in the Chapter Room of the Tennessee Omega Chapter of the Sigma Alpha Epsilon
Sigma Alpha Epsilon
Sigma Alpha Epsilon is a North American Greek-letter social college fraternity founded at the University of Alabama on March 9, 1856. Of all existing national social fraternities today, Sigma Alpha Epsilon is the only one founded in the Antebellum South...
Fraternity House. During World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
the 422 feet (129 m) Liberty Ship
Liberty ship
Liberty ships were cargo ships built in the United States during World War II. Though British in conception, they were adapted by the U.S. as they were cheap and quick to build, and came to symbolize U.S. wartime industrial output. Based on vessels ordered by Britain to replace ships torpedoed by...
SS E. Kirby Smith was built in Panama City, Florida
Panama City, Florida
-Personal income:The median income for a household in the city was $31,572, and the median income for a family was $40,890. Males had a median income of $30,401 versus $21,431 for females. The per capita income for the city was $17,830...
, in 1943, named in his honor.
Alexander Darnes
Alexander H. DarnesAlexander Darnes
Alexander H. Darnes was an African American born into slavery in the city of St. Augustine, Florida who became one of the first black physicians in the state of Florida...
(1840 - February 11, 1894) was an African American
African American
African Americans are citizens or residents of the United States who have at least partial ancestry from any of the native populations of Sub-Saharan Africa and are the direct descendants of enslaved Africans within the boundaries of the present United States...
born into slavery in the same home as Smith in St. Augustine, Florida. Darnes was the son of Violent Pinkney, a black slave owned by Smith's parents. He served as Smith's personal valet starting from 1855 and continuing throughout the Civil War after which he would go on to medical school and became one of the first black physicians in the state of Florida.
See also
- List of American Civil War generals
Further reading
- Forsyth, Michael J. The Camden Expedition of 1864 and the Opportunity Lost by the Confederacy to Change the Civil War. Jefferson, NC: McFarland & Co., 2003. ISBN 978-0-7864-1554-0.
- Parks, Joseph Howard. General Edmund Kirby Smith, CSA. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press, 1954. ISBN 978-0-8071-1800-9.
- Pollard, Edward Alfred. Lee and His Lieutenants: Comprising the Early Life, Public Services, and Campaigns of General Robert E. Lee and His Companions in Arms, with a Record of Their Campaigns and Heroic Deeds. New York: E.B. Treat & Co, 1867. .
- Prushankin, Jeffery S. A Crisis in Confederate Command: Edmund Kirby Smith, Richard Taylor and the Army of the Trans-Mississippi. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press, 2005. ISBN 978-0-8071-3088-9.
- Sifakis, Stewart. Who Was Who in the Civil War. New York: Facts on File, 1988. ISBN 978-0-8160-2202-1.

