
Educational attainment in the United States
Encyclopedia
American middle class
The American middle class is a social class in the United States. While the concept is typically ambiguous in popular opinion and common language use, contemporary social scientists have put forward several, more or less congruent, theories on the American middle class...
and status. As with income
Household income in the United States
Household income is a measure commonly used by the United States government and private institutions, that counts the income of all residents over the age of 18 in each household, including not only all wages and salaries, but such items as unemployment insurance, disability payments, child support...
, levels differ by race, age, household configuration and geography. Overall the households and demographics featuring the highest educational attainment in the United States are also among those with the highest household income
Household income in the United States
Household income is a measure commonly used by the United States government and private institutions, that counts the income of all residents over the age of 18 in each household, including not only all wages and salaries, but such items as unemployment insurance, disability payments, child support...
and wealth
Wealth in the United States
Wealth in the United States is commonly measured in terms of net worth, which is the sum of all assets, including home equity, minus all liabilities....
. Thus, while the population as a whole is proceeding further in formal educational programs, income and educational attainment remain highly correlated.
General attainment of degrees/diplomas
| Education | Percentage |
|---|---|
| High school graduate | 86.68% |
| Some college | 55.60% |
| Associate's and/or Bachelor's degree | 38.54% |
| Bachelor's degree | 29.54% |
| Master's degree | 7.62% |
| Doctorate or professional degree | 2.94% |
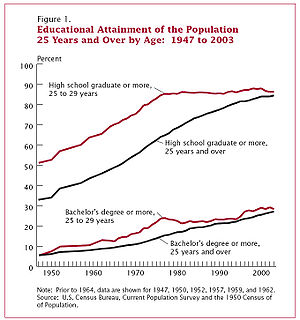
In 2005, the proportion of the population having finished high school
High school
High school is a term used in parts of the English speaking world to describe institutions which provide all or part of secondary education. The term is often incorporated into the name of such institutions....
and the percentage of those having earned bachelor's degree
Bachelor's degree
A bachelor's degree is usually an academic degree awarded for an undergraduate course or major that generally lasts for three or four years, but can range anywhere from two to six years depending on the region of the world...
s remained at an all-time high, while the growth in both categories has slowed down over the past two decades. The vast majority of the population, 85.2%, had finished high school and nearly a quarter, 22%, had earned a Bachelor's degree. The percentage of both college and high school graduates continued to increase since 2000. Since 1983 the percentage of people graduating from high school has increased from 85% to 88%. The greatest increases in educational attainment were documented in the 1950s, 60s and 70s. In the 1950s and much of the 1960s high school graduates constituted about 50% of those considered adults (25 and above). For young adults aged between 25 and 29, the percentage of high school graduates was roughly 50% in 1950 versus 90% today.
Gender
Overall, women have surpassed men in terms of completing secondary and post-secondary education with the gender gap almost completely reversed. In 2006, 10.3% of males and 8.3% of females dropped out of high school. In 2005/2006, women earned 62% of Associate's degrees, 58% of Bachelor's degrees, 60.0% of Master's degrees, and 48.9% of Doctorates. In 2016/2017, women are projected to earn 64.2% of Associate's degrees, 59.9% of Bachelor's degrees, 62.9% of Master's degrees, and 55.5% of Doctorates.Race
While the educational attainment of all races increased during the 1990s, with the gap between African Americans and non-Hispanic whites decreasing, severe differences between the races remain, especially among those with a bachelor's degreeBachelor's degree
A bachelor's degree is usually an academic degree awarded for an undergraduate course or major that generally lasts for three or four years, but can range anywhere from two to six years depending on the region of the world...
or higher. Asian Americans had the highest educational attainment of any race, followed by whites who had a higher percentage of high school graduates but a lower percentage of college graduates. Persons identifying as Hispanic
Hispanic
Hispanic is a term that originally denoted a relationship to Hispania, which is to say the Iberian Peninsula: Andorra, Gibraltar, Portugal and Spain. During the Modern Era, Hispanic sometimes takes on a more limited meaning, particularly in the United States, where the term means a person of ...
or Latino, without regard to race, had the lowest educational attainment. The gap was the largest between foreign-born Asian Americans, over half (50.1%) of whom had a bachelor's degree or higher
Bachelor's degree or higher
Bachelor's degree or higher is a commonly used term by the United States Census Bureau and other U.S. government agencies on the federal as well as state and local level. The term describes the portion of the population that has either a bachelor's degree or a higher degree such as a master's or...
and foreign-born Hispanics, 9.8% of whom had a four-year college degree. Hispanics and Latinos also trailed far behind in terms of graduating from high school; it was the only major group for which high school graduates constituted less than 80% of the population. This large inequality might partially be explained thorough the influx of uneducated foreign-born Hispanic Americans who had not been offered the chance to complete secondary education in their home country and who had not completed secondary education in the United States. Overall nearly half (49.8%) of Asian Americans, nearly a third (30%) of non-Hispanic Whites, 17.3% of non-Hispanic Blacks, and just over a tenth (11.4%) of Hispanics or Latinos had a four-year college degree. The same differences decrease significantly at the high school level with 89.4% of non-Hispanic whites, 87.6% of Asian Americans, 80.0% of African Americans, and only 57% of Hispanics or Latinos having graduated from high school.
Foreign born & Immigrants

Only among Hispanics and Latinos was the proportion of college graduates larger among the native born population. In the general population the proportion of persons with a bachelor's degree or higher was the same among the foreign-born and native-born population (27.2%). As stated above fewer foreign born Americans
Foreign born Americans
Foreign born Americans are citizens of the United States who were not yet citizens at the moment of birth and thus were born outside the country...
completed high school than native born Americans. Overall 87.5% of the native born population had graduated from high school, versus 67.2%. Among whites the difference was three percentage points, the same as for African Americans. Among Asian Americans the difference was five percentage points. It was thirty percentage points among Hispanics or Latinos.
African Attainment Rates: According to the U.S census, since the 1990's when the Journal of Blacks inhigher Education revealed that continental Africans have the highest educational rates in the U.S, Africans immigrants to the U.S. have continued to be the most highly educated group of people in the U.S.They have also been shown to be more educated than all other immigrant groups including Asian Americans that have long been held as the model minority
Model minority
Model minority refers to a minority ethnic, racial, or religious group whose members achieve a higher degree of success than the population average. It is most commonly used to label one ethnic minority higher achieving than another ethnic minority...
. Their educated attainment rates surpass any native-born ethnic groups including White Americans and Asian Americans and African Americans This has contributed to the large brain drain
Brain drain
Human capital flight, more commonly referred to as "brain drain", is the large-scale emigration of a large group of individuals with technical skills or knowledge. The reasons usually include two aspects which respectively come from countries and individuals...
on the African contient. Even though they are the most educated group, they were the hardest hit by the recession that began in 2007.
Income
Household income in the United States
Household income is a measure commonly used by the United States government and private institutions, that counts the income of all residents over the age of 18 in each household, including not only all wages and salaries, but such items as unemployment insurance, disability payments, child support...
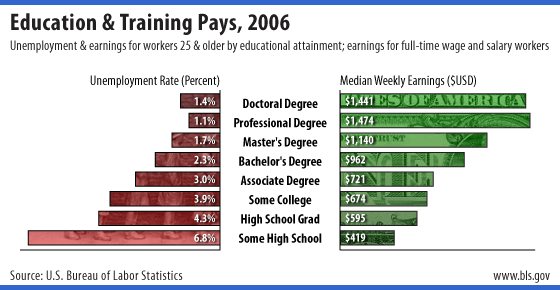
. Although the incomes of both men and women are associated with higher educational attainment (higher incomes for higher educational attainment), the income gap between races and genders remained at each educational level. In 2003 average incomes ranged from $13,459 for a male high-school dropout to $90,761 for a male with an advanced degree. The most significant average income difference was between those who had some college education or an Associates degree and those who had a Bachelor's degree
Bachelor's degree
A bachelor's degree is usually an academic degree awarded for an undergraduate course or major that generally lasts for three or four years, but can range anywhere from two to six years depending on the region of the world...
. While the former averaged $31,046 for both sexes the latter average
Average
In mathematics, an average, or central tendency of a data set is a measure of the "middle" value of the data set. Average is one form of central tendency. Not all central tendencies should be considered definitions of average....
d $51,194, over $20,000 (64.9%) more. The second most dramatic difference in average income
Household income in the United States
Household income is a measure commonly used by the United States government and private institutions, that counts the income of all residents over the age of 18 in each household, including not only all wages and salaries, but such items as unemployment insurance, disability payments, child support...
was between those with a Bachelor's degree
Bachelor's degree
A bachelor's degree is usually an academic degree awarded for an undergraduate course or major that generally lasts for three or four years, but can range anywhere from two to six years depending on the region of the world...
with $51,940 and those with an advanced degree who made $72,824, roughly $21,000 (42.2%) more. The least significant difference was between those who had graduated from high school and those who had either some college or an Associates degree. Here the difference was a mere $3,766 or 13.8%. The difference between those with a high school diploma ($30,000) and those who did not complete high school ($18,826) was $8,454 or 45%.
Overall, the income
Household income in the United States
Household income is a measure commonly used by the United States government and private institutions, that counts the income of all residents over the age of 18 in each household, including not only all wages and salaries, but such items as unemployment insurance, disability payments, child support...
in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
for all sexes, races and levels of educational attainment was $36,308 annually. Even though African immigrants have the highest educational attainment rates then any other group, they were the hardest hit in times of recession in the U.S. in 2007 This show that race
Race
Race is classification of humans into large and distinct populations or groups by factors such as heritable phenotypic characteristics or geographic ancestry, but also often influenced by and correlated with traits such as appearance, culture, ethnicity, and socio-economic status...
and/or ethnicity may play a role in income levels and job selection.
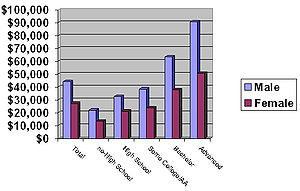
| Criteria | Overall | Less than 9th grade | High school drop-out | High school graduate | Some college | Associates degree | Bachelor's degree | Bachelor's degree or more | Master's degree | Professional degree | Doctorate degree | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median individual income | Male, age 25+ | $33,517 | $15,461 | $18,990 | $28,763 | $35,073 | $39,015 | $50,916 | $55,751 | $61,698 | $88,530 | $73,853 |
| Female, age 25+ | $19,679 | $9,296 | $10,786 | $15,962 | $21,007 | $24,808 | $31,309 | $35,125 | $41,334 | $48,536 | $53,003 | |
| Median household income | $45,016 | $18,787 | $22,718 | $36,835 | $45,854 | $51,970 | $68,728 | $73,446 | $78,541 | $100,000 | $96,830 | |
SOURCE: US Census Bureau, 2003
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
was $40,873 in 2003 dollars, while the median household income in 2003 was $45,016. In 1999, however, the median household income was $46,236, 2.7% higher than today. While this trend held true for all levels of educational attainment the extent of chorinical fluctuations in income were greatly influenced by educational attainment. Overall the median household and personal income decreased for those with more than a 9th grade education but less than a four-year college degree since 1991. In other words, the median household income decreased for households and individuals at the high school drop-outs and graduate, some-college, and an Associates degree level. Income did, however, increase for those with a Bachelor's degree
Bachelor's degree
A bachelor's degree is usually an academic degree awarded for an undergraduate course or major that generally lasts for three or four years, but can range anywhere from two to six years depending on the region of the world...
or more. The following table shows the median household income according to the educational attainment of the householder. All data is in 2003 dollars and only applies to householders whose householder is aged twenty-five or older. The highest and lowest points of the median household income are presented in bold face.
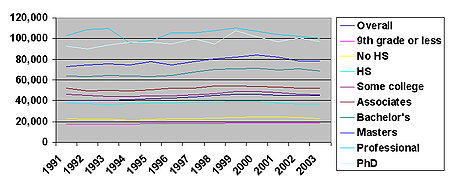
| Year | Overall Median | Less than 9th grade | High school drop-out | High school graduate | Some college | Associates degree | Bachelor's degree | Bachelor's degree or more | Master's degree | Professional degree | Doctorate degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1991 | $40,873 | $17,414 | $23,096 | $37,520 | $46,296 | $52,289 | $64,150 | $68,845 | $72,669 | $102,667 | $92,614 |
| 1993 | $40,324 | $17,450 | $22,523 | $35,979 | $44,153 | $49,622 | $64,537 | $70,349 | $75,645 | $109,900 | $93,712 |
| 1995 | $42,235 | $18,031 | $21,933 | $37,609 | $44,537 | $50,485 | $63,357 | $69,584 | $77,865 | $98,302 | $95,899 |
| 1997 | $43,648 | $17,762 | $22,688 | $38,607 | $45,734 | $51,726 | $67,487 | $72,338 | $77,850 | $105,409 | $99,699 |
| 1999 | $46,236 | $19,008 | $23,977 | $39,322 | $48,588 | $54,282 | $70,925 | $76,958 | $82,097 | $110,383 | $107,217 |
| 2001 | $45,300 | $18,830 | $24,162 | $37,468 | $47,605 | $53,166 | $69,796 | $75,116 | $81,993 | $103,918 | $96,442 |
| 2003 | $45,016 | $18,787 | $22,718 | $36,835 | $45,854 | $51,970 | $68,728 | $73,446 | $78,541 | $100,000 | $96,830 |
| Average | $43,376 | $18,183 | $23,013 | $37,620 | $46,109 | $51,934 | $66,997 | $72,376 | $78,094 | $104,368 | $94,487 |
SOURCE: US Census Bureau, 2003
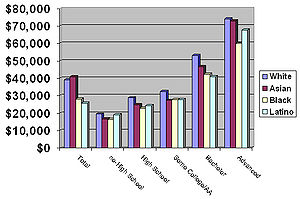
Household income in the United States
Household income is a measure commonly used by the United States government and private institutions, that counts the income of all residents over the age of 18 in each household, including not only all wages and salaries, but such items as unemployment insurance, disability payments, child support...
which varies significantly at each educational level. European Americans (White Americans) had the highest average income at every level of educational attainment. However, the proportion of those having college degrees is greater among Asian Americans than among non-Hispanic whites, and the overall highest average income is found among Asians. All races except Whites ranked last on at least one level with African Americans ranking last on the non-high school, high school and advanced degree level. Asians were second highest on the college graduate level and had the highest overall income among the general population. They also had the lowest average annual income for those with some college education or an Associates degree. Racial income difference were also significant at every level of educational attainment with the largest racial inequality being between European and African Americans who did not complete high school and those with advanced college degrees. Overall European Americans with an advanced degree had the highest average annual income with $74,122. Asian Americans had the second highest with $72,852. Hispanic
Hispanic
Hispanic is a term that originally denoted a relationship to Hispania, which is to say the Iberian Peninsula: Andorra, Gibraltar, Portugal and Spain. During the Modern Era, Hispanic sometimes takes on a more limited meaning, particularly in the United States, where the term means a person of ...
s and African Americans had the lowest annual incomes among those with advanced degrees averaging $67,679 and $59,944 annually. The largest racial inequity was between European Americans with a Bachelor's degree
Bachelor's degree
A bachelor's degree is usually an academic degree awarded for an undergraduate course or major that generally lasts for three or four years, but can range anywhere from two to six years depending on the region of the world...
who made $53,185 than Hispanic
Hispanic
Hispanic is a term that originally denoted a relationship to Hispania, which is to say the Iberian Peninsula: Andorra, Gibraltar, Portugal and Spain. During the Modern Era, Hispanic sometimes takes on a more limited meaning, particularly in the United States, where the term means a person of ...
s who made $12,263 or 29.9% less with an average annual income
Household income in the United States
Household income is a measure commonly used by the United States government and private institutions, that counts the income of all residents over the age of 18 in each household, including not only all wages and salaries, but such items as unemployment insurance, disability payments, child support...
of $40,949.
Occupation
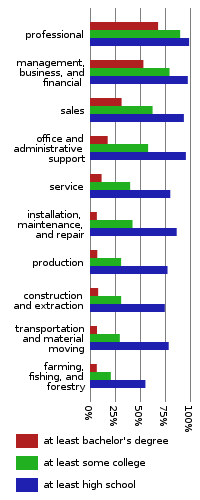
Bachelor's degree or higher
Bachelor's degree or higher is a commonly used term by the United States Census Bureau and other U.S. government agencies on the federal as well as state and local level. The term describes the portion of the population that has either a bachelor's degree or a higher degree such as a master's or...
represented the majority. Among professional occupations, 99.1% of the population graduated from high school, 90.2% had some college education or an Associates degree and over two thirds, 68.2% had a Bachelor's degree or higher
Bachelor's degree or higher
Bachelor's degree or higher is a commonly used term by the United States Census Bureau and other U.S. government agencies on the federal as well as state and local level. The term describes the portion of the population that has either a bachelor's degree or a higher degree such as a master's or...
. Business and managerial occupations were second with 97.8% having graduated from high school, 79.5% having some college or an associates degree and just over half, 53.4% having a Bachelor's degree or higher
Bachelor's degree or higher
Bachelor's degree or higher is a commonly used term by the United States Census Bureau and other U.S. government agencies on the federal as well as state and local level. The term describes the portion of the population that has either a bachelor's degree or a higher degree such as a master's or...
. While nearly all employment fields feature a population where over 80% had graduated from high school with over a third having some college education or an Associates degree, the fields relating to agriculture, construction, manufacturing
Blue collar
Blue collar can refer to:*Blue-collar worker, a traditional designation of the working class*Blue-collar crime, the types of crimes typically associated with the working class*A census designation...
, and transportation
Blue collar
Blue collar can refer to:*Blue-collar worker, a traditional designation of the working class*Blue-collar crime, the types of crimes typically associated with the working class*A census designation...
did not. These, often described as blue collar
Blue collar
Blue collar can refer to:*Blue-collar worker, a traditional designation of the working class*Blue-collar crime, the types of crimes typically associated with the working class*A census designation...
, fields featured a labor force where less than a tenth of the population had a Bachelor's degree or higher
Bachelor's degree or higher
Bachelor's degree or higher is a commonly used term by the United States Census Bureau and other U.S. government agencies on the federal as well as state and local level. The term describes the portion of the population that has either a bachelor's degree or a higher degree such as a master's or...
, less than half had some college or an Associates, and less than 80% had graduated from high school. Overall the least educated occupational field was agriculture
Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
, ranking dead last on all educational levels. Here only 55.4% had graduated from high school, roughly one fifth (20.8%) had some college education or an Associates degree and only 6.8% had a Bachelor's degree or higher
Bachelor's degree or higher
Bachelor's degree or higher is a commonly used term by the United States Census Bureau and other U.S. government agencies on the federal as well as state and local level. The term describes the portion of the population that has either a bachelor's degree or a higher degree such as a master's or...
. While the largest occupational field, that consisting of professionals and relating occupations was also the largest field, the fields with lower educational attainment combined were larger than the professional and managerial fields combined. Overall 38.02% were employed in the professional and managerial fields while 61.89% were employed in the other white and blue collar fields were those with a Bachelor's degree or higher constituted less than a third of the work force.
Geography
Northeastern United States
The Northeastern United States is a region of the United States as defined by the United States Census Bureau.-Composition:The region comprises nine states: the New England states of Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island and Vermont; and the Mid-Atlantic states of New...
, which had the smallest population of any region with thirty-six million residents, had the highest percentage of high-school and college graduates. The western United States
Western United States
.The Western United States, commonly referred to as the American West or simply "the West," traditionally refers to the region comprising the westernmost states of the United States. Because the U.S. expanded westward after its founding, the meaning of the West has evolved over time...
had the highest percentage of those with some college or an Associates degree and ranked second for college graduates
Bachelor's degree or higher
Bachelor's degree or higher is a commonly used term by the United States Census Bureau and other U.S. government agencies on the federal as well as state and local level. The term describes the portion of the population that has either a bachelor's degree or a higher degree such as a master's or...
. The South
Southern United States
The Southern United States—commonly referred to as the American South, Dixie, or simply the South—constitutes a large distinctive area in the southeastern and south-central United States...
which had by far the largest population with roughly sixty-six million people had the lowest educational attainment at every level. The proportion of high school graduates was the largest in the Midwest
Midwestern United States
The Midwestern United States is one of the four U.S. geographic regions defined by the United States Census Bureau, providing an official definition of the American Midwest....
while the proportion of those with some college or an Associates degree was the second and that of those with a Bachelor's degree or higher
Bachelor's degree or higher
Bachelor's degree or higher is a commonly used term by the United States Census Bureau and other U.S. government agencies on the federal as well as state and local level. The term describes the portion of the population that has either a bachelor's degree or a higher degree such as a master's or...
was the third largest of any region. Overall it is fair to assume that the Northeast
Northeastern United States
The Northeastern United States is a region of the United States as defined by the United States Census Bureau.-Composition:The region comprises nine states: the New England states of Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island and Vermont; and the Mid-Atlantic states of New...
followed by the Western states
Western United States
.The Western United States, commonly referred to as the American West or simply "the West," traditionally refers to the region comprising the westernmost states of the United States. Because the U.S. expanded westward after its founding, the meaning of the West has evolved over time...
were the most educated regions in the US on the college level, with the Midwest
Midwestern United States
The Midwestern United States is one of the four U.S. geographic regions defined by the United States Census Bureau, providing an official definition of the American Midwest....
leading on the High-school level and the South
Southern United States
The Southern United States—commonly referred to as the American South, Dixie, or simply the South—constitutes a large distinctive area in the southeastern and south-central United States...
falling behind on all levels.
Social class and education
Educational attainment is one of the primary indicators of social class in the United StatesAmerican middle class
The American middle class is a social class in the United States. While the concept is typically ambiguous in popular opinion and common language use, contemporary social scientists have put forward several, more or less congruent, theories on the American middle class...
. While the American social class system is a vaguely defined concept with many contradicting theories, educational attainment emerges as one of the top assessments of social class. Not only is a high educational attainment a status symbol by itself but it is also very closely related to the other two main indicators of social class: occupation and income
Household income in the United States
Household income is a measure commonly used by the United States government and private institutions, that counts the income of all residents over the age of 18 in each household, including not only all wages and salaries, but such items as unemployment insurance, disability payments, child support...
. A graduate degree and the roughly seven to eight years of post-secondary education serve as the main requirement for entering "The professions" and becoming part of the professional middle class. Education is a major key in becoming a more privileged member of the American middle class
American middle class
The American middle class is a social class in the United States. While the concept is typically ambiguous in popular opinion and common language use, contemporary social scientists have put forward several, more or less congruent, theories on the American middle class...
. Overall, educational attainment is the main entrance barrier into more privileged parts of the middle class as it is not only of high value but is also the requirement for becoming a professional and earning the corresponding income. This corresponding income is typically significantly higher than that of someone without this higher level of educational attainment in the United States. The only exception are entrepreneurs who can rank anywhere in the class system but are usually not referred to as professional middle class unless they are of the professions.
In the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
it also important to differentiate between the statistical middle class, often defined as consisting of those who are neither rich nor poor, and the professional middle class. Recent research has shown that not only is the statistical middle of society (those with income roughly 80% to 120% of the national median or members of the mid-quintile) no longer able to afford the lifestyle indicative of the middle class, but there also seems to a widening income gap in between those who may be described as being middle class. Those in the statistical middle may have to fear lay-offs and cost-cutting downsizing as well as out-sourcing, while those in the professional middle class are largely immune to economic fluctuations and can enjoy upper-middle range incomes even in the face of recessions. As stated above education is the main requirement of becoming a member of the professional middle class and thus is also key to economic security as well as a comfortable lifestyle.
Bourdieu and cultural capital
Many scholars have studied educational attainment in the US as a form of social reproduction and stratification. In 1977, Pierre BourdieuPierre Bourdieu
Pierre Bourdieu was a French sociologist, anthropologist, and philosopher.Starting from the role of economic capital for social positioning, Bourdieu pioneered investigative frameworks and terminologies such as cultural, social, and symbolic capital, and the concepts of habitus, field or location,...
presented the idea that education leads to social reproduction and a stratified society by honoring the cultural capital of elite classes. Students who possess the valued cultural capital
Cultural capital
The term cultural capital refers to non-financial social assets; they may be educational or intellectual, which might promote social mobility beyond economic means....
, according to Bourdieu, are rewarded with high academic achievement. When elite
Elite
Elite refers to an exceptional or privileged group that wields considerable power within its sphere of influence...
class members enter the workforce, they are channeled into high paying jobs and powerful positions within society, while those who did not achieve the same level of academic success fall into subordinate occupations and status levels. By rewarding the desired cultural capital with high academic achievement, upper classes are able and prepared to reach higher levels of educational attainment. Members of the working class, on the other hand, are not rewarded for their cultural capital in schools, and are instead socialized for working class jobs.
Lareau and concerted cultivation
Annette LareauAnnette Lareau
Annette Lareau is a sociologist working at the University of Pennsylvania. She is a graduate of U.C. Santa Cruz and earned her PhD in Sociology from U.C. Berkeley. She started her career at South Illinois University at Carbondale and also previously worked as a Professor of Sociology at Temple...
also addresses the factors that lead to social stratification in educational attainment. Lareau’s idea of concerted cultivation refers to an active involvement of parents in a child’s learning and development experiences by creating and controlling organized activities for their children. According to Lareau, middle class parents engage in concerted cultivation
Concerted cultivation
Concerted cultivation is a style of parenting that is marked by a parent's attempts to foster their child's talents through organized leisure activities. This parenting style is commonly exhibited in middle and upper class American families...
to teach their children, while lower and working class parents do not. Laureau further explains that schools firmly encourage and expect parents to use concerted cultivation as a child-rearing strategy. The child-rearing practices of lower and working class families thus do not comply with the standards of educational institutions. As a result, lower and working class students develop a sense of “distance, distrust, and constraint” in educational institutions, while children of middle class families gain a sense of entitlement. These differences in child rearing practices lead to children of lower and working class families to lack the necessary life skills that the children of the middle class possess, further isolating them from educational opportunities.
Collins and credentialism
Randall CollinsRandall Collins
Randall Collins, Ph.D. is the Dorothy Swaine Thomas Professor in Sociology at the University of Pennsylvania and a member of the Advisory Editors Council of the Social Evolution & History Journal. He is considered to be one of the leading non-Marxist conflict theorists in the United...
contributed the idea of credentialism
Credentialism
Credentialism is a term used to describe a primary reliance on credentials for purposes of conferring jobs or social status. In some jobs, employers require a diploma, academic degree, security clearance, or professional license for a job which does not require the specific training that is part of...
to the study of class-based differences in educational attainment. Collins maintains that public schools are socializing institutions that teach and reward middle class values of competition and achievement. Anglo-Protestant elites are selectively separated from other students and placed into prestigious schools and colleges, where they are trained to hold positions of power. By teaching middle-class culture through the public education system, the elite class ensures a monopoly over positions of power, while others acquire the credentials to compete in a subordinate job market and economy. In this way, schools of medicine, law, and elite institutions have remained closed to members of lower classes.
See also
- American middle classAmerican middle classThe American middle class is a social class in the United States. While the concept is typically ambiguous in popular opinion and common language use, contemporary social scientists have put forward several, more or less congruent, theories on the American middle class...
- Education in the United StatesEducation in the United StatesEducation in the United States is mainly provided by the public sector, with control and funding coming from three levels: federal, state, and local. Child education is compulsory.Public education is universally available...
- Household income in the United StatesHousehold income in the United StatesHousehold income is a measure commonly used by the United States government and private institutions, that counts the income of all residents over the age of 18 in each household, including not only all wages and salaries, but such items as unemployment insurance, disability payments, child support...
- Literacy in the United StatesLiteracy in the United StatesRates of literacy in the United States depend on which of the various definitions of literacy is used. Governments may label individuals who can read a couple of thousand simple words they learned by sight in the first four grades in school as literate...
- Poverty in the United StatesPoverty in the United StatesPoverty is defined as the state of one who lacks a usual or socially acceptable amount of money or material possessions. According to the U.S. Census Bureau data released Tuesday September 13th, 2011, the nation's poverty rate rose to 15.1% in 2010, up from 14.3% in 2009 and to its highest level...
- List of U.S. States by Education attainment
General:
- Academic degreeAcademic degreeAn academic degree is a position and title within a college or university that is usually awarded in recognition of the recipient having either satisfactorily completed a prescribed course of study or having conducted a scholarly endeavour deemed worthy of his or her admission to the degree...
- Status attainmentStatus attainmentStatus attainment or status attainment theory is a concept of sociology.It deals largely with one's position in society, or class. Status attainment is affected by both achieved factors, such as educational attainment, and ascribed factors, such as family income. It is achieved by a combination of...
External links
- Educational Attainment in the United States: 2003, U.S. Census Bureau
- The Big Payoff: Educational Attainment and Synthetic Estimates of Work-Life Earnings, U.S. Census Bureau

