
Effects of parasitic worms on the immune system
Encyclopedia
The effects of parasitic worms, or helminths, on the immune system
is a recently emerging topic of study among immunologists
and other biologists. Experiments have involved a wide range of parasites
, diseases, and hosts
. The effects on humans have been of special interest. The tendency of many parasitic worms to pacify the host's immune response allows them to mollify some diseases, while worsening others.
, and the body itself.
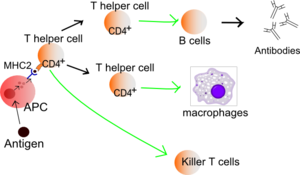 In the past, helminths were thought to simply suppress T-helper Type 1 (Th1) cells while inducing T-helper Type 2 (Th2) cells. Rook points out that this hypothesis would only explain the regulatory effects of parasitic worms on autoimmune diseases caused by Th1 cells. However, helminths also regulate Th2-caused diseases, such as allergy
In the past, helminths were thought to simply suppress T-helper Type 1 (Th1) cells while inducing T-helper Type 2 (Th2) cells. Rook points out that this hypothesis would only explain the regulatory effects of parasitic worms on autoimmune diseases caused by Th1 cells. However, helminths also regulate Th2-caused diseases, such as allergy
and asthma
. Professor Rook postulates that different parasitic worms suppress different Th types, but always in favor of regulatory T (Treg) cells
.
Professor Rook explains that these regulatory T cells release interleukins that fight inflammation
. In the Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology, Dr. Osada et al. note that macrophages induced by Treg cells fight not only the parasitic disease, but also resist the immune system's response to allergens and the body. According to Dr. Hopkin, the author of a 2009 Parasite Immunology article on asthma and parasitic worms, other immunoregulatory mechanisms are also activated, including Mast cells, eosinophils, and cytokines that invoke a strong immunoglobulin E (IgE)
response. All these fight a hyperactive immune response, reduce the inflammation throughout the body, and thus lead to less severe autoimmune diseases.
Dr. Osada et al. state that because parasitic worms may and often do consist of allergens themselves, the degree to which they pacify or agitate the immune response against allergens is a balance of their regulating effects and their allergenic components. Therefore, depending on both of these variables, some parasitic worms may worsen allergies.
In their Parasite Immunology article on worms and viral infections, Dr. Kamal et al. explain why some parasitic worms aggravate the immune response. Because parasitic worms often induce Th2 cells and lead to suppressed Th1 cells, problems arise when Th1 cells are needed. Such cases occur with viral diseases. Several examples of viral infections worsened by parasitic worms are described below.
, when humans and human ancestors
would have been constantly inhabited by parasitic worms. In the academic journal EMBO Reports, Dr. Rook says that such helminths “are all either things that really do us no harm, or things where the immune system is forced to give in and avoid a fight because it’s just a waste of time.” In the scientific journal Immunology, Rook states that, because parasitic worms were almost always present, the human immune system developed a way to treat them that didn't cause tissue damage.
The immune system extends this response to its treatments of self-antigens
, softening reactions against allergens, the body, and digestive microorganisms. As the worms developed ways of triggering a beneficial immune response, humans came to rely on parasitic interaction to help regulate their immune systems.
As developed countries advanced in technology, medicine, and sanitation, parasitic worms were mostly eradicated in those countries, according to Dr. Weinstock in the medical journal GUT. Because these events took place very recently on the evolutionary timeline and humans have progressed much faster technologically than genetically, the human immune system has not yet adapted to the absence of internal worms. This theory attempts to explain the rapid increase in allergies and asthma in the last century in the developed world, as well as the relative absence of autoimmune diseases in the developing world, where parasites are more common.
postulates that decreasing exposure to pathogens and other microorganisms results in an increase of autoimmune diseases, according to Dr. Rook. This theory and the theory that certain parasitic worms pacify the immune response are similar in that both attribute the recent rise of autoimmune diseases to the decrease of pathogens in developed countries. However, the Hygiene Hypothesis claims that the absence of pathogenic organisms in general has led to this. In contrast, the parasitic worm theory only analyzes helminths, and specifically ones found to have a regulating effect.
In an experiment with mice, infection with parasitic worms or helminth-products generally inhibited the spontaneous development of T1D, according to Dr. Anne Cook in the journal Immunology. However, results varied among the different species of parasitic worms. Some, like a protein of the nematode
Acanthocheilonema viteae
, didn't have any effect. Of those that did have effect, Salmonella typhimurium was successful even when administered late in the development of T1D.
, which in turn involves the release of mediators that induce inflammation. In 2007, Dr. Melendez and his associates studied filarial nematodes and ES-62, a protein that nematodes secrete in their host. They discovered that pure ES-62 prevents the release of allergenic inflammatory mediators in mice, resulting in weaker allergic and asthmatic symptoms. In the Journal of Immunology, Dr. Bashir et al. describe their experimental findings that an allergic response against peanuts is inhibited in mice infected with an intestinal parasite.
is an autoimmune disease involving the inflammation of mucus
. Ulcerative colitis (UC)
and Crohn's Disease (CD)
are both types of IBD. In the medical journal GUT, Dr. Moreels et al. describe their experiments on induced colitis in rats. They found that infecting the rats with the parasitic worm Schistosoma mansoni
resulted in alleviated colitis effects. According to Dr. Weinstock, human patients of UC or CD improve when infected with the parasitic worm whipworm
.
. Dr. Correale evaluated several MS patients infected with parasites, comparable MS patients without parasites, and similar healthy subjects over the course of 4.6 years. During the study, the MS patients that were infected with parasites experienced far less effects of MS than the non-infected MS patients.
because such worms induce a Th2-biased immune response that is less responsive than normal to antigens. This is a major concern in developing countries where parasitic worms and the need for vaccinations exist in large number. It may explain why vaccines are often ineffective in developing countries.
and the parasitic worm Schistosoma
(the bloodfluke) are relatively common in developing countries, there are many cases where both are present in the human body. According to Dr. Kamal, bloodflukes have been adequately shown to worsen HCV. Dr. Kamal explains that, in order to maintain an immune response against HCV, patients must sustain a certain level of CD4+ T-cells. However, the presence of bloodflukes closely and negatively correlates to the presence of CD4+ T-cells, and so a much higher percentage of those infected with bloodflukes are unable to combat HCV effectively and develop chronic HCV. Parasitic effects of Hepatitis B virus, however, are contested—some studies show little association, while others show exacerbation of the disease.
and parasites, and specifically bloodflukes. In his article, Dr. Kamal relates the findings that those infected with parasites are more likely to be infected by HIV. However, it is disputed whether or not the viral infection is more severe because of the parasites.
. Since the immune system often responds to parasitic worms by inhibiting Th1 cells, parasitic worms generally worsen tuberculosis
. In fact, Tuberculosis patients who receive successful parasitic therapy experience major improvement.
 In 2004, Dr. Sokhna et al. performed a study of Senegalese children. Those infected with blood flukes had significantly higher rates of malaria
In 2004, Dr. Sokhna et al. performed a study of Senegalese children. Those infected with blood flukes had significantly higher rates of malaria
attacks than those who were not. Furthermore, children with the highest counts of blood flukes also had the most malaria attacks. Based on this study, Dr. Hartgers et al. drew a “cautious conclusion” that helminths make humans more susceptible to contracting malaria and experiencing some of its lighter symptoms, while actually protecting them from the worst symptoms. Hartgers reasons that a Th2-skewed immune system resulting from helminth infection would lower the immune system's ability to counter an initial malarial infection. However, it would also prevent a hyperimmune response resulting in severe inflammation.
See also=
Immune system
An immune system is a system of biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease by identifying and killing pathogens and tumor cells. It detects a wide variety of agents, from viruses to parasitic worms, and needs to distinguish them from the organism's own...
is a recently emerging topic of study among immunologists
Immunology
Immunology is a broad branch of biomedical science that covers the study of all aspects of the immune system in all organisms. It deals with the physiological functioning of the immune system in states of both health and diseases; malfunctions of the immune system in immunological disorders ; the...
and other biologists. Experiments have involved a wide range of parasites
Parasitism
Parasitism is a type of symbiotic relationship between organisms of different species where one organism, the parasite, benefits at the expense of the other, the host. Traditionally parasite referred to organisms with lifestages that needed more than one host . These are now called macroparasites...
, diseases, and hosts
Host (biology)
In biology, a host is an organism that harbors a parasite, or a mutual or commensal symbiont, typically providing nourishment and shelter. In botany, a host plant is one that supplies food resources and substrate for certain insects or other fauna...
. The effects on humans have been of special interest. The tendency of many parasitic worms to pacify the host's immune response allows them to mollify some diseases, while worsening others.
Mechanisms of Immune Regulation
Extensive research shows that parasitic worms have the ability to deactivate certain immune system cells, leading to a gentler immune response. Often, such a response is beneficial to both parasite and host, according to Professor of Medical Microbiology Graham Rook of University College London. This immune “relaxation” is incorporated throughout the immune system, decreasing immune responses against harmless allergens, gut floraGut flora
Gut flora consists of microorganisms that live in the digestive tracts of animals and is the largest reservoir of human flora. In this context, gut is synonymous with intestinal, and flora with microbiota and microflora....
, and the body itself.

Allergy
An Allergy is a hypersensitivity disorder of the immune system. Allergic reactions occur when a person's immune system reacts to normally harmless substances in the environment. A substance that causes a reaction is called an allergen. These reactions are acquired, predictable, and rapid...
and asthma
Asthma
Asthma is the common chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and bronchospasm. Symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath...
. Professor Rook postulates that different parasitic worms suppress different Th types, but always in favor of regulatory T (Treg) cells
Regulatory T cell
Regulatory T cells , sometimes known as suppressor T cells, are a specialized subpopulation of T cells which suppresses activation of the immune system and thereby maintains tolerance to self-antigens. The existence of regulatory T cells was the subject of significant controversy among...
.
Professor Rook explains that these regulatory T cells release interleukins that fight inflammation
Inflammation
Inflammation is part of the complex biological response of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. Inflammation is a protective attempt by the organism to remove the injurious stimuli and to initiate the healing process...
. In the Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology, Dr. Osada et al. note that macrophages induced by Treg cells fight not only the parasitic disease, but also resist the immune system's response to allergens and the body. According to Dr. Hopkin, the author of a 2009 Parasite Immunology article on asthma and parasitic worms, other immunoregulatory mechanisms are also activated, including Mast cells, eosinophils, and cytokines that invoke a strong immunoglobulin E (IgE)
IGE
IGE was one of the largest services company buying and selling virtual currencies and accounts for MMORPG. During its peak time, it had offices in Los Angeles, China , and headquarters & customer service centre in Hong Kong. IGE was one of the main monopoly in virtual economy services, also known...
response. All these fight a hyperactive immune response, reduce the inflammation throughout the body, and thus lead to less severe autoimmune diseases.
Dr. Osada et al. state that because parasitic worms may and often do consist of allergens themselves, the degree to which they pacify or agitate the immune response against allergens is a balance of their regulating effects and their allergenic components. Therefore, depending on both of these variables, some parasitic worms may worsen allergies.
In their Parasite Immunology article on worms and viral infections, Dr. Kamal et al. explain why some parasitic worms aggravate the immune response. Because parasitic worms often induce Th2 cells and lead to suppressed Th1 cells, problems arise when Th1 cells are needed. Such cases occur with viral diseases. Several examples of viral infections worsened by parasitic worms are described below.
Evolutionary Theory
The positive effects of parasitic worms are theorized to be a result of millions of years of evolutionEvolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
, when humans and human ancestors
Human evolution
Human evolution refers to the evolutionary history of the genus Homo, including the emergence of Homo sapiens as a distinct species and as a unique category of hominids and mammals...
would have been constantly inhabited by parasitic worms. In the academic journal EMBO Reports, Dr. Rook says that such helminths “are all either things that really do us no harm, or things where the immune system is forced to give in and avoid a fight because it’s just a waste of time.” In the scientific journal Immunology, Rook states that, because parasitic worms were almost always present, the human immune system developed a way to treat them that didn't cause tissue damage.
The immune system extends this response to its treatments of self-antigens
Autoimmunity
Autoimmunity is the failure of an organism to recognize its own constituent parts as self, which allows an immune response against its own cells and tissues. Any disease that results from such an aberrant immune response is termed an autoimmune disease...
, softening reactions against allergens, the body, and digestive microorganisms. As the worms developed ways of triggering a beneficial immune response, humans came to rely on parasitic interaction to help regulate their immune systems.
As developed countries advanced in technology, medicine, and sanitation, parasitic worms were mostly eradicated in those countries, according to Dr. Weinstock in the medical journal GUT. Because these events took place very recently on the evolutionary timeline and humans have progressed much faster technologically than genetically, the human immune system has not yet adapted to the absence of internal worms. This theory attempts to explain the rapid increase in allergies and asthma in the last century in the developed world, as well as the relative absence of autoimmune diseases in the developing world, where parasites are more common.
Comparison with the Hygiene hypothesis
The Hygiene hypothesisHygiene hypothesis
In medicine, the Hygiene Hypothesis states that a lack of early childhood exposure to infectious agents, symbiotic microorganisms , and parasites increases susceptibility to allergic diseases by suppressing natural development of the immune system...
postulates that decreasing exposure to pathogens and other microorganisms results in an increase of autoimmune diseases, according to Dr. Rook. This theory and the theory that certain parasitic worms pacify the immune response are similar in that both attribute the recent rise of autoimmune diseases to the decrease of pathogens in developed countries. However, the Hygiene Hypothesis claims that the absence of pathogenic organisms in general has led to this. In contrast, the parasitic worm theory only analyzes helminths, and specifically ones found to have a regulating effect.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) is an autoimmune disease where the immune system destroys the body's pancreatic beta cells.In an experiment with mice, infection with parasitic worms or helminth-products generally inhibited the spontaneous development of T1D, according to Dr. Anne Cook in the journal Immunology. However, results varied among the different species of parasitic worms. Some, like a protein of the nematode
Nematode
The nematodes or roundworms are the most diverse phylum of pseudocoelomates, and one of the most diverse of all animals. Nematode species are very difficult to distinguish; over 28,000 have been described, of which over 16,000 are parasitic. It has been estimated that the total number of nematode...
Acanthocheilonema viteae
Acanthocheilonema viteae
Acanthocheilonema viteae is a parasitic nematode.-External links:*...
, didn't have any effect. Of those that did have effect, Salmonella typhimurium was successful even when administered late in the development of T1D.
Allergy and Asthma
According to Dr. Hopkin, asthma involves atopic allergyAllergy
An Allergy is a hypersensitivity disorder of the immune system. Allergic reactions occur when a person's immune system reacts to normally harmless substances in the environment. A substance that causes a reaction is called an allergen. These reactions are acquired, predictable, and rapid...
, which in turn involves the release of mediators that induce inflammation. In 2007, Dr. Melendez and his associates studied filarial nematodes and ES-62, a protein that nematodes secrete in their host. They discovered that pure ES-62 prevents the release of allergenic inflammatory mediators in mice, resulting in weaker allergic and asthmatic symptoms. In the Journal of Immunology, Dr. Bashir et al. describe their experimental findings that an allergic response against peanuts is inhibited in mice infected with an intestinal parasite.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory Bowel Disease(IBD)Inflammatory bowel disease
In medicine, inflammatory bowel disease is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine. The major types of IBD are Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.-Classification:...
is an autoimmune disease involving the inflammation of mucus
Mucus
In vertebrates, mucus is a slippery secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. Mucous fluid is typically produced from mucous cells found in mucous glands. Mucous cells secrete products that are rich in glycoproteins and water. Mucous fluid may also originate from mixed glands, which...
. Ulcerative colitis (UC)
Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a form of inflammatory bowel disease . Ulcerative colitis is a form of colitis, a disease of the colon , that includes characteristic ulcers, or open sores. The main symptom of active disease is usually constant diarrhea mixed with blood, of gradual onset...
and Crohn's Disease (CD)
Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease, also known as regional enteritis, is a type of inflammatory bowel disease that may affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract from mouth to anus, causing a wide variety of symptoms...
are both types of IBD. In the medical journal GUT, Dr. Moreels et al. describe their experiments on induced colitis in rats. They found that infecting the rats with the parasitic worm Schistosoma mansoni
Schistosoma mansoni
Schistosoma mansoni is a significant parasite of humans, a trematode that is one of the major agents of the disease schistosomiasis. The schistosomiasis caused by Schistosoma mansoni is intestinal schistosomiasis....
resulted in alleviated colitis effects. According to Dr. Weinstock, human patients of UC or CD improve when infected with the parasitic worm whipworm
Whipworm
The human tapworm is a roundworm, which causes trichuriasis when it infects a human large intestine. The name whipworm refers to the shape of the worm; they look like whips with wider "handles" at the posterior end.-Life cycle:The female T. trichiura produces 2,000–10,000 single celled eggs per day...
.
Arthritis
In 2003, Dr. Iain McInnes et al. found that arthritic-induced mice experienced less inflammation and other arthritic effects when infected with ES-62, a protein derived from filarial nematodes, a kind of parasitic worm. Similarly, in the International Journal for Parasitology, Dr. Osada et al. published their experimental findings that arthritis-induced mice infected with the parasitic worm Schistosoma mansoni had down-regulated immune systems. This led to resistance to arthritis.Multiple Sclerosis
In 2007, Dr. Jorge Correale et al. studied the effects of parasitic infection on Multiple Sclerosis (MS)Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is an inflammatory disease in which the fatty myelin sheaths around the axons of the brain and spinal cord are damaged, leading to demyelination and scarring as well as a broad spectrum of signs and symptoms...
. Dr. Correale evaluated several MS patients infected with parasites, comparable MS patients without parasites, and similar healthy subjects over the course of 4.6 years. During the study, the MS patients that were infected with parasites experienced far less effects of MS than the non-infected MS patients.
Vaccination
In the journal Parasite Immunulogy, Dr. Kamal et al. explains that parasitic worms often weaken the immune system's ability to effectively respond to a vaccineVaccine
A vaccine is a biological preparation that improves immunity to a particular disease. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism, and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe or its toxins...
because such worms induce a Th2-biased immune response that is less responsive than normal to antigens. This is a major concern in developing countries where parasitic worms and the need for vaccinations exist in large number. It may explain why vaccines are often ineffective in developing countries.
Hepatitis
Because Hepatitis C virus (HCV)Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease primarily affecting the liver, caused by the hepatitis C virus . The infection is often asymptomatic, but chronic infection can lead to scarring of the liver and ultimately to cirrhosis, which is generally apparent after many years...
and the parasitic worm Schistosoma
Schistosoma
A genus of trematodes, Schistosoma, commonly known as blood-flukes and bilharzia, includes flatworms which are responsible for a highly significant parasitic infection of humans by causing the disease schistosomiasis, and are considered by the World Health Organization as the second most...
(the bloodfluke) are relatively common in developing countries, there are many cases where both are present in the human body. According to Dr. Kamal, bloodflukes have been adequately shown to worsen HCV. Dr. Kamal explains that, in order to maintain an immune response against HCV, patients must sustain a certain level of CD4+ T-cells. However, the presence of bloodflukes closely and negatively correlates to the presence of CD4+ T-cells, and so a much higher percentage of those infected with bloodflukes are unable to combat HCV effectively and develop chronic HCV. Parasitic effects of Hepatitis B virus, however, are contested—some studies show little association, while others show exacerbation of the disease.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
Because the two diseases are abundant in developing countries, there are many patients with both Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus is a lentivirus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome , a condition in humans in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive...
and parasites, and specifically bloodflukes. In his article, Dr. Kamal relates the findings that those infected with parasites are more likely to be infected by HIV. However, it is disputed whether or not the viral infection is more severe because of the parasites.
Tuberculosis
According to Dr. Kamal, the human immune system needs Th1 cells to effectively fight TBTuberculosis
Tuberculosis, MTB, or TB is a common, and in many cases lethal, infectious disease caused by various strains of mycobacteria, usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis usually attacks the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body...
. Since the immune system often responds to parasitic worms by inhibiting Th1 cells, parasitic worms generally worsen tuberculosis
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis, MTB, or TB is a common, and in many cases lethal, infectious disease caused by various strains of mycobacteria, usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis usually attacks the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body...
. In fact, Tuberculosis patients who receive successful parasitic therapy experience major improvement.
Malaria

Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease of humans and other animals caused by eukaryotic protists of the genus Plasmodium. The disease results from the multiplication of Plasmodium parasites within red blood cells, causing symptoms that typically include fever and headache, in severe cases...
attacks than those who were not. Furthermore, children with the highest counts of blood flukes also had the most malaria attacks. Based on this study, Dr. Hartgers et al. drew a “cautious conclusion” that helminths make humans more susceptible to contracting malaria and experiencing some of its lighter symptoms, while actually protecting them from the worst symptoms. Hartgers reasons that a Th2-skewed immune system resulting from helminth infection would lower the immune system's ability to counter an initial malarial infection. However, it would also prevent a hyperimmune response resulting in severe inflammation.
See also=
- Hygiene hypothesisHygiene hypothesisIn medicine, the Hygiene Hypothesis states that a lack of early childhood exposure to infectious agents, symbiotic microorganisms , and parasites increases susceptibility to allergic diseases by suppressing natural development of the immune system...
- Evolutionary medicineEvolutionary medicineEvolutionary medicine or Darwinian medicine is the application of modern evolutionary theory to understanding health and disease. It provides a complementary scientific approach to the present mechanistic explanations that dominate medical science, and particularly modern medical education...
- Helminthic therapyHelminthic therapyHelminthic therapy, a type of immunotherapy, is the treatment of autoimmune diseases and immune disorders by means of deliberate infestation with a helminth or with the ova of a helminth. Helminths are parasitic worms such as hookworms and whipworms....
- ImmunotherapyImmunotherapyImmunotherapy is a medical term defined as the "treatment of disease by inducing, enhancing, or suppressing an immune response". Immunotherapies designed to elicit or amplify an immune response are classified as activation immunotherapies. While immunotherapies that reduce or suppress are...
- Disease of affluence

