
Einiosaurus
Encyclopedia
Einiosaurus is a medium-sized centrosaurine (“short-frilled”) ceratopsian from the Upper Cretaceous
(Campanian
stage) of northwestern Montana
. The name means 'buffalo lizard', in a combination of Blackfeet
Indian and Latinized Ancient Greek
; the specific name (E. procurvicornis) means 'forward-curving horn' in Latin
.
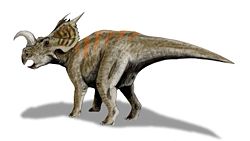 Einiosaurus was a herbivorous dinosaur and grew to 6 m (19.8 ft) in length. It is typically portrayed with a low, strongly forward-curving nasal horn that resembles a bottle opener, though this may only occur in some adults. Supraorbital (over-the-eye) horns are low and rounded if present at all, as opposed to ceratopsids with prominent supraorbital horns such as Triceratops
Einiosaurus was a herbivorous dinosaur and grew to 6 m (19.8 ft) in length. It is typically portrayed with a low, strongly forward-curving nasal horn that resembles a bottle opener, though this may only occur in some adults. Supraorbital (over-the-eye) horns are low and rounded if present at all, as opposed to ceratopsids with prominent supraorbital horns such as Triceratops
. A pair of large spikes projects backwards from the relatively small frill. Einiosaurus lived in an inland habitat.
and Centrosaurus
, were herding animals similar in behavior to modern-day bison
or wildebeest
. In contrast, ceratopsine (“long-frilled”) ceratopsids, such as Triceratops
and Torosaurus
, are typically found singly, implying that they may have been somewhat solitary in life, though fossilized footprints may provide evidence to the contrary.
Like all ceratopsids, Einiosaurus had a complex dental battery capable of processing even the toughest plants.
Einiosaurus fossils are found in the upper part of the Two Medicine Formation
of Montana, dating to the mid-late Campanian stage of the late Cretaceous Period, about 74.5-74 million years ago. Dinosaurs that lived alongside Einiosaurus include the basal ornithopod
Orodromeus
, hadrosaurids (such as Hypacrosaurus
, Maiasaura
, and Prosaurolophus
), the ankylosaurs Edmontonia
and Euoplocephalus
, the tyrannosaurid Daspletosaurus
(which appears to have been a specialist of preying on ceratopsians), as well as the smaller theropods
Bambiraptor
, Chirostenotes
, Troodon
, and Avisaurus
. Einiosaurus lived in a climate that was seasonal, warm, and semi-arid. Other fossils found with the Einiosaurus material include freshwater bivalves and gastropods, which imply that these bones were deposited in a shallow lake environment.
, and all its known remains are currently held at the Museum of the Rockies
in Bozeman, Montana. At least 15 individuals of varying ages are represented by three adult skulls and hundreds of other bones from two low-diversity (in species) bonebeds, which were discovered by Jack Horner in 1985 and excavated from 1985-1989 by Museum of the Rockies
field crews. These bonebeds were originally thought to contain a new species of Styracosaurus
and are referred to as such in the comprehensive taphonomic study by Ray Rogers. In 1995 Scott D. Sampson formally described and named Einiosaurus procurvicornis from this material, as well as Achelousaurus horneri
, also from a bonebed in this region.
is problematic due to the transitional nature of several of its skull characters, and its closest relatives are either Centrosaurus
and Styracosaurus
or Achelousaurus
and Pachyrhinosaurus
. The latter hypothesis is supported by Horner and colleagues, where Einiosaurus is the earliest of an evolutionary series in which the nasal horns gradually change to rough bosses, as in Achelousaurus and Pachyrhinosaurus which are the second and third in this series. The frills also grow in complexity.
Regardless of which hypothesis is correct, Einiosaurus appears to occupy an intermediate position with respect to the evolution
of the centrosaurines.
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
(Campanian
Campanian
The Campanian is, in the ICS' geologic timescale, the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous epoch . The Campanian spans the time from 83.5 ± 0.7 Ma to 70.6 ± 0.6 Ma ...
stage) of northwestern Montana
Montana
Montana is a state in the Western United States. The western third of Montana contains numerous mountain ranges. Smaller, "island ranges" are found in the central third of the state, for a total of 77 named ranges of the Rocky Mountains. This geographical fact is reflected in the state's name,...
. The name means 'buffalo lizard', in a combination of Blackfeet
Blackfeet
The Piegan Blackfeet are a tribe of Native Americans of the Algonquian language family based in Montana, having lived in this area since around 6,500 BC. Many members of the tribe live as part of the Blackfeet Nation in northwestern Montana, with population centered in Browning...
Indian and Latinized Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek is the stage of the Greek language in the periods spanning the times c. 9th–6th centuries BC, , c. 5th–4th centuries BC , and the c. 3rd century BC – 6th century AD of ancient Greece and the ancient world; being predated in the 2nd millennium BC by Mycenaean Greek...
; the specific name (E. procurvicornis) means 'forward-curving horn' in Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
.
Description

Triceratops
Triceratops is a genus of herbivorous ceratopsid dinosaur which lived during the late Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous Period, around 68 to 65 million years ago in what is now North America. It was one of the last dinosaur genera to appear before the great Cretaceous–Paleogene...
. A pair of large spikes projects backwards from the relatively small frill. Einiosaurus lived in an inland habitat.
Paleobiology
Low-diversity and single-species bonebeds are thought to represent herds that may have died in catastrophic events, such as during a drought or flood. This is evidence that Einiosaurus, as well as other centrosaurine ceratopsians such as PachyrhinosaurusPachyrhinosaurus
Pachyrhinosaurus is a genus of ceratopsid dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous period of North America. The first examples were discovered by Charles M. Sternberg in Alberta, Canada, in 1946, and named in 1950. Over a dozen partial skulls and a large assortment of other fossils from various species...
and Centrosaurus
Centrosaurus
Centrosaurus is a genus of herbivorous ceratopsian dinosaurs from the late Cretaceous of Canada. Their remains have been found in the Dinosaur Park Formation and uppermost Oldman Formation, dating from 76.5 to 75.5 million years ago....
, were herding animals similar in behavior to modern-day bison
Bison
Members of the genus Bison are large, even-toed ungulates within the subfamily Bovinae. Two extant and four extinct species are recognized...
or wildebeest
Wildebeest
The wildebeest , also called the gnu is an antelope of the genus Connochaetes. It is a hooved mammal...
. In contrast, ceratopsine (“long-frilled”) ceratopsids, such as Triceratops
Triceratops
Triceratops is a genus of herbivorous ceratopsid dinosaur which lived during the late Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous Period, around 68 to 65 million years ago in what is now North America. It was one of the last dinosaur genera to appear before the great Cretaceous–Paleogene...
and Torosaurus
Torosaurus
Torosaurus is a genus of ceratopsid dinosaur that lived during the late Cretaceous period , between 70 and 65 million years ago. It possessed one of the largest skulls of any known land animal. The frilled skull reached in length...
, are typically found singly, implying that they may have been somewhat solitary in life, though fossilized footprints may provide evidence to the contrary.
Like all ceratopsids, Einiosaurus had a complex dental battery capable of processing even the toughest plants.
Einiosaurus fossils are found in the upper part of the Two Medicine Formation
Two Medicine Formation
The Two Medicine Formation is a geologic formation, or rock body, that was deposited between 83.5 ± 0.7 Ma to 70.6 ± 0.6 Ma , during Campanian time, and is located in northwestern Montana...
of Montana, dating to the mid-late Campanian stage of the late Cretaceous Period, about 74.5-74 million years ago. Dinosaurs that lived alongside Einiosaurus include the basal ornithopod
Ornithopod
Ornithopods or members of the clade Ornithopoda are a group of ornithischian dinosaurs that started out as small, bipedal running grazers, and grew in size and numbers until they became one of the most successful groups of herbivores in the Cretaceous world, and dominated the North American...
Orodromeus
Orodromeus
Orodromeus is a genus of herbivorous ornithopod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of North America.-Discovery and naming:...
, hadrosaurids (such as Hypacrosaurus
Hypacrosaurus
Hypacrosaurus was a genus of duckbill dinosaur similar in appearance to Corythosaurus. Like Corythosaurus, it had a tall, hollow rounded crest, although not as large and straight...
, Maiasaura
Maiasaura
Maiasaura is a large duck-billed dinosaur genus that lived in the area currently covered by the state of Montana in the Upper Cretaceous Period , about 74 million years ago....
, and Prosaurolophus
Prosaurolophus
Prosaurolophus is a genus of hadrosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of North America. It is known from the remains of at least 25 individuals belonging to two species, including skulls and skeletons, but it remains obscure...
), the ankylosaurs Edmontonia
Edmontonia
Edmontonia was an armoured dinosaur, a part of the nodosaur family from the Late Cretaceous Period. It is named after the Edmonton Formation , the unit of rock it was found in.-Description:...
and Euoplocephalus
Euoplocephalus
Euoplocephalus was one of the largest genera of ankylosaurian dinosaurs, at about the size of a small elephant. It is also the ankylosaurian with the best fossil record, so its extensive spiked armor, low-slung body and great club-like tail are well documented.-Description:Among the...
, the tyrannosaurid Daspletosaurus
Daspletosaurus
Daspletosaurus is a genus of tyrannosaurid theropod dinosaur that lived in western North America between 77 and 74 million years ago, during the Late Cretaceous Period. Fossils of the only named species were found in Alberta, although other possible species from Alberta and Montana await...
(which appears to have been a specialist of preying on ceratopsians), as well as the smaller theropods
Theropoda
Theropoda is both a suborder of bipedal saurischian dinosaurs, and a clade consisting of that suborder and its descendants . Dinosaurs belonging to the suborder theropoda were primarily carnivorous, although a number of theropod groups evolved herbivory, omnivory, and insectivory...
Bambiraptor
Bambiraptor
Bambiraptor is a Late Cretaceous, 75 million year old, bird-like dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaur described by scientists at the University of Kansas, Yale University, and the University of New Orleans....
, Chirostenotes
Chirostenotes
Chirostenotes is a genus of oviraptorosaurian dinosaur from the late Cretaceous of Alberta, Canada. The type species is Chirostenotes pergracilis. Some researchers recognize a second species, C...
, Troodon
Troodon
Troodon is a genus of relatively small, bird-like dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous period . Discovered in 1855, it was among the first dinosaurs found in North America...
, and Avisaurus
Avisaurus
Avisaurus is a genus of enantiornithine bird from the Late Cretaceous of North America.Two species are known; the type species A. archibaldi and A. gloriae...
. Einiosaurus lived in a climate that was seasonal, warm, and semi-arid. Other fossils found with the Einiosaurus material include freshwater bivalves and gastropods, which imply that these bones were deposited in a shallow lake environment.
History of discovery
Einiosaurus is an exclusively Montanan dinosaurDinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of animals of the clade and superorder Dinosauria. They were the dominant terrestrial vertebrates for over 160 million years, from the late Triassic period until the end of the Cretaceous , when the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event led to the extinction of...
, and all its known remains are currently held at the Museum of the Rockies
Museum of the Rockies
The Museum of the Rockies, is located in Bozeman, Montana. The museum, originally affiliated with Montana State University in Bozeman, and now, also the Smithsonian Institution, is known for its paleontological collections, although these are not its sole focus...
in Bozeman, Montana. At least 15 individuals of varying ages are represented by three adult skulls and hundreds of other bones from two low-diversity (in species) bonebeds, which were discovered by Jack Horner in 1985 and excavated from 1985-1989 by Museum of the Rockies
Museum of the Rockies
The Museum of the Rockies, is located in Bozeman, Montana. The museum, originally affiliated with Montana State University in Bozeman, and now, also the Smithsonian Institution, is known for its paleontological collections, although these are not its sole focus...
field crews. These bonebeds were originally thought to contain a new species of Styracosaurus
Styracosaurus
Styracosaurus was a genus of herbivorous ceratopsian dinosaur from the Cretaceous Period , about 76.5 to 75.0 million years ago...
and are referred to as such in the comprehensive taphonomic study by Ray Rogers. In 1995 Scott D. Sampson formally described and named Einiosaurus procurvicornis from this material, as well as Achelousaurus horneri
Achelousaurus
Achelousaurus is a genus of centrosaurine ceratopsid dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now North America, dated to 74 million years ago...
, also from a bonebed in this region.
Classification
The placement of Einiosaurus within CentrosaurinaeCentrosaurinae
The Centrosaurinae is a subfamily of ceratopsid dinosaurs named by paleontologist Lawrence Lambe, in 1915, with Centrosaurus as the type genus...
is problematic due to the transitional nature of several of its skull characters, and its closest relatives are either Centrosaurus
Centrosaurus
Centrosaurus is a genus of herbivorous ceratopsian dinosaurs from the late Cretaceous of Canada. Their remains have been found in the Dinosaur Park Formation and uppermost Oldman Formation, dating from 76.5 to 75.5 million years ago....
and Styracosaurus
Styracosaurus
Styracosaurus was a genus of herbivorous ceratopsian dinosaur from the Cretaceous Period , about 76.5 to 75.0 million years ago...
or Achelousaurus
Achelousaurus
Achelousaurus is a genus of centrosaurine ceratopsid dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now North America, dated to 74 million years ago...
and Pachyrhinosaurus
Pachyrhinosaurus
Pachyrhinosaurus is a genus of ceratopsid dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous period of North America. The first examples were discovered by Charles M. Sternberg in Alberta, Canada, in 1946, and named in 1950. Over a dozen partial skulls and a large assortment of other fossils from various species...
. The latter hypothesis is supported by Horner and colleagues, where Einiosaurus is the earliest of an evolutionary series in which the nasal horns gradually change to rough bosses, as in Achelousaurus and Pachyrhinosaurus which are the second and third in this series. The frills also grow in complexity.
Regardless of which hypothesis is correct, Einiosaurus appears to occupy an intermediate position with respect to the evolution
Evolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
of the centrosaurines.
External links
- Einiosaurus at DinoData
- Einiosaurus, from the Dinosaur Encyclopaedia at Dino Russ's Lair

