
Electric actuator
Encyclopedia
Actuator
s are used for the automation of industrial valves and can be found in all kinds of technical process plants: they are used in waste water treatment plants, power plants and even refineries
. This is where they play a major part in automating process control. The valves to be automated vary both in design and dimension. The diameters of the valves range from a few inches to a few meters.
Depending on their type of supply, the actuators may be classified as pneumatic, hydraulic, or electric actuators.
"A multi-turn actuator is an actuator which transmits to the valve a torque
for at least one full revolution. It is capable of withstanding thrust."
A valve stem
is mounted to the gate valve
disc. The multi-turn actuator moves the gate valve disc from OPEN to CLOSED and vice versa via a stem nut. To cover the complete valve travel, the so-called valve stroke, the actuator has to perform – depending on the valve – a few or several hundred rotations. Due to their design, the stroke of electric actuators, contrary to that of their pneumatic counterparts, has no limits. Therefore, gate valves are exclusively automated by means of electric multi-turn actuators.
The multi-turn actuator has to be able to withstand the weight of the gate valve disc by means of the valve attachment, the interface to the valve. This is expressed in the second sentence of the definition.
Gate valves may have a diameter of approx. 4 inches to several meters. The torque requirement for multi-turn solutions ranges from approx. 10 N m to 30,000 N m.
s and ball valve
s. The basic requirements on part-turn actuators are described in the standard EN ISO 5211 as follows:
"A part-turn actuator is an actuator which transmits a torque to the valve for less than one full revolution. It need not be capable of withstanding thrust."
Less than one full revolution usually means a swivel movement of 90°; however, there are some valve types requiring a different swing angle, such as two-way valves. The closing elements in part-turn actuators are always supported by the valve housing, i.e. the weight of the closing element does not act upon the part-turn actuator. This is expressed in the second sentence of the definition.
Part-turn valves diameters range from a few inches to several metres. The torque requirement for operating the closing element has a comparable range from approximately 10 N m to several 100,000 N m. Electric actuators are unrivalled for large-diameter valves with high torque requirements.
Most of the linear actuators used are pneumatic diaphragm actuators. They are characterised by a simple design principle and are therefore cost-effective. A compressed air
supply is a prerequisite for their use. In case this is not possible, the use of thrust units is recommended which can easily be supplied with power.
s are mostly used as the driving force, for some applications also single-phase AC or DC motors are used. These motors are specially adapted for valve automation as they provide higher torques from standstill than comparable conventional motors, a necessary requirement to unseat sticky valves. The actuators are expected to operate under extreme ambient conditions, however they are generally not used for continuous operation since the motor heat buildup can be excessive.
is used to reduce the high output speed of the electric motor. This enables a high reduction ratio within the gear
stage, leading to a low efficiency which is desired for the actuators. The gearing is therefore self-locking i.e. it prevents accidental and undesired changes of the valve position by acting upon the valve’s closing element. This is of major importance for multi-turn actuators which are axially loaded with the weight of the gate valve disc.
used to firmly connect the actuator to the counterpart on the valve side. The higher the torque to be transmitted, the larger the flange required.
Second: The output drive type used to transmit the torque or the thrust from the actuator to the valve shaft. Just like there is a multitude of valves there is also a multitude of valve attachments.
Dimensions and design of valve mounting flange and valve attachments are stipulated in the standards EN ISO 5210 for multi-turn actuators or EN ISO 5211 for part-turn actuators. The design of valve attachments for linear actuators is generally based on DIN 3358.
are processed within the actuator controls. This task can in principle be assumed by external controls, e.g. a PLC
. Modern actuators include integral controls which process signals locally without any delay. The controls also include the switchgear required to control the electric motor. This can either be reversing contactor
s or thyristor
s which, being an electric component, are not subject to mechanic wear. Controls use the switchgear to switch the electric motor on or off depending on the signals or commands present. Another task of the actuator controls is to provide the DCS with feedback signals, e.g. when reaching a valve end position.
technology is increasingly used for data transmission in process automation applications. Electric actuators can therefore be equipped with all common fieldbus interfaces used in process automation. Special connections are required for the connection of fieldbus data cables..
Temperature sensors are required to protect the motor against overheating. For some applications by other manufacturers, the increase of the motor current is also monitored. Thermoswitches or PTC thermistor
s which are embedded in the motor windings mostly reliably fulfil this task. They trip when the temperature limit has been exceeded and the controls switch off the motor.
]
The simplest example is the position control. Modern positioners are equipped with self-adaptation i.e. the positioning behaviour is monitored and continuously optimised via controller parameters.
Meanwhile, electric actuators are equipped with fully-fledged process controllers (PID controllers). Especially for remote installations, e.g. the flow control to an elevated tank, the actuator can assume the tasks of a PLC which otherwise would have to be additionally installed.
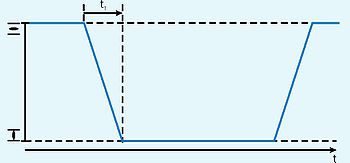
The 'Short-time duty
S2’ operation mode of the electric motor in accordance with the IEC 34-1 standard indicates that the actuator is suitable for this kind of applications. Another characteristic of this duty type is the maximum permissible running time without interruption. A typical time for actuators is 15 min.
e.g. to set a certain flow rate. Sensitive closed-loop applications require adjustments within intervals of a few seconds. The demands on the actuator are higher than in open-close or positioning duty. Both mechanics and motor have to be designed as to be able to withstand the high number of starts without any deterioration in control accuracy.
The duty type of the electric motors suitable for this application is called intermittent duty S4 or intermittent duty S5. The running time is limited by the relative on-time; for modulating actuators this is usually 25 %.
local ambient conditions. The applications are often safety related, therefore the plant operators put high demands on the reliability of the devices. Failure of an actuator may cause accidents in process-controlled plants and toxic substances may leak into the environment.
Process-controlled plants are often operated for several decades which justifies the higher demands put on the lifetime of the devices.
For this reason, actuators are always designed in high enclosure protection. The manufacturers put a lot of work and knowledge into corrosion
protection.
, temperatures down to – 60 °C may occur, and in technical process plants + 100 °C may be exceeded. Using the proper lubricant is crucial for full operation under these conditions. Grease
s which may be used at room temperature can become too solid at low temperatures for the actuator to overcome the resistance within the device. At high temperatures, these greases can liquify and lose their lubricating power. When sizing the actuator, the ambient temperature and the selection of the correct lubricant are of major importance.
s, oil and gas exploration or even mining
. When a potentially explosive gas-air-mixture or gas-dust-mixture occurs, the actuator must not act as ignition source. Hot surfaces on the actuator as well as ignition sparks created by the actuator have to be avoided. This can be achieved by a flameproof
enclosure, where the housing is designed to prevent ignition sparks from leaving the housing even if there is an explosion inside.
Actuators designed for these applications, being explosion-proof devices, have to be qualified by a test authority (notified body). There is no worldwide standard: depending on the country where the actuators are used, different directives and regulations have to be observed. Within the European Union, ATEX 94/9/EC applies, in US, the NEC (approval by FM
) or the CEC in Canada (approval by the CSA
). Explosion-proof actuators have to meet the design requirements of these directives and regulations.
, packaging and testing
applications. Such actuators can be linear
, rotary, or a combination of the two, and can be combined to perform work in three dimensions. Such actuators are often used to replace pneumatic cylinder
s.
Actuator
An actuator is a type of motor for moving or controlling a mechanism or system. It is operated by a source of energy, usually in the form of an electric current, hydraulic fluid pressure or pneumatic pressure, and converts that energy into some kind of motion. An actuator is the mechanism by which...
s are used for the automation of industrial valves and can be found in all kinds of technical process plants: they are used in waste water treatment plants, power plants and even refineries
Refinery
A refinery is a production facility composed of a group of chemical engineering unit processes and unit operations refining certain materials or converting raw material into products of value.-Types of refineries:Different types of refineries are as follows:...
. This is where they play a major part in automating process control. The valves to be automated vary both in design and dimension. The diameters of the valves range from a few inches to a few meters.
Depending on their type of supply, the actuators may be classified as pneumatic, hydraulic, or electric actuators.
Classification of actuators according to their movement
Travel means the distance the closing element within the valve has to cover to completely open or close that valve. Typical closing elements include butterfly, globe or gate valve discs. These three closing elements stand for the three basic movements required for covering the travel. The butterfly valve disc is operated by a 90° swivel movement from end position OPEN to CLOSED, the globe valve disc is operated by a rather short linear movement (stroke) while the gate valve disc movement covers the full diameter of the valve. Each movement type requires a specific actuator type.Multi-turn actuators
Multi-turn actuators are required for the automation of multi-turn valves. One of the major representatives of this type is the gate valve. The basic requirements on multi-turn actuators are described in the standard EN ISO 5210 as follows:"A multi-turn actuator is an actuator which transmits to the valve a torque
Torque
Torque, moment or moment of force , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist....
for at least one full revolution. It is capable of withstanding thrust."
A valve stem
Valve stem
A valve stem is a self-contained valve which opens to admit gas to a chamber , and is then automatically closed and kept sealed by the pressure in the chamber, or a spring, or both, to prevent the gas from escaping...
is mounted to the gate valve
Gate valve
The gate valve, also known as a sluice valve, is a valve that opens by lifting a round or rectangular gate/wedge out of the path of the fluid. The distinct feature of a gate valve is the sealing surfaces between the gate and seats are planar, so gate valves are often used when a straight-line flow...
disc. The multi-turn actuator moves the gate valve disc from OPEN to CLOSED and vice versa via a stem nut. To cover the complete valve travel, the so-called valve stroke, the actuator has to perform – depending on the valve – a few or several hundred rotations. Due to their design, the stroke of electric actuators, contrary to that of their pneumatic counterparts, has no limits. Therefore, gate valves are exclusively automated by means of electric multi-turn actuators.
The multi-turn actuator has to be able to withstand the weight of the gate valve disc by means of the valve attachment, the interface to the valve. This is expressed in the second sentence of the definition.
Gate valves may have a diameter of approx. 4 inches to several meters. The torque requirement for multi-turn solutions ranges from approx. 10 N m to 30,000 N m.
Part-turn actuators
Part-turn actuators are required for the automation of part-turn valves. Major representatives of this type are butterfly valveButterfly valve
A butterfly valve is a valve which can be used for isolating or regulating flow. The closing mechanism takes the form of a disk. Operation is similar to that of a ball valve, which allows for quick shut off. Butterfly valves are generally favored because they are lower in cost to other valve...
s and ball valve
Ball valve
A ball valve is a valve with a spherical disc, the part of the valve which controls the flow through it. The sphere has a hole, or port, through the middle so that when the port is in line with both ends of the valve, flow will occur. When the valve is closed, the hole is perpendicular to the ends...
s. The basic requirements on part-turn actuators are described in the standard EN ISO 5211 as follows:
"A part-turn actuator is an actuator which transmits a torque to the valve for less than one full revolution. It need not be capable of withstanding thrust."
Less than one full revolution usually means a swivel movement of 90°; however, there are some valve types requiring a different swing angle, such as two-way valves. The closing elements in part-turn actuators are always supported by the valve housing, i.e. the weight of the closing element does not act upon the part-turn actuator. This is expressed in the second sentence of the definition.
Part-turn valves diameters range from a few inches to several metres. The torque requirement for operating the closing element has a comparable range from approximately 10 N m to several 100,000 N m. Electric actuators are unrivalled for large-diameter valves with high torque requirements.
Linear actuators
Currently there is no international standard describing linear actuators or linear thrust units. A typical representative of the valves to be automated is the control valve. Just like the plug in the bathtub is pressed into the drain, the plug is pressed into the plug seat by a stroke movement. The pressure of the medium acts upon the plug while the thrust unit has to provide the same amount of thrust to be able to hold and move the plug against this pressure.Most of the linear actuators used are pneumatic diaphragm actuators. They are characterised by a simple design principle and are therefore cost-effective. A compressed air
Compressed air
Compressed air is air which is kept under a certain pressure, usually greater than that of the atmosphere. In Europe, 10 percent of all electricity used by industry is used to produce compressed air, amounting to 80 terawatt hours consumption per year....
supply is a prerequisite for their use. In case this is not possible, the use of thrust units is recommended which can easily be supplied with power.
Design
Motor (1)
Robust asynchronous three-phase AC motorAC motor
An AC motor is an electric motor driven by an alternating current.It commonly consists of two basic parts, an outside stationary stator having coils supplied with alternating current to produce a rotating magnetic field, and an inside rotor attached to the output shaft that is given a torque by the...
s are mostly used as the driving force, for some applications also single-phase AC or DC motors are used. These motors are specially adapted for valve automation as they provide higher torques from standstill than comparable conventional motors, a necessary requirement to unseat sticky valves. The actuators are expected to operate under extreme ambient conditions, however they are generally not used for continuous operation since the motor heat buildup can be excessive.
Limit and torque sensors (2)
The limit switching measures the travel and signals when an end position has been reached, the torque switching measures the torque present in the valve. When exceeding a set limit, this is signalled in the same way. Actuators are often equipped with a remote position transmitter which indicates the valve position as continuous current or voltage signal .Gearing (3)
Often a worm gearingWorm drive
A worm drive is a gear arrangement in which a worm meshes with a worm gear...
is used to reduce the high output speed of the electric motor. This enables a high reduction ratio within the gear
Gear
A gear is a rotating machine part having cut teeth, or cogs, which mesh with another toothed part in order to transmit torque. Two or more gears working in tandem are called a transmission and can produce a mechanical advantage through a gear ratio and thus may be considered a simple machine....
stage, leading to a low efficiency which is desired for the actuators. The gearing is therefore self-locking i.e. it prevents accidental and undesired changes of the valve position by acting upon the valve’s closing element. This is of major importance for multi-turn actuators which are axially loaded with the weight of the gate valve disc.
Valve attachment (4)
The valve attachment consists of two elements. First: The flangeFlange
A flange is an external or internal ridge, or rim , for strength, as the flange of an iron beam such as an I-beam or a T-beam; or for attachment to another object, as the flange on the end of a pipe, steam cylinder, etc., or on the lens mount of a camera; or for a flange of a rail car or tram wheel...
used to firmly connect the actuator to the counterpart on the valve side. The higher the torque to be transmitted, the larger the flange required.
Second: The output drive type used to transmit the torque or the thrust from the actuator to the valve shaft. Just like there is a multitude of valves there is also a multitude of valve attachments.
Dimensions and design of valve mounting flange and valve attachments are stipulated in the standards EN ISO 5210 for multi-turn actuators or EN ISO 5211 for part-turn actuators. The design of valve attachments for linear actuators is generally based on DIN 3358.
Manual operation (5)
In their basic version most electric actuators are equipped with a handwheel for operating the actuators during commissioning or power failure. The handwheel does not move during motor operation.Actuator controls (6)
Both actuator signals and operation commands of the DCSDistributed control system
A distributed control system refers to a control system usually of a manufacturing system, process or any kind of dynamic system, in which the controller elements are not central in location but are distributed throughout the system with each component sub-system controlled by one or more...
are processed within the actuator controls. This task can in principle be assumed by external controls, e.g. a PLC
Programmable logic controller
A programmable logic controller or programmable controller is a digital computer used for automation of electromechanical processes, such as control of machinery on factory assembly lines, amusement rides, or light fixtures. PLCs are used in many industries and machines...
. Modern actuators include integral controls which process signals locally without any delay. The controls also include the switchgear required to control the electric motor. This can either be reversing contactor
Contactor
A contactor is an electrically controlled switch used for switching a power circuit, similar to a relay except with higher current ratings. A contactor is controlled by a circuit which has a much lower power level than the switched circuit....
s or thyristor
Thyristor
A thyristor is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating N and P-type material. They act as bistable switches, conducting when their gate receives a current trigger, and continue to conduct while they are forward biased .Some sources define silicon controlled rectifiers and...
s which, being an electric component, are not subject to mechanic wear. Controls use the switchgear to switch the electric motor on or off depending on the signals or commands present. Another task of the actuator controls is to provide the DCS with feedback signals, e.g. when reaching a valve end position.
Electrical connection (7)
The supply cables of the motor and the signal cables for transmitting the commands to the actuator and sending feedback signals on the actuator status are connected to the electrical connection. The electrical connection can be designed as a separately sealed terminal bung or plug/socket connector. For maintenance purposes, the wiring should be easily disconnected and reconnected.Fieldbus connection (8)
FieldbusFieldbus
Fieldbus is the name of a family of industrial computer network protocols used for real-time distributed control, now standardized as IEC 61158....
technology is increasingly used for data transmission in process automation applications. Electric actuators can therefore be equipped with all common fieldbus interfaces used in process automation. Special connections are required for the connection of fieldbus data cables..
Automatic switching off in the end positions
After receiving an operation command, the actuator moves the valve in direction OPEN or CLOSE. When reaching the end position, an automatic switch-off procedure is started. Two fundamentally different switch-off mechanisms can be used. The controls switch off the actuator as soon as the set tripping point has been reached. This is called limit seating. However there are valve types for which the closing element has to be moved in the end position at a defined force or a defined torque to ensure that the valve seals tightly. This is called torque seating. The controls are programmed as to ensure that the actuator is switched off when exceeding the set torque limit. The end position signal of the limit switching is used for signalling the end position.Safety functions
The torque switching is not only used for torque seating in the end position, but it also serves as overload protection over the whole travel and protects the valve against excessive torque. If excessive torque acts upon the closing element in an intermediate position, e.g. due to a trapped object, the torque switching will trip when reaching the set tripping torque. In this situation the end position is not signalled by the limit switching. The controls can therefore distinguish between normal operation torque switch tripping in one of the end positions and switching off in an intermediate position due to excessive torque.Temperature sensors are required to protect the motor against overheating. For some applications by other manufacturers, the increase of the motor current is also monitored. Thermoswitches or PTC thermistor
Thermistor
A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance varies significantly with temperature, more so than in standard resistors. The word is a portmanteau of thermal and resistor...
s which are embedded in the motor windings mostly reliably fulfil this task. They trip when the temperature limit has been exceeded and the controls switch off the motor.
]
Process control functions
Due to increasing decentralisation in automation technology and the introduction of micro processors, more and more functions have been transferred from the DCS to the field devices. The data volume to be transmitted was reduced accordingly, in particular by the introduction of fieldbus technology. Electric actuators whose functions have been considerably expanded are also affected by this development.The simplest example is the position control. Modern positioners are equipped with self-adaptation i.e. the positioning behaviour is monitored and continuously optimised via controller parameters.
Meanwhile, electric actuators are equipped with fully-fledged process controllers (PID controllers). Especially for remote installations, e.g. the flow control to an elevated tank, the actuator can assume the tasks of a PLC which otherwise would have to be additionally installed.
Diagnosis
Modern actuators have extensive diagnostic functions which can help identify the cause of a failure. They also log the operating data. Study of the logged data allows the operation to be optimised by changing the parameters and the wear of both actuator and valve to be reduced.Duty types


Open-close duty
If a valve is used as a shut-off valve, then it will be either open or closed and intermediate positions are not held. Shut-off valves are rarely operated, the interval between operations may be a few minutes or even several months.The 'Short-time duty
Short time duty
The short time duty indicates an operating mode of increased performance but for a shorter length of time. Commonly it is also referred to the maximum load at which and the related maximum length of time a device can be operated without to failure.-Device applications:The load can be a maximum...
S2’ operation mode of the electric motor in accordance with the IEC 34-1 standard indicates that the actuator is suitable for this kind of applications. Another characteristic of this duty type is the maximum permissible running time without interruption. A typical time for actuators is 15 min.
Positioning duty
Defined intermediate positions are approached for setting a static flow through a pipeline. The same running time limits as in open-close duty apply.Modulating duty
The most distinctive feature of a closed-loop application is that changing conditions require frequent adjustment of the MOVMOV
MOV may refer to:* MOV , a mnemonic for the copying of data from one location to another in the X86 assembly language* .mov, filename extension for the QuickTime multimedia file format...
e.g. to set a certain flow rate. Sensitive closed-loop applications require adjustments within intervals of a few seconds. The demands on the actuator are higher than in open-close or positioning duty. Both mechanics and motor have to be designed as to be able to withstand the high number of starts without any deterioration in control accuracy.
The duty type of the electric motors suitable for this application is called intermittent duty S4 or intermittent duty S5. The running time is limited by the relative on-time; for modulating actuators this is usually 25 %.
Service conditions
Electric actuators are used worldwide, in all climate zones, in all kinds of industrial plants under speciallocal ambient conditions. The applications are often safety related, therefore the plant operators put high demands on the reliability of the devices. Failure of an actuator may cause accidents in process-controlled plants and toxic substances may leak into the environment.
Process-controlled plants are often operated for several decades which justifies the higher demands put on the lifetime of the devices.
For this reason, actuators are always designed in high enclosure protection. The manufacturers put a lot of work and knowledge into corrosion
Corrosion
Corrosion is the disintegration of an engineered material into its constituent atoms due to chemical reactions with its surroundings. In the most common use of the word, this means electrochemical oxidation of metals in reaction with an oxidant such as oxygen...
protection.
Enclosure protection
The enclosure protection types are defined according to the IP codes of EN 60529. The basic versions of most electric actuators are designed to the second highest enclosure protection IP 67. This means they are protected against the ingress of dust and water during immersion (30 min at a max. head of water of 1 m). Most actuator manufacturers also supply devices to enclosure protection IP 68 which provides protection against submersion up to a max. head of water of 6 m.Ambient temperatures
In SiberiaSiberia
Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
, temperatures down to – 60 °C may occur, and in technical process plants + 100 °C may be exceeded. Using the proper lubricant is crucial for full operation under these conditions. Grease
Grease (lubricant)
The term grease is used to describe semisolid lubricants. Although the word grease is also used to describe rendered fat of animals, in the context of lubrication, grease typically applies to a material consisting of a soap emulsified with mineral or vegetable oil...
s which may be used at room temperature can become too solid at low temperatures for the actuator to overcome the resistance within the device. At high temperatures, these greases can liquify and lose their lubricating power. When sizing the actuator, the ambient temperature and the selection of the correct lubricant are of major importance.
Explosion protection
Electric actuators are used in applications where potentially explosive atmospheres may occur. This includes among others refineries, pipelinePipeline transport
Pipeline transport is the transportation of goods through a pipe. Most commonly, liquids and gases are sent, but pneumatic tubes that transport solid capsules using compressed air are also used....
s, oil and gas exploration or even mining
Mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the earth, from an ore body, vein or seam. The term also includes the removal of soil. Materials recovered by mining include base metals, precious metals, iron, uranium, coal, diamonds, limestone, oil shale, rock...
. When a potentially explosive gas-air-mixture or gas-dust-mixture occurs, the actuator must not act as ignition source. Hot surfaces on the actuator as well as ignition sparks created by the actuator have to be avoided. This can be achieved by a flameproof
Electrical Equipment in Hazardous Areas
In electrical engineering, a hazardous location is defined as a place where concentrations of flammable gases, vapors, or dusts occur. Electrical equipment that must be installed in such locations is especially designed and tested to ensure it does not initiate an explosion, due to arcing contacts...
enclosure, where the housing is designed to prevent ignition sparks from leaving the housing even if there is an explosion inside.
Actuators designed for these applications, being explosion-proof devices, have to be qualified by a test authority (notified body). There is no worldwide standard: depending on the country where the actuators are used, different directives and regulations have to be observed. Within the European Union, ATEX 94/9/EC applies, in US, the NEC (approval by FM
FM Global
FM Global is a U.S.-based insurance company, with offices worldwide, that specializes in loss prevention services primarily to large corporations throughout the world in the Highly Protected Risk property insurance market sector. "FM Global" is the communicative name of the company, whereas the...
) or the CEC in Canada (approval by the CSA
Canadian Standards Association
The Canadian Standards Association, also known as the CSA, is a not-for-profit Standards organization with the stated aim of developing standards for use in 57 different areas of specialisation...
). Explosion-proof actuators have to meet the design requirements of these directives and regulations.
Additional uses
Small electric actuators can be used in a wide variety of assemblyManufacturing
Manufacturing is the use of machines, tools and labor to produce goods for use or sale. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high tech, but is most commonly applied to industrial production, in which raw materials are transformed into finished goods on a large scale...
, packaging and testing
Test method
A test method is a definitive procedure that produces a test result.A test can be considered as technical operation that consists of determination of one or more characteristics of a given product, process or service according to a specified procedure. Often a test is part of an experiment.The test...
applications. Such actuators can be linear
Linear
In mathematics, a linear map or function f is a function which satisfies the following two properties:* Additivity : f = f + f...
, rotary, or a combination of the two, and can be combined to perform work in three dimensions. Such actuators are often used to replace pneumatic cylinder
Pneumatic cylinder
Pneumatic cylinders are mechanical devices which utilize the power of compressed gas to produce a force in a reciprocating linear motion....
s.

