
Electrical length
Encyclopedia
In telecommunications, electrical length is the length of a transmission medium
or antenna element expressed as the number of wavelength
s of the signal propagating in the medium.
Electromagnetic waves propagate more slowly in a medium than in free space, so a wave in a medium will have a larger number of waves than a wave of the same frequency
propagating over the same distance in free space. Alternatively put, the distance covered in free space by the same number of waves as are in the transmission medium will be greater, hence the transmission medium is said to have an electrical length greater than its physical length. The electrical length is most commonly expressed in units of the wavelength, λ, which is related to the velocity of propagation
, v and frequency, f by
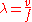
A length may be stated as 2λ or 3λ or 0.5λ etc. It is also sometimes expressed in radian
s or degrees
. A length of ν λ can be converted to θ radians by
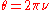
In both coaxial cable
s and optical fibers, the velocity of wave propagation is approximately two-thirds that of free space. Consequently, the wavelength will be approximately two-thirds that in free space, and the electrical length approximately 1.5 times the physical length.
In conducting cables, distributed resistances
, capacitance
s and inductance
s impede the propagation of the signal. In an optical fiber
interaction of the light wave with the materials of which the fiber is made (and fiber geometry) affect the velocity of signal propagation.
The electrical length of an antenna element is, in general, different from the physical length. This is especially true of elements on a printed board, which will be affected by the dielectric medium on which they are printed. The electrical length required for antenna elements is often λ/2 or λ/4. At lower frequencies, this can mean an impractically large antenna. This problem is frequently solved by loading the antenna with an inductance to artificially lengthen
the electrical length. Elements can also be electrically shortened with a capacitive load.
Transmission medium
A transmission medium is a material substance that can propagate energy waves...
or antenna element expressed as the number of wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
s of the signal propagating in the medium.
Electromagnetic waves propagate more slowly in a medium than in free space, so a wave in a medium will have a larger number of waves than a wave of the same frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
propagating over the same distance in free space. Alternatively put, the distance covered in free space by the same number of waves as are in the transmission medium will be greater, hence the transmission medium is said to have an electrical length greater than its physical length. The electrical length is most commonly expressed in units of the wavelength, λ, which is related to the velocity of propagation
Wave propagation
Wave propagation is any of the ways in which waves travel.With respect to the direction of the oscillation relative to the propagation direction, we can distinguish between longitudinal wave and transverse waves....
, v and frequency, f by
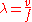
A length may be stated as 2λ or 3λ or 0.5λ etc. It is also sometimes expressed in radian
Radian
Radian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius. The radian is the standard unit of angular measure, used in many areas of mathematics. The unit was formerly a SI supplementary unit, but this category was abolished in 1995 and the radian is now considered a SI derived unit...
s or degrees
Degree (angle)
A degree , usually denoted by ° , is a measurement of plane angle, representing 1⁄360 of a full rotation; one degree is equivalent to π/180 radians...
. A length of ν λ can be converted to θ radians by
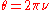
In both coaxial cable
Coaxial cable
Coaxial cable, or coax, has an inner conductor surrounded by a flexible, tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield. The term coaxial comes from the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing the same geometric axis...
s and optical fibers, the velocity of wave propagation is approximately two-thirds that of free space. Consequently, the wavelength will be approximately two-thirds that in free space, and the electrical length approximately 1.5 times the physical length.
In conducting cables, distributed resistances
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
, capacitance
Capacitance
In electromagnetism and electronics, capacitance is the ability of a capacitor to store energy in an electric field. Capacitance is also a measure of the amount of electric potential energy stored for a given electric potential. A common form of energy storage device is a parallel-plate capacitor...
s and inductance
Inductance
In electromagnetism and electronics, inductance is the ability of an inductor to store energy in a magnetic field. Inductors generate an opposing voltage proportional to the rate of change in current in a circuit...
s impede the propagation of the signal. In an optical fiber
Optical fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
interaction of the light wave with the materials of which the fiber is made (and fiber geometry) affect the velocity of signal propagation.
The electrical length of an antenna element is, in general, different from the physical length. This is especially true of elements on a printed board, which will be affected by the dielectric medium on which they are printed. The electrical length required for antenna elements is often λ/2 or λ/4. At lower frequencies, this can mean an impractically large antenna. This problem is frequently solved by loading the antenna with an inductance to artificially lengthen
Electrical lengthening
Electrical lengthening is the modification of an aerial which is shorter than a whole-number multiple of a quarter of the radiated wavelength, by means of a suitable electronic device, without changing the physical length of the aerial, in such a way that it corresponds electrically to the next...
the electrical length. Elements can also be electrically shortened with a capacitive load.

