Electronic medical record
Encyclopedia
An electronic medical record (EMR) is a computerized medical record
created in an organization that delivers care, such as a hospital or physician's office. Electronic medical records tend to be a part of a local stand-alone health information system that allows storage, retrieval and modification of records.
). When paper-based records are required in multiple locations, copying, faxing, and transporting costs are significant compared to duplication and transfer of digital records. Because of these many "after entry" benefits, federal and state governments, insurance companies and other large medical institutions are heavily promoting the adoption of electronic medical records. Congress included a formula of both incentives (up to $44K per physician under Medicare or up to $65K over 6 years, under Medicaid) and penalties (i.e. decreased Medicare/Medicaid reimbursements for covered patients to doctors who fail to use EMR's by 2015) for EMR/EHR adoption versus continued use of paper records as part of the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act, enacted as part of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009
.
One study estimates electronic medical records improve overall efficiency by 6% per year, and the monthly cost of an EMR may (depending on the cost of the EMR) be offset by the cost of only a few "unnecessary" tests or admissions. Jerome Groopman disputed these results, publicly asking "how such dramatic claims of cost-saving and quality improvement could be true".
However, the increased portability and accessibility of electronic medical records may also increase the ease with which they can be accessed and stolen by unauthorized persons or unscrupulous users versus paper medical records as acknowledged by the increased security requirements for electronic medical records included in the Health Information and Accessibility Act and by recent large-scale breaches in confidential records reported by EMR users. Concerns about security contribute to the resistance shown to their widespread adoption.
Handwritten paper medical records can be associated with poor legibility, which can contribute to medical error
s. Pre-printed forms, the standardization of abbreviations, and standards for penmanship were encouraged to improve reliability of paper medical records. Electronic records help with the standardization of forms, terminology and abbreviations, and data input. Digitization of forms facilitates the collection of data for epidemiology and clinical studies.
In contrast, EMRs can be continuously updated (within certain legal limitations - see below). The ability to exchange records between different EMR systems ("interoperability") would facilitate the co-ordination of healthcare delivery in non-affiliated healthcare facilities. In addition, data from an electronic system can be used anonymously for statistical reporting in matters such as quality improvement, resource management and public health communicable disease surveillance.
World Health Organisation (WHO) administration intentionally does not contribute to an internationally standardized view of medical records nor to personal health records. However, WHO contributes to minimum requirements definition for developing countries.
The United Nations accredited standardisation body International Organization for Standardization
(ISO) however has settled thorough word for standards in the scope of the HL7 platform for health care informatics. Respective standards are available with ISO/HL7 10781:2009 Electronic Health Record-System Functional Model, Release 1.1 and subsequent set of detailing standards.
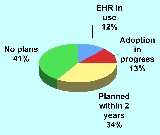
In the United States, the CDC reported that the EMR adoption rate had steadily risen to 48.3 percent at the end of 2009. This is an increase over 2008, when only 38.4% of office-based physicians reported using fully or partially electronic medical record systems (EMR) in 2008. However, the same study found that only 20.4% of all physicians reported using a system described as minimally functional and including the following features: orders for prescriptions, orders for tests, viewing laboratory or imaging results, and clinical notes.
to predict, detect and potentially prevent adverse events. This can include discharge/transfer orders, pharmacy orders, radiology results, laboratory results and any other data from ancillary services or provider notes.
. Exception is with those states where health care system is unified, as in United Kingdom
.
Automated handwriting recognition of ambulance medical forms have also been successful. These systems allow paper based medical documents to be converted to digital text with substantially less cost overhead. Patient identifying information would not be converted to comply with government privacy regulations. The data can then be efficiently used for epidemiological analysis.
Connecting for Health project in the United Kingdom. It enables GPs to transfer a patient's electronic medical record to another practice when the patient moves onto the listctice.
In the United States, this class of information is referred to as Protected Health Information (PHI) and its management is addressed under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
(HIPAA) as well as many local laws.
In the European Union
(EU), several Directives of the European Parliament and of the Council protect the processing and free movement of personal data, including for purposes of health care.
The future vision of many connected health systems is the ability to connect the electronic medical record system to a personal health record creating a "shared record". This sharing will have to include elements of granular permissions at the data type level and the ability for patient generated content to be "tagged" allowing the provider to maintain clinical integrity of information. An example of this can be seen in implementations of connected health platforms that have this capability built in like HealthyCircles.
Veterinary electronic medical record data are being used to investigate antimicrobial efficacy; risk factors for canine cancer; and inherited diseases in dogs and cats, in the small animal disease surveillance project 'VEctAR' (Veterinary Electronic Animal Record) at the Royal Veterinary College
, London, in collaboration with the University of Sydney
and RxWorks.
Medical record
The terms medical record, health record, and medical chart are used somewhat interchangeably to describe the systematic documentation of a single patient's medical history and care across time within one particular health care provider's jurisdiction....
created in an organization that delivers care, such as a hospital or physician's office. Electronic medical records tend to be a part of a local stand-alone health information system that allows storage, retrieval and modification of records.
Contrast with paper-based record
Paper based records are still by far the most common method of recording patient information for most hospitals and practices in the U.S. The majority of doctors still find their ease of data entry and low cost hard to part with. However, as easy as they are for the doctor to record medical data at the point of care, they require a significant amount of storage space compared to digital records. In the US, most states require physical records be held for a minimum of seven years. The costs of storage media, such as paper and film, per unit of information differ dramatically from that of electronic storage media. When paper records are stored in different locations, collating them to a single location for review by a health care provider is time consuming and complicated, whereas the process can be simplified with electronic records. This is particularly true in the case of person-centered records, which are impractical to maintain if not electronic (thus difficult to centralise or federateFederated identity
A federated identity in information technology is the means of linking a person's electronic identity and attributes, stored across multiple distinct identity management systems....
). When paper-based records are required in multiple locations, copying, faxing, and transporting costs are significant compared to duplication and transfer of digital records. Because of these many "after entry" benefits, federal and state governments, insurance companies and other large medical institutions are heavily promoting the adoption of electronic medical records. Congress included a formula of both incentives (up to $44K per physician under Medicare or up to $65K over 6 years, under Medicaid) and penalties (i.e. decreased Medicare/Medicaid reimbursements for covered patients to doctors who fail to use EMR's by 2015) for EMR/EHR adoption versus continued use of paper records as part of the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act, enacted as part of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009
American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009
The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, abbreviated ARRA and commonly referred to as the Stimulus or The Recovery Act, is an economic stimulus package enacted by the 111th United States Congress in February 2009 and signed into law on February 17, 2009, by President Barack Obama.To...
.
One study estimates electronic medical records improve overall efficiency by 6% per year, and the monthly cost of an EMR may (depending on the cost of the EMR) be offset by the cost of only a few "unnecessary" tests or admissions. Jerome Groopman disputed these results, publicly asking "how such dramatic claims of cost-saving and quality improvement could be true".
However, the increased portability and accessibility of electronic medical records may also increase the ease with which they can be accessed and stolen by unauthorized persons or unscrupulous users versus paper medical records as acknowledged by the increased security requirements for electronic medical records included in the Health Information and Accessibility Act and by recent large-scale breaches in confidential records reported by EMR users. Concerns about security contribute to the resistance shown to their widespread adoption.
Handwritten paper medical records can be associated with poor legibility, which can contribute to medical error
Medical error
A medical error may be defined as a preventable adverse effect of care, whether or not it is evident or harmful to the patient. This might include an inaccurate or incomplete diagnosis or treatment of a disease, injury, syndrome, behavior, infection, or other ailment.-Definitions:As a general...
s. Pre-printed forms, the standardization of abbreviations, and standards for penmanship were encouraged to improve reliability of paper medical records. Electronic records help with the standardization of forms, terminology and abbreviations, and data input. Digitization of forms facilitates the collection of data for epidemiology and clinical studies.
In contrast, EMRs can be continuously updated (within certain legal limitations - see below). The ability to exchange records between different EMR systems ("interoperability") would facilitate the co-ordination of healthcare delivery in non-affiliated healthcare facilities. In addition, data from an electronic system can be used anonymously for statistical reporting in matters such as quality improvement, resource management and public health communicable disease surveillance.
Contribution under UN administration and accredited organisations
The United NationsUnited Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
World Health Organisation (WHO) administration intentionally does not contribute to an internationally standardized view of medical records nor to personal health records. However, WHO contributes to minimum requirements definition for developing countries.
The United Nations accredited standardisation body International Organization for Standardization
International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
(ISO) however has settled thorough word for standards in the scope of the HL7 platform for health care informatics. Respective standards are available with ISO/HL7 10781:2009 Electronic Health Record-System Functional Model, Release 1.1 and subsequent set of detailing standards.
Usage
Even though EMR systems with a computerized provider order entry (CPOE) have existed for more than 30 years, fewer than 10 percent of hospitals as of 2006 had a fully integrated system.In the United States, the CDC reported that the EMR adoption rate had steadily risen to 48.3 percent at the end of 2009. This is an increase over 2008, when only 38.4% of office-based physicians reported using fully or partially electronic medical record systems (EMR) in 2008. However, the same study found that only 20.4% of all physicians reported using a system described as minimally functional and including the following features: orders for prescriptions, orders for tests, viewing laboratory or imaging results, and clinical notes.
Legal status
Electronic medical records, like medical records, must be kept in unaltered form and authenticated by the creator. Under data protection legislation, responsibility for patient records (irrespective of the form they are kept in) is always on the creator and custodian of the record, usually a health care practice or facility. The physical medical records are the property of the medical provider (or facility) that prepares them. This includes films and tracings from diagnostic imaging procedures such as X-ray, CT, PET, MRI, ultrasound, etc. The patient, however, according to HIPAA, has a right to view the originals, and to obtain copies under law.Technical features
Using an EMR to read and write a patient's record is not only possible through a workstation but depending on the type of system and health care settings may also be possible through mobile devices that are handwriting capable. Electronic Medical Records may include access to Personal Health Records (PHR) which makes individual notes from an EMR readily visible and accessible for consumers.Event monitoring
Some EMR systems automatically monitor clinical events, by analyzing patient data from an Electronic Health RecordElectronic Health Record
An electronic health record is an evolving concept defined as a systematic collection of electronic health information about individual patients or populations...
to predict, detect and potentially prevent adverse events. This can include discharge/transfer orders, pharmacy orders, radiology results, laboratory results and any other data from ancillary services or provider notes.
Role in an electronic research network
The electronic Primary Care Research Network connects medical practitioners to researchers; promoting practice based research networks and facilitating clinical research. The internet-based infrastructure provides researchers with electronic medical records and standardized clinical report forms, shifting dependence away from paper based data collection tools that are not standardized. This mode of communication improves the quality of primary care and increases the number of clinical research opportunities. The information exchange between health care organizations encourages the translation of research into primary care practices.EMRs in Europe
There is no common standard on EMR in Europe neither in the entire member states of the European UnionEuropean Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
. Exception is with those states where health care system is unified, as in United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
.
EMRs in ambulances
Ambulance Services in Australia have recently introduced the use of EMR systems The benefits of EMR in Ambulance include the following: better training for paramedics, review of clinical standards, better research options for pre-hospital care and design of future treatment optionsAutomated handwriting recognition of ambulance medical forms have also been successful. These systems allow paper based medical documents to be converted to digital text with substantially less cost overhead. Patient identifying information would not be converted to comply with government privacy regulations. The data can then be efficiently used for epidemiological analysis.
GP2GP project
GP2GP is an NHSNational Health Service
The National Health Service is the shared name of three of the four publicly funded healthcare systems in the United Kingdom. They provide a comprehensive range of health services, the vast majority of which are free at the point of use to residents of the United Kingdom...
Connecting for Health project in the United Kingdom. It enables GPs to transfer a patient's electronic medical record to another practice when the patient moves onto the listctice.
Privacy concerns
A major concern is adequate confidentiality of the individual records being managed electronically. According to the Los Angeles Times, roughly 150 people (from doctors and nurses to technicians and billing clerks) have access to at least part of a patient's records during a hospitalization, and over 600,000 payers, providers and other entities that handle providers' billing data have some access.In the United States, this class of information is referred to as Protected Health Information (PHI) and its management is addressed under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 was enacted by the U.S. Congress and signed by President Bill Clinton in 1996. It was originally sponsored by Sen. Edward Kennedy and Sen. Nancy Kassebaum . Title I of HIPAA protects health insurance coverage for workers and their...
(HIPAA) as well as many local laws.
In the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
(EU), several Directives of the European Parliament and of the Council protect the processing and free movement of personal data, including for purposes of health care.
Technical standards
Though there are few standards for modern day EMR systems as a whole, there are many standards relating to specific aspects of EMRs. These include:- HL7 - messages format for interchange between different record systems and practice management systems.
- ANSI X12 (EDIElectronic Data InterchangeElectronic data interchange is the structured transmission of data between organizations by electronic means. It is used to transfer electronic documents or business data from one computer system to another computer system, i.e...
) - A set of transaction protocols used in the US for transmitting virtually any aspect of patient data. - CENCENCEN may refer to:*Cen, or sen, is the currency of the fictional nation of Amestris of the anime/manga "Fullmetal Alchemist"As a three-letter acronym:* Cambridge Evening News, former name for the Cambridge News...
- CONTSYS (EN 13940), a system of concepts to support continuity of care. - CEN - EHRcom (EN 13606), a standard for the communication of information from EHR systems.
- CEN - HISAHISAThe CEN Standard Architecture for Healthcare Information Systems , Health Informatics Service Architecture or HISA is a standard aimed at enabling the development modular open systems to support healthcare...
(EN 12967), a services standard for inter-system communication in a clinical information environment. - DICOM - a standard for representing and communicating radiology images and reporting
Interoperability towards sharing records
In the United States, the development of standards for EMR interoperability is at the forefront of the national health care agenda. EMRs, while an important factor in interoperability, are not a critical first step to sharing data between practicing physicians, pharmacies and hospitals. Many physicians currently have computerized practice management systems that can be used in conjunction with a health information exchange (HIE), allowing for first steps in sharing patient information (lab results, public health reporting) which are necessary for timely, patient-centered and portable care.The future vision of many connected health systems is the ability to connect the electronic medical record system to a personal health record creating a "shared record". This sharing will have to include elements of granular permissions at the data type level and the ability for patient generated content to be "tagged" allowing the provider to maintain clinical integrity of information. An example of this can be seen in implementations of connected health platforms that have this capability built in like HealthyCircles.
Regulatory compliance
- HIPAA
- Health Level 7Health Level 7Health Level Seven , is an all-volunteer, non-profit organization involved in development of international healthcare informatics interoperability standards...
- DICOM
- Title 21 CFR Part 11Title 21 CFR Part 11Title 21 CFR Part 11 of the Code of Federal Regulations deals with the Food and Drug Administration guidelines on electronic records and electronic signatures in the United States...
In veterinary medicine
In UK veterinary practice, the replacement of paper recording systems with electronic methods of storing animal patient information escalated from the 1980s and the majority of clinics now use electronic medical records. In a sample of 129 veterinary practices, 89% used a Practice Management System (PMS) for data recording. There are more than 10 PMS providers currently in the UK. Collecting data directly from PMSs for epidemiological analysis abolishes the need for veterinarians to manually submit individual reports per animal visit and therefore increases the reporting rate.Veterinary electronic medical record data are being used to investigate antimicrobial efficacy; risk factors for canine cancer; and inherited diseases in dogs and cats, in the small animal disease surveillance project 'VEctAR' (Veterinary Electronic Animal Record) at the Royal Veterinary College
Royal Veterinary College
The Royal Veterinary College is a veterinary school located in London, United Kingdom and a constituent college of the federal University of London. The RVC was founded in 1791 and joined the University of London in 1949...
, London, in collaboration with the University of Sydney
University of Sydney
The University of Sydney is a public university located in Sydney, New South Wales. The main campus spreads across the suburbs of Camperdown and Darlington on the southwestern outskirts of the Sydney CBD. Founded in 1850, it is the oldest university in Australia and Oceania...
and RxWorks.
See also
- List of open source healthcare software
- Microchip implant (human)Microchip implant (human)A human microchip implant is an integrated circuit device or RFID transponder encased in silicate glass and implanted in the body of a human being...
- Medical billing (United States)Medical billing (United States)Medical billing & coding is the process of submitting and following up on claims to insurance companies in order to receive payment for services rendered by a healthcare provider. The same process is used for most insurance companies, whether they are private companies or government-owned...

