
Electrospinning
Encyclopedia
Electrospinning uses an electrical charge to draw very fine (typically on the micro or nano scale) fibres from a liquid. Electrospinning shares characteristics of both electrospray
ing and conventional solution dry spinning of fibers. The process does not require the use of coagulation chemistry or high temperatures to produce solid threads from solution. This makes the process particularly suited to the production of fibers using large and complex molecules. Electrospinning from molten precursors is also practiced; this method ensures that no solvent can be carried over into the final product.

 When a sufficiently high voltage
When a sufficiently high voltage
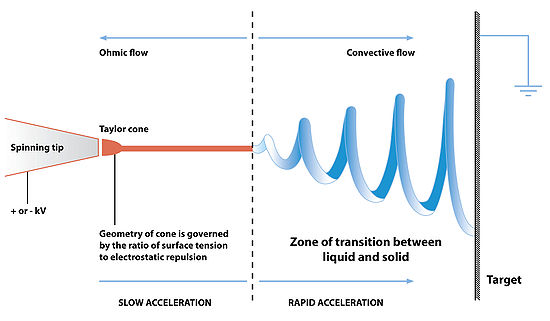
is applied to a liquid droplet, the body of the liquid becomes charged, and electrostatic repulsion counteracts the surface tension and the droplet is stretched; at a critical point a stream of liquid erupts from the surface. This point of eruption is known as the Taylor cone
. If the molecular cohesion of the liquid is sufficiently high, stream breakup does not occur (if it does, droplets are electrosprayed) and a charged liquid jet is formed.
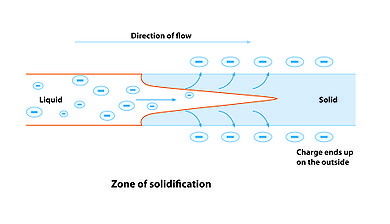
As the jet dries in flight, the mode of current flow changes from ohmic to convective as the charge migrates to the surface of the fiber. The jet is then elongated by a whipping process caused by electrostatic repulsion initiated at small bends in the fiber, until it is finally deposited on the grounded collector. The elongation and thinning of the fiber resulting from this bending instability leads to the formation of uniform fibers with nanometer-scale diameters.
2. Solution properties (viscosity, conductivity and surface tension)
3. Electric potential, flow rate and concentration
4. Distance between the capillary and collection screen
5. Ambient parameters (temperature, humidity and air velocity in the chamber)
6. Motion of target screen (collector)
7. Needle gauge
, and a grounded collector. A polymer
solution, sol-gel, particulate suspension or melt is loaded into the syringe and this liquid is extruded from the needle tip at a constant rate by a syringe pump. Alternatively, the droplet at the tip of the spinneret can be replenished by feeding from a header tank providing a constant feed pressure (figure 3). This constant pressure type feed works better for lower viscosity feedstocks.
ing.
The process of electrospinning was patented by J.F. Cooley in February 1902 and by W.J. Morton in July 1902 (.
In 1914 John Zeleny
, published work on the behavior of fluid droplets at the end of metal capillaries. His effort began the attempt to mathematically model the behavior of fluids under electrostatic forces.
Further developments toward commercialization were made by Anton Formhals, and described in a sequence of patents from 1934 to 1944 for the fabrication of textile yarns. Electrospinning from a melt rather than a solution was patented by C.L. Norton in 1936 using an air-blast to assist fiber formation.
In 1938 Nathalie D. Rozenblum and Igor V. Petryanov-Sokolov, working in Prof. Nicolai A. Fuchs' group at the Aerosol Laboratory of the L.Ya Karpov Institute in the USSR, generated electrospun fibers , which they developed into filter materials known as "Petryanov filters". By 1939, this work had led to the establishment of a factory in Tver' for the manufacture of electrospun smoke filter elements for gas masks. The material, dubbed BF (Battlefield Filter) was spun from cellulose acetate
in a solvent mixture of dichloroethane
and ethanol
. By the 1960s output of spun filtration material was claimed as 20 million m2 per annum
Between 1964 and 1969 Sir Geoffrey Ingram Taylor
produced the theoretical underpinning of electrospinning. Taylor’s work contributed to electrospinning by mathematically modeling the shape of the cone formed by the fluid droplet under the effect of an electric field; this characteristic droplet shape is now known as the Taylor cone. He further worked with J. R. Melcher to develop the “leaky dielectric model” for conducting fluids.
In the early 1990s several research groups (notably that of Reneker and Rutledge who popularised the name electrospinning for the process) demonstrated that many organic
polymers could be electrospun into nanofibers. Since then, the number of publications about electrospinning has been increasing exponentially every year.
Since 1995 there have been further theoretical developments of the driving mechanisms of the electrospinning process. Reznik et al. describes extensive work on the shape of the Taylor cone and the subsequent ejection of a fluid jet. Work by Hohman et al. investigates the relative growth rates of the numerous proposed instabilities in an electrically forced jet once in flight and endeavors to describe the most important instability to the electrospinning process, the bending (whipping) instability.
are an important method of adhesion between the fibers and the captured materials. Polymeric nanofibers have been used in air filtration applications for more than seven decades. Due to poor bulk mechanical properties of thin nanowebs, they are laid over a filtration medium substrate. The small fiber diameters cause slip flows at fiber surfaces, causing an increase in the interception and inertial impaction efficiencies of these composite filter media. The enhanced filtration efficiency at the same pressure drop is possible with fibers having diameters less than 0.5 micrometer. Since the essential properties of protective clothing are high moisture vapor transport, increased fabric breath-ability, and enhanced toxic chemical resistance, electrospun nanofiber membranes are good candidates for these applications.
) layers in combination with polymer
coatings.
2. Tissue engineering
3. Implant materials
4. Drug delivery
5. Wound dressing
6. Medical textile materials
Application is limited by difficulties in making sufficient quantities of fiber to make substantial large scale articles in a reasonable time scale. For this reason medical applications requiring relatively small amounts of fiber are a popular area of application for electrospun fiber reinforced materials.
Electrospinning is being investigated as a source of cost-effective, easy to manufacture wound dressings, medical implants, and scaffolds for the production of artificial human tissues. These scaffolds fulfill a similar purpose as the extracellular matrix
in natural tissue. Biodegradable polymers, such as polycaprolactone
, are typically used for this purpose. These fibers may then be coated with collagen
to promote cell attachment, although collagen has successfully been spun directly into membranes.
s to be immobilized on. These enzymes could be used to break down toxic chemicals in the environment, among other things.
Electrospray
The name electrospray is used for a device that employs electricity to disperse a liquid or for the fine aerosol resulted in this process. The method is sometimes improperly called electrohydrodynamic atomization. High voltage is applied to a liquid supplied through an emitter...
ing and conventional solution dry spinning of fibers. The process does not require the use of coagulation chemistry or high temperatures to produce solid threads from solution. This makes the process particularly suited to the production of fibers using large and complex molecules. Electrospinning from molten precursors is also practiced; this method ensures that no solvent can be carried over into the final product.

Process

Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
is applied to a liquid droplet, the body of the liquid becomes charged, and electrostatic repulsion counteracts the surface tension and the droplet is stretched; at a critical point a stream of liquid erupts from the surface. This point of eruption is known as the Taylor cone
Taylor cone
A Taylor cone refers to the cone observed in electrospinning, electrospraying and hydrodynamic spray processes from which a jet of charged particles emanates above a threshold voltage...
. If the molecular cohesion of the liquid is sufficiently high, stream breakup does not occur (if it does, droplets are electrosprayed) and a charged liquid jet is formed.
As the jet dries in flight, the mode of current flow changes from ohmic to convective as the charge migrates to the surface of the fiber. The jet is then elongated by a whipping process caused by electrostatic repulsion initiated at small bends in the fiber, until it is finally deposited on the grounded collector. The elongation and thinning of the fiber resulting from this bending instability leads to the formation of uniform fibers with nanometer-scale diameters.
 |
 |
Parameters
1. Molecular Weight, Molecular-Weight Distribution and Architecture (branched, linear etc.) of the polymer2. Solution properties (viscosity, conductivity and surface tension)
3. Electric potential, flow rate and concentration
4. Distance between the capillary and collection screen
5. Ambient parameters (temperature, humidity and air velocity in the chamber)
6. Motion of target screen (collector)
7. Needle gauge
Apparatus
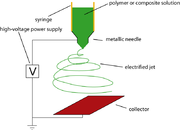
The standard laboratory setup for electrospinning consists of a spinneret (typically a hypodermic syringe needle) connected to a high-voltage (5 to 50 kV) direct current power supply, a syringe pumpSyringe driver
A syringe driver or syringe pump is a small infusion pump , used to gradually administer small amounts of fluid to a patient or for use in chemical and biomedical research....
, and a grounded collector. A polymer
Polymer
A polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating structural units. These subunits are typically connected by covalent chemical bonds...
solution, sol-gel, particulate suspension or melt is loaded into the syringe and this liquid is extruded from the needle tip at a constant rate by a syringe pump. Alternatively, the droplet at the tip of the spinneret can be replenished by feeding from a header tank providing a constant feed pressure (figure 3). This constant pressure type feed works better for lower viscosity feedstocks.
 |
 |
History
In the late 16th century William Gilbert set out to describe the behavior of magnetic and electrostatic phenomena. He observed that when a suitably electrically charged piece of amber was brought near a droplet of water it would form a cone shape and small droplets would be ejected from the tip of the cone: this is the first recorded observation of electrosprayElectrospray
The name electrospray is used for a device that employs electricity to disperse a liquid or for the fine aerosol resulted in this process. The method is sometimes improperly called electrohydrodynamic atomization. High voltage is applied to a liquid supplied through an emitter...
ing.
The process of electrospinning was patented by J.F. Cooley in February 1902 and by W.J. Morton in July 1902 (.
In 1914 John Zeleny
John Zeleny
John Zeleny was a Czech-American physicist at the University of Minnesota, who in 1911 invented the Zeleny electroscope. He also studied the effect of an electric field on a liquid meniscus....
, published work on the behavior of fluid droplets at the end of metal capillaries. His effort began the attempt to mathematically model the behavior of fluids under electrostatic forces.
Further developments toward commercialization were made by Anton Formhals, and described in a sequence of patents from 1934 to 1944 for the fabrication of textile yarns. Electrospinning from a melt rather than a solution was patented by C.L. Norton in 1936 using an air-blast to assist fiber formation.
In 1938 Nathalie D. Rozenblum and Igor V. Petryanov-Sokolov, working in Prof. Nicolai A. Fuchs' group at the Aerosol Laboratory of the L.Ya Karpov Institute in the USSR, generated electrospun fibers , which they developed into filter materials known as "Petryanov filters". By 1939, this work had led to the establishment of a factory in Tver' for the manufacture of electrospun smoke filter elements for gas masks. The material, dubbed BF (Battlefield Filter) was spun from cellulose acetate
Cellulose acetate
Cellulose acetate , first prepared in 1865, is the acetate ester of cellulose. Cellulose acetate is used as a film base in photography, as a component in some adhesives, and as a frame material for eyeglasses; it is also used as a synthetic fiber and in the manufacture of cigarette filters and...
in a solvent mixture of dichloroethane
Dichloroethane
Dichloroethane can refer to either of two isomeric organochlorides with the molecular formula C2H4Cl2:* 1,1-Dichloroethane * 1,2-Dichloroethane...
and ethanol
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
. By the 1960s output of spun filtration material was claimed as 20 million m2 per annum
Between 1964 and 1969 Sir Geoffrey Ingram Taylor
Geoffrey Ingram Taylor
Sir Geoffrey Ingram Taylor OM was a British physicist, mathematician and expert on fluid dynamics and wave theory. His biographer and one-time student, George Batchelor, described him as "one of the most notable scientists of this century".-Biography:Taylor was born in St. John's Wood, London...
produced the theoretical underpinning of electrospinning. Taylor’s work contributed to electrospinning by mathematically modeling the shape of the cone formed by the fluid droplet under the effect of an electric field; this characteristic droplet shape is now known as the Taylor cone. He further worked with J. R. Melcher to develop the “leaky dielectric model” for conducting fluids.
In the early 1990s several research groups (notably that of Reneker and Rutledge who popularised the name electrospinning for the process) demonstrated that many organic
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
polymers could be electrospun into nanofibers. Since then, the number of publications about electrospinning has been increasing exponentially every year.
Since 1995 there have been further theoretical developments of the driving mechanisms of the electrospinning process. Reznik et al. describes extensive work on the shape of the Taylor cone and the subsequent ejection of a fluid jet. Work by Hohman et al. investigates the relative growth rates of the numerous proposed instabilities in an electrically forced jet once in flight and endeavors to describe the most important instability to the electrospinning process, the bending (whipping) instability.
Uses
The size of an electrospun fiber can be in the nano scale and the fibers may possess nano scale surface texture, leading to different modes of interaction with other materials compared with macroscale materials. In addition to this, the ultra-fine fibers produced by electrospinning are expected to have two main properties, a very high surface to volume ratio, and a relatively defect free structure at the molecular level. This first property makes electrospun material suitable for activities requiring a high degree of physical contact, such as providing sites for chemical reactions, or the capture of small sized particulate material by physical entanglement - filtration. The second property should allow electrospun fibers to approach the theoretical maximum strength of the spun material, opening up the possibility of making high mechanical performance composite materials.Filtration
The use of nanofiber webs as a filtering medium is well established. Due to the small size of the fibers London-Van Der Waals forcesVan der Waals force
In physical chemistry, the van der Waals force , named after Dutch scientist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, is the sum of the attractive or repulsive forces between molecules other than those due to covalent bonds or to the electrostatic interaction of ions with one another or with neutral...
are an important method of adhesion between the fibers and the captured materials. Polymeric nanofibers have been used in air filtration applications for more than seven decades. Due to poor bulk mechanical properties of thin nanowebs, they are laid over a filtration medium substrate. The small fiber diameters cause slip flows at fiber surfaces, causing an increase in the interception and inertial impaction efficiencies of these composite filter media. The enhanced filtration efficiency at the same pressure drop is possible with fibers having diameters less than 0.5 micrometer. Since the essential properties of protective clothing are high moisture vapor transport, increased fabric breath-ability, and enhanced toxic chemical resistance, electrospun nanofiber membranes are good candidates for these applications.
 |
Textile manufacturing
The majority of early patents for electrospinning were for textile applications, however little woven fabric was actually produced, perhaps due to difficulties in handling the barely visible fibers. However, electrospinning has the potential to produce seamless non-woven garments by integrating advanced manufacturing with fiber electrospinning. This would introduce multi-functionality (flame, chemical, environmental protection) by blending fibers into electrospinlaced (using electrospinning to combine different fibers and coatings to form three dimensional shapes, such as clothingClothing
Clothing refers to any covering for the human body that is worn. The wearing of clothing is exclusively a human characteristic and is a feature of nearly all human societies...
) layers in combination with polymer
Polymer
A polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating structural units. These subunits are typically connected by covalent chemical bonds...
coatings.
Medical
1. Artificial organ components2. Tissue engineering
3. Implant materials
4. Drug delivery
5. Wound dressing
6. Medical textile materials
Composites
Ultra-fine electrospun fibers show clear potential for the manufacture of long fiber composite materials.Application is limited by difficulties in making sufficient quantities of fiber to make substantial large scale articles in a reasonable time scale. For this reason medical applications requiring relatively small amounts of fiber are a popular area of application for electrospun fiber reinforced materials.
Electrospinning is being investigated as a source of cost-effective, easy to manufacture wound dressings, medical implants, and scaffolds for the production of artificial human tissues. These scaffolds fulfill a similar purpose as the extracellular matrix
Extracellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix is the extracellular part of animal tissue that usually provides structural support to the animal cells in addition to performing various other important functions. The extracellular matrix is the defining feature of connective tissue in animals.Extracellular...
in natural tissue. Biodegradable polymers, such as polycaprolactone
Polycaprolactone
Polycaprolactone is a biodegradable polyester with a low melting point of around 60°C and a glass transition temperature of about −60°C. PCL is prepared by ring opening polymerization of ε-caprolactone using a catalyst such as stannous octoate. Recently a wide range of catalysts for the ring...
, are typically used for this purpose. These fibers may then be coated with collagen
Collagen
Collagen is a group of naturally occurring proteins found in animals, especially in the flesh and connective tissues of mammals. It is the main component of connective tissue, and is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up about 25% to 35% of the whole-body protein content...
to promote cell attachment, although collagen has successfully been spun directly into membranes.
 |
 |
Catalysts
Electrospun fibers may have potential as a surface for enzymeEnzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s to be immobilized on. These enzymes could be used to break down toxic chemicals in the environment, among other things.
External links
- Electrospinning machine manufacturer
- Spinrati electrospinning gateway
- Polish Academy of Science's page on electrospinning
- UC NanoLab Electrospinning group at the University of Cincinnati
- The Electrospinning Group on LinkedIn
- Lab scale electrospinning from Linari Engineering
Further reading
- Science and Technology of Polymer Nanofibers, A. L. Andrady, A. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, USA, 2008, ISBN 978-0-471-79059-4.
- Electrospinning, J. Stanger, N. Tucker, and M. Staiger, I-Smithers Rapra publishing (UK), ISBN 9781847350916.
- An Introduction to Electrospinning and Nanofibers, S. Ramakrishna , K. Fujihara , W-E Teo, World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte Ltd (Jun 2005), ISBN 9812564152.
- Electrospinning of micro- and nanofibers: fundamentals and applications in separation and filtration processes, Y. Fillatov, A. Budyka, and V. Kirichenko (Trans. D. Letterman), Begell House Inc., New York, USA, 2007, ISBN 978-1-56700-241-6.

