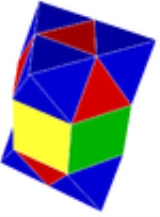
Elongated alternated cubic honeycomb
Encyclopedia
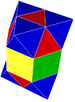 |
|
| Type | Uniform honeycomb Convex uniform honeycomb In geometry, a convex uniform honeycomb is a uniform tessellation which fills three-dimensional Euclidean space with non-overlapping convex uniform polyhedral cells.Twenty-eight such honeycombs exist:* the familiar cubic honeycomb and 7 truncations thereof;... |
| Schläfli symbol | h{4,3,4}:e |
| Cell types | {3,3} Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... , {3,4} Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... , (3.4.4) Triangular prism In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides.... |
| Face types | {3} Triangle A triangle is one of the basic shapes of geometry: a polygon with three corners or vertices and three sides or edges which are line segments. A triangle with vertices A, B, and C is denoted .... , {4} Square (geometry) In geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral. This means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles... |
| Vertex figure | triangular cupola Triangular cupola In geometry, the triangular cupola is one of the Johnson solids . It can be seen as half a cuboctahedron.The 92 Johnson solids were named and described by Norman Johnson in 1966.-Formulae:... joined to isosceles hexagonal pyramid  |
| Cells/vertex | {3,4}3+{3,3}4+(3.4.4)4 |
| Symmetry group Symmetry group The symmetry group of an object is the group of all isometries under which it is invariant with composition as the operation... |
P63/mmc |
| Dual | ? |
| Properties | vertex-uniform |

Tessellation
A tessellation or tiling of the plane is a pattern of plane figures that fills the plane with no overlaps and no gaps. One may also speak of tessellations of parts of the plane or of other surfaces. Generalizations to higher dimensions are also possible. Tessellations frequently appeared in the art...
(or honeycomb
Honeycomb (geometry)
In geometry, a honeycomb is a space filling or close packing of polyhedral or higher-dimensional cells, so that there are no gaps. It is an example of the more general mathematical tiling or tessellation in any number of dimensions....
) in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of octahedra
Octahedron
In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex....
, triangular prism
Triangular prism
In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides....
s, and tetrahedra
Tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids...
in a ratio of 1:2:2.
It is vertex-uniform with 3 octahedra, 4 tetrahedra, 6 triangular prisms around each vertex. Each prism meets an octahedron at one end and a tetrahedron at the other.
It is one of 28 convex uniform honeycomb
Convex uniform honeycomb
In geometry, a convex uniform honeycomb is a uniform tessellation which fills three-dimensional Euclidean space with non-overlapping convex uniform polyhedral cells.Twenty-eight such honeycombs exist:* the familiar cubic honeycomb and 7 truncations thereof;...
s.
It has a gyrated form called the gyroelongated alternated cubic honeycomb
Gyroelongated alternated cubic honeycomb
The gyroelongated alternated cubic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of octahedra, triangular prisms, and tetrahedra in a ratio of 1:2:2....
with the same arrangement of cells at each vertex.

