Elongation
Encyclopedia
In astronomy
, a planet's elongation is the angle between the Sun
and the planet, as viewed from Earth
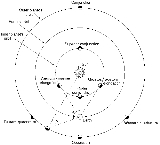
. Elongations occur when an inner planet’s position, in its orbital path, is at tangent to the view from Earth. Because these inner planets are inside the Earth’s orbits their positions as viewed from the Earth are never very far from the position of the Sun. When a planet is at Elongation, it is farthest from the Sun as viewed from Earth, so its view is best at that point.
When an inferior planet is visible after sunset, it is near its greatest eastern elongation. When an inferior planet is visible before sunrise, it is near its greatest western elongation. The value of the greatest elongation (west or east), for Mercury
, is between 18° and 28°; and for Venus
between 45° and 47°. This value varies because the orbits of the planets are elliptical, rather than perfect circles. Another minor contributor to this inconsistency is orbital inclination
: each planet's orbit is in a slightly different plane.
Refer to astronomical tables and websites such as heavens-above to see when the planets reach their next maximum elongations.
of Earth and the planet, as seen from the Sun. The time it takes to complete this period is the synodic period of the planet.
Let T be the period (for example the time between two greatest eastern elongations), ω be the relative angular velocity
, ωe Earth's angular velocity
and ωp the planet's angular velocity
. Then
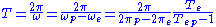
where Te and Tp are Earth's and the planet's years (i.e. periods of revolution around the Sun, called sidereal periods).
For example, Venus
's year (sidereal period) is 225 days, and Earth
's is 365 days. Thus Venus' synodic period, which gives the time between two subsequent eastern (or western) greatest elongations, is 584 days.
These values are approximate, because (as mentioned above) the planets do not have perfectly circular, coplanar orbits. When a planet is closer to the Sun it moves faster than when it is further away, so exact determination of the date and time of greatest elongation requires a much more complicated analysis of orbital mechanics.
s and asteroid
s undergo a different cycle. After superior conjunction, such an object's elongation continues to increase until it approaches a maximum value larger than 90° (impossible with inferior planets) and typically very near 180°, which is known as opposition
and corresponds to a heliocentric conjunction with Earth. In other words, as seen from an observer on the superior planet at opposition, the Earth appears at inferior conjunction with the Sun. Technically, the exact moment of opposition is slightly different from the moment of maximum elongation. Opposition is defined as the moment when the apparent ecliptic longitudes of the superior planet and the Sun differ by 180°, which ignores the fact that the planet is outside the plane of the Earth's orbit. For example, Pluto
, whose orbit is highly inclined to the Earth's orbital plane, can have a maximum elongation significantly less than 180° at opposition.
All superior planets are most easily visible at their oppositions because they are near their closest approach to Earth and are also above the horizon all night. The variation in magnitude
caused by changes in elongation are greater the closer the planet's orbit is to the Earth's. Mars
' magnitude in particular changes with elongation: it can be as low as +1.8 when in conjunction near aphelion but at a rare favourable opposition it is as high as −2.9, or seventy-five times brighter than its minimum brightness. As one moves further out, the difference in magnitude caused by the difference in elongation gradually fall. The maximum and minimum brightness of Jupiter
differ by only a factor of 3.3 times, whilst those of Uranus
– which is the most distant Solar System body visible to the naked eye
– differ by a factor of 1.7 times.
Since asteroids travel in an orbit not much larger than the Earth's, their magnitude can vary greatly depending on elongation. Although more than a dozen objects in the asteroid belt
can be seen with 10x50 binoculars
at an average opposition, only Ceres and Vesta
are always above the binocular limit of +9.5 at small elongations.
from Jupiter
. Here we can also talk about greatest eastern elongation and greatest western elongation. In the case of the moons of Uranus
, one often talks about greatest northern elongation and greatest southern elongation instead, due to the very high inclination of Uranus' axis of rotation..
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
, a planet's elongation is the angle between the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
and the planet, as viewed from Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
. Elongations occur when an inner planet’s position, in its orbital path, is at tangent to the view from Earth. Because these inner planets are inside the Earth’s orbits their positions as viewed from the Earth are never very far from the position of the Sun. When a planet is at Elongation, it is farthest from the Sun as viewed from Earth, so its view is best at that point.
When an inferior planet is visible after sunset, it is near its greatest eastern elongation. When an inferior planet is visible before sunrise, it is near its greatest western elongation. The value of the greatest elongation (west or east), for Mercury
Mercury (planet)
Mercury is the innermost and smallest planet in the Solar System, orbiting the Sun once every 87.969 Earth days. The orbit of Mercury has the highest eccentricity of all the Solar System planets, and it has the smallest axial tilt. It completes three rotations about its axis for every two orbits...
, is between 18° and 28°; and for Venus
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun, orbiting it every 224.7 Earth days. The planet is named after Venus, the Roman goddess of love and beauty. After the Moon, it is the brightest natural object in the night sky, reaching an apparent magnitude of −4.6, bright enough to cast shadows...
between 45° and 47°. This value varies because the orbits of the planets are elliptical, rather than perfect circles. Another minor contributor to this inconsistency is orbital inclination
Inclination
Inclination in general is the angle between a reference plane and another plane or axis of direction.-Orbits:The inclination is one of the six orbital parameters describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit...
: each planet's orbit is in a slightly different plane.
Refer to astronomical tables and websites such as heavens-above to see when the planets reach their next maximum elongations.
Elongation period
Greatest elongations of a planet happen periodically, with a greatest eastern elongation followed by a greatest western elongation, and vice versa. The period depends on the relative angular velocityAngular velocity
In physics, the angular velocity is a vector quantity which specifies the angular speed of an object and the axis about which the object is rotating. The SI unit of angular velocity is radians per second, although it may be measured in other units such as degrees per second, revolutions per...
of Earth and the planet, as seen from the Sun. The time it takes to complete this period is the synodic period of the planet.
Let T be the period (for example the time between two greatest eastern elongations), ω be the relative angular velocity
Angular velocity
In physics, the angular velocity is a vector quantity which specifies the angular speed of an object and the axis about which the object is rotating. The SI unit of angular velocity is radians per second, although it may be measured in other units such as degrees per second, revolutions per...
, ωe Earth's angular velocity
Angular velocity
In physics, the angular velocity is a vector quantity which specifies the angular speed of an object and the axis about which the object is rotating. The SI unit of angular velocity is radians per second, although it may be measured in other units such as degrees per second, revolutions per...
and ωp the planet's angular velocity
Angular velocity
In physics, the angular velocity is a vector quantity which specifies the angular speed of an object and the axis about which the object is rotating. The SI unit of angular velocity is radians per second, although it may be measured in other units such as degrees per second, revolutions per...
. Then
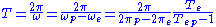
where Te and Tp are Earth's and the planet's years (i.e. periods of revolution around the Sun, called sidereal periods).
For example, Venus
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun, orbiting it every 224.7 Earth days. The planet is named after Venus, the Roman goddess of love and beauty. After the Moon, it is the brightest natural object in the night sky, reaching an apparent magnitude of −4.6, bright enough to cast shadows...
's year (sidereal period) is 225 days, and Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
's is 365 days. Thus Venus' synodic period, which gives the time between two subsequent eastern (or western) greatest elongations, is 584 days.
These values are approximate, because (as mentioned above) the planets do not have perfectly circular, coplanar orbits. When a planet is closer to the Sun it moves faster than when it is further away, so exact determination of the date and time of greatest elongation requires a much more complicated analysis of orbital mechanics.
Elongation of superior planets
Superior planets, dwarf planetDwarf planet
A dwarf planet, as defined by the International Astronomical Union , is a celestial body orbiting the Sun that is massive enough to be spherical as a result of its own gravity but has not cleared its neighboring region of planetesimals and is not a satellite...
s and asteroid
Asteroid
Asteroids are a class of small Solar System bodies in orbit around the Sun. They have also been called planetoids, especially the larger ones...
s undergo a different cycle. After superior conjunction, such an object's elongation continues to increase until it approaches a maximum value larger than 90° (impossible with inferior planets) and typically very near 180°, which is known as opposition
Opposition (astronomy)
In positional astronomy, two celestial bodies are said to be in opposition when they are on opposite sides of the sky, viewed from a given place . In particular, two planets are in opposition to each other when their ecliptic longitudes differ by 180°.The astronomical symbol for opposition is ☍...
and corresponds to a heliocentric conjunction with Earth. In other words, as seen from an observer on the superior planet at opposition, the Earth appears at inferior conjunction with the Sun. Technically, the exact moment of opposition is slightly different from the moment of maximum elongation. Opposition is defined as the moment when the apparent ecliptic longitudes of the superior planet and the Sun differ by 180°, which ignores the fact that the planet is outside the plane of the Earth's orbit. For example, Pluto
Pluto
Pluto, formal designation 134340 Pluto, is the second-most-massive known dwarf planet in the Solar System and the tenth-most-massive body observed directly orbiting the Sun...
, whose orbit is highly inclined to the Earth's orbital plane, can have a maximum elongation significantly less than 180° at opposition.
All superior planets are most easily visible at their oppositions because they are near their closest approach to Earth and are also above the horizon all night. The variation in magnitude
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
caused by changes in elongation are greater the closer the planet's orbit is to the Earth's. Mars
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. The planet is named after the Roman god of war, Mars. It is often described as the "Red Planet", as the iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance...
' magnitude in particular changes with elongation: it can be as low as +1.8 when in conjunction near aphelion but at a rare favourable opposition it is as high as −2.9, or seventy-five times brighter than its minimum brightness. As one moves further out, the difference in magnitude caused by the difference in elongation gradually fall. The maximum and minimum brightness of Jupiter
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet within the Solar System. It is a gas giant with mass one-thousandth that of the Sun but is two and a half times the mass of all the other planets in our Solar System combined. Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn,...
differ by only a factor of 3.3 times, whilst those of Uranus
Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It has the third-largest planetary radius and fourth-largest planetary mass in the Solar System. It is named after the ancient Greek deity of the sky Uranus , the father of Cronus and grandfather of Zeus...
– which is the most distant Solar System body visible to the naked eye
Naked eye
The naked eye is a figure of speech referring to human visual perception unaided by a magnifying or light-collecting optical device, such as a telescope or microscope. Vision corrected to normal acuity using corrective lenses is considered "naked"...
– differ by a factor of 1.7 times.
Since asteroids travel in an orbit not much larger than the Earth's, their magnitude can vary greatly depending on elongation. Although more than a dozen objects in the asteroid belt
Asteroid belt
The asteroid belt is the region of the Solar System located roughly between the orbits of the planets Mars and Jupiter. It is occupied by numerous irregularly shaped bodies called asteroids or minor planets...
can be seen with 10x50 binoculars
Binoculars
Binoculars, field glasses or binocular telescopes are a pair of identical or mirror-symmetrical telescopes mounted side-by-side and aligned to point accurately in the same direction, allowing the viewer to use both eyes when viewing distant objects...
at an average opposition, only Ceres and Vesta
4 Vesta
Vesta, formally designated 4 Vesta, is one of the largest asteroids, with a mean diameter of about . It was discovered by Heinrich Wilhelm Olbers on March 29, 1807, and is named after the Roman virgin goddess of home and hearth, Vesta....
are always above the binocular limit of +9.5 at small elongations.
Elongation of moons of other planets
Sometimes elongation may instead refer to the angular distance of a moon of another planet from its central planet, for instance the angular distance of IoIO
Io, IO, I/O, i/o, or i.o. may refer to:-An abbreviation:* I.O., a theater in Chicago, Illinois dedicated to improvisational comedy* i.o., "in illo ordine", Latin phrase meaning "respectively"...
from Jupiter
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet within the Solar System. It is a gas giant with mass one-thousandth that of the Sun but is two and a half times the mass of all the other planets in our Solar System combined. Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn,...
. Here we can also talk about greatest eastern elongation and greatest western elongation. In the case of the moons of Uranus
Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It has the third-largest planetary radius and fourth-largest planetary mass in the Solar System. It is named after the ancient Greek deity of the sky Uranus , the father of Cronus and grandfather of Zeus...
, one often talks about greatest northern elongation and greatest southern elongation instead, due to the very high inclination of Uranus' axis of rotation..
See also
- Aspects of Mercury for greatest elongations of MercuryMercury (planet)Mercury is the innermost and smallest planet in the Solar System, orbiting the Sun once every 87.969 Earth days. The orbit of Mercury has the highest eccentricity of all the Solar System planets, and it has the smallest axial tilt. It completes three rotations about its axis for every two orbits...
- Aspects of VenusAspects of VenusThe table contains special positions of Venus until 2021.Note: Greatest brilliancy is often confused with "maximum brightness". Although they are related, they are not quite the same thing. The "greatest brilliancy" is really a geometric maximum: it occurs when the apparent area of the sunlit...
for greatest elongations of VenusVenusVenus is the second planet from the Sun, orbiting it every 224.7 Earth days. The planet is named after Venus, the Roman goddess of love and beauty. After the Moon, it is the brightest natural object in the night sky, reaching an apparent magnitude of −4.6, bright enough to cast shadows... - Astronomical conjunction
External links
- Mercury Chaser's Calculator (Greatest Elongations of Mercury)

