
Emission nebula
Encyclopedia
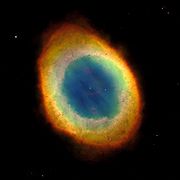
Nebula
A nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen gas, helium gas and other ionized gases...
is a cloud
Interstellar cloud
Interstellar cloud is the generic name given to an accumulation of gas, plasma and dust in our and other galaxies. Put differently, an interstellar cloud is a denser-than-average region of the interstellar medium. Depending on the density, size and temperature of a given cloud, the hydrogen in it...
of ionized gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
emitting light of various colors. The most common source of ionization
Ionization
Ionization is the process of converting an atom or molecule into an ion by adding or removing charged particles such as electrons or other ions. This is often confused with dissociation. A substance may dissociate without necessarily producing ions. As an example, the molecules of table sugar...
is high-energy photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
s emitted from a nearby hot star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
. Among the several different types of emission nebulae are H II region
H II region
An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived, blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light, ionizing the surrounding gas...
s, in which star formation is taking place and young, massive stars are the source of the ionizing photons; and planetary nebula
Planetary nebula
A planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life...
e, in which a dying star has thrown off its outer layers, with the exposed hot core then ionizing them.
General information
Usually, a young star will ionize part of the same cloud from which it was born although only massive, hot stars can release sufficient energy to ionize a significant part of a cloud. In many emission nebulae, an entire clusterStar cluster
Star clusters or star clouds are groups of stars. Two types of star clusters can be distinguished: globular clusters are tight groups of hundreds of thousands of very old stars which are gravitationally bound, while open clusters, more loosely clustered groups of stars, generally contain less than...
of young stars is doing the work.
The nebula's color depends on its chemical composition and degree of ionization
Ionization
Ionization is the process of converting an atom or molecule into an ion by adding or removing charged particles such as electrons or other ions. This is often confused with dissociation. A substance may dissociate without necessarily producing ions. As an example, the molecules of table sugar...
. Due to the prevalence of hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
in interstellar gas, and its relatively low energy of ionization, many emission nebulae appear red due to the strong emissions of the Balmer series
Balmer series
The Balmer series or Balmer lines in atomic physics, is the designation of one of a set of six different named series describing the spectral line emissions of the hydrogen atom....
. If more energy is available, other elements will be ionized and green and blue nebulae become possible. By examining the spectra
Electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. The "electromagnetic spectrum" of an object is the characteristic distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by that particular object....
of nebulae, astronomers deduce their chemical content. Most emission nebulae are about 90% hydrogen, with the remainder helium
Helium
Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
, oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
, nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
, and other elements.
Some of the most prominent emission nebulae visible from the northern hemisphere
Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
are the North America Nebula
North America Nebula
The North America Nebula is an emission nebula in the constellation Cygnus, close to Deneb . The remarkable shape of the emission nebula resembles that of the continent of North America, complete with a prominent Gulf of Mexico...
(NGC 7000) and Veil Nebula
Veil Nebula
The Veil Nebula is a cloud of heated and ionized gas and dust in the constellation Cygnus. It constitutes the visible portions of the Cygnus Loop , a large but relatively faint supernova remnant...
NGC 6960/6992 in Cygnus
Cygnus (constellation)
Cygnus is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way. Its name is the Latinized Hellenic word for swan. One of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross...
, while in the south celestial hemisphere, the Lagoon Nebula
Lagoon Nebula
The Lagoon Nebula is a giant interstellar cloud in the constellation Sagittarius. It is classified as an emission nebula and as an H II region....
M8 / NGC 6523 in Sagittarius
Sagittarius (constellation)
Sagittarius is a constellation of the zodiac, the one containing the galactic center. Its name is Latin for the archer, and its symbol is , a stylized arrow. Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow...
and the Orion Nebula
Orion Nebula
The Orion Nebula is a diffuse nebula situated south of Orion's Belt. It is one of the brightest nebulae, and is visible to the naked eye in the night sky. M42 is located at a distance of and is the closest region of massive star formation to Earth. The M42 nebula is estimated to be 24 light...
M42. Further in the southern hemisphere is the bright Carina Nebula NGC 3372.
Emission nebulae often have dark areas in them which result from clouds
Interstellar medium
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter that exists in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, dust, and cosmic rays. It fills interstellar space and blends smoothly into the surrounding intergalactic space...
of dust which block the light.
Many nebulae are made up of both reflection
Reflection nebula
In Astronomy, reflection nebulae are clouds of dust which are simply reflecting the light of a nearby star or stars. The energy from the nearby star, or stars, is insufficient to ionize the gas of the nebula to create an emission nebula, but is enough to give sufficient scattering to make the dust...
and emission components such as the Trifid Nebula
Trifid Nebula
The Trifid Nebula is an H II region located in Sagittarius. Its name means 'divided into three lobes'...
.

