Employment Protection Legislation
Encyclopedia
Employment protection legislation (EPL) refers to all types of employment protection measures, whether grounded primarily in legislation, court rulings, collectively bargained conditions of employment or customary practice. The term is common among circles of economist
s. Employment protection refers both to regulations concerning hiring (e.g. rules favouring disadvantaged groups, conditions for using temporary or fixed-term contracts, training requirements) and firing (e.g. redundancy procedures, mandated prenotification periods and severance payments, special requirements for collective dismissals and short-time work schemes).
There exist various institutional arrangements that can provide employment protection: the private market, labour legislation, collective bargaining arrangements and not the least, court interpretations of legislative and contractual provisions. Some forms of de facto regulations are likely to be adopted even in the absence of legislation, simply because both workers and firms derive advantages from long-term employment relations.
of the social partners, or are a consequence of court rulings. In particular, provisions favouring the employment of disadvantaged groups in society, determining the conditions for the use of temporary or fixed-term contracts, or imposing training requirements on the firm, affect hiring policies, while redundancy procedures, mandated pre-notification periods and severance payments, special requirements for collective dismissals and short-time work schemes influence firing decisions. The nature of these restrictions on the firms’ freedom to adjust the labour input is quite similar in all OECD countries, but the actual procedural details and the overall degree of stringency implied by them varies considerably. These provisions are enforced through the worker’s right to appeal against his lay-off.
Some aspects of these regulations, like the length of advance notices or the dimension of severance payments can be measured with precision. Other important features of EPL, like for example the willingness of labour courts to entertain appeals by fired workers, or how judges interpret the concept of “just cause” for termination, are much more difficult to quantify.
The 18 first-digit inputs are then expressed in either of the following forms:
Then, these different scoring is converted into cardinal scores that are normalized to range from 0 to 6, with higher scores representing stricter regulation. Therefore, each of the different items is normalized according to weighted averages, thus constructing three sets of summary indicators that correspond to successively more aggregated measures of EPL strictness.
The last step of the procedure involves computing, for each country, an overall summary indicator based on the three subcomponents:
The summary measure for collective dismissals is attributed just 40% of the weight assigned to regular and temporary contracts. The rationale for this is that the collective dismissals indicator only reflects additional employment protection triggered by the collective nature of the dismissal. In most countries, these additional requirements are quite modest. Moreover, summary measures for collective dismissals are only available since the late 1990s. An alternative overall index, so-called Version 1, has been thus calculated as an unweighted average of the summary measures for regular and temporary contracts only. While more restrictive than the previous one (so-called Version 2), this alternative measure of the overall EPL strictness allows comparisons over a longer period of time (since the late 1980s compared with the late 1990s).
in the labour market between the so-called insiders, the workers with a protected job, and the outsiders, who are people that are either unemployed
or employed
with fixed-term, part-time or temporary contracts, or even in the black economy, and face big difficulties to find a job covered by EPL because of the firms’ reduced propensity to hire. This latter group is mainly constituted by youths, women, racial minorities and unskilled workers
.
and unemployment
are not identifiable a priori. What is instead agreed among economists, is that more stringent EPL lowers the fluctuations in the quantity of labour demand
ed over the business cycle
, leading to smoother dynamic patterns of those aggregates.
Economists considering that EPL has no effect on unemployment include Blanchard and Portugal (2000). In their article they compare two opposite countries as regards their EPL stance: Portugal
with one of the more strict legislations in the world and the US with one of the more flexible ones. In spite of these differences, both countries have similar unemployment rates which undermines the argument considering that EPL has any effect on unemployment. Instead, the authors claim that EPL does affect two other variables: job flows and unemployment duration. EPL would reduce job flows (from employment to unemployment: employers are less willing to fire, given that they must pay indemnizations to workers) therefore reducing unemployment but would increase unemployment duration, increasing the unemployment rate. These two effects would neutralize each other, explaining why overall, EPL has no effect on unemployment.
Nickell (1997) arrived to similar conclusions when stating that labor market rigidities that do not appear to have serious implications for average levels of unemployment included strict employment protection legislation and general legislation on labor market standards.
Among those that have found evidence suggesting that EPL increases unemployment are Lazear
(1990). The author argued that mandated severance pay seemed to increase unemployment rates. His estimates suggested that an increase from zero to three months of severance pay would raise the unemployment rate by 5.5 percent in the United States.
. In his article he claims that the best estimates suggest that moving from no required severance pay to three months of required severance pay to employees with ten years of service would reduce the employment-population ratio by about one percent. In the United States
that would mean over a million jobs. Lazear argues that the young could bear a disproportionate amount of the burden.
To the contrary, Bertola and Bentolila (1990) found evidence supporting the idea that firing costs have a larger effect on firms' propensity to fire than to hire, and therefore (slightly) increase average long-run employment
.
an EPL reform in 1990 had as effect to reduce entry wages by 6 percent, implying that firms tend to transfer the increase in the cost of firing (due to EPL) onto workers. In fact, in their study they find that 25 percent of the firing cost was shifted onto lower wages in the case of Italy.
s. On the other hand, if firms
operated in a context of efficiency wages, by inducing more stable relationships with the workers and reducing their job and income insecurity, EPL could allow them to pay lower wages, without reducing the effort provided by the labour force employed, with beneficial effects on profits.
between product market and employment regulation
. Although employment protection legislation is only one aspect of the wide range of regulatory interventions in the labour market, Nicoletti et al. (2000) find evidence suggesting that, across countries, restrictive regulatory environments in the product market tend to be associated with restrictive employment protection policies. They claim that the indicators presented in their paper are closely related, with a statistical correlation
of 0.73 (significant
at the 1% level). In other words, according to these results, restrictive product market regulations are matched by analogous EPL restrictions to generate a tight overall regulatory environment for firms in their product market as well as in the allocation of labour inputs. The strong correlation between regulatory regimes in
the product market and EPL also suggests that their influence may have compounded effects on labour market outcomes, making regulatory reform in only one market less effective than simultaneous reform in the two markets.
Kugler and Pica (2003) find similar results in the case of the Italian economy
. They present a matching model which illustrates how barriers to entry
in the product market
(product market regulation) mitigate the impact of labor market deregulation
, (that is, mitigate the effects of a reduction in the strictness of EPL). In the author's opinion, this means that there are economic complementarities between labor and product market policies in their model, in the sense that the effectiveness of one policy depends on the implementation of the other policy. Thus, an important implication of their model is that labor market deregulation will be less effective in the presence of heavier regulations of entry. Similar results are obtained by Koeniger and Vindigni (2003).
effect on unemployment, strict EPL gives incentives to the firms to resort to other sources of flexibility
like overtime, which, as shown by Abraham and Houseman (1994), indeed tends to be used much more in Continental European countries, where the variability of hours per worker is significantly higher than in the Anglo-Saxon labour markets.
Economist
An economist is a professional in the social science discipline of economics. The individual may also study, develop, and apply theories and concepts from economics and write about economic policy...
s. Employment protection refers both to regulations concerning hiring (e.g. rules favouring disadvantaged groups, conditions for using temporary or fixed-term contracts, training requirements) and firing (e.g. redundancy procedures, mandated prenotification periods and severance payments, special requirements for collective dismissals and short-time work schemes).
There exist various institutional arrangements that can provide employment protection: the private market, labour legislation, collective bargaining arrangements and not the least, court interpretations of legislative and contractual provisions. Some forms of de facto regulations are likely to be adopted even in the absence of legislation, simply because both workers and firms derive advantages from long-term employment relations.
Definition
According to Barone (2001) with the acronym EPL economists refer to the entire set of regulations that place some limits to the faculties of firms to hire and fire workers, even if they are not grounded primarily in the law, but originate from the collective bargainingCollective bargaining
Collective bargaining is a process of negotiations between employers and the representatives of a unit of employees aimed at reaching agreements that regulate working conditions...
of the social partners, or are a consequence of court rulings. In particular, provisions favouring the employment of disadvantaged groups in society, determining the conditions for the use of temporary or fixed-term contracts, or imposing training requirements on the firm, affect hiring policies, while redundancy procedures, mandated pre-notification periods and severance payments, special requirements for collective dismissals and short-time work schemes influence firing decisions. The nature of these restrictions on the firms’ freedom to adjust the labour input is quite similar in all OECD countries, but the actual procedural details and the overall degree of stringency implied by them varies considerably. These provisions are enforced through the worker’s right to appeal against his lay-off.
Some aspects of these regulations, like the length of advance notices or the dimension of severance payments can be measured with precision. Other important features of EPL, like for example the willingness of labour courts to entertain appeals by fired workers, or how judges interpret the concept of “just cause” for termination, are much more difficult to quantify.
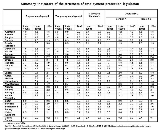
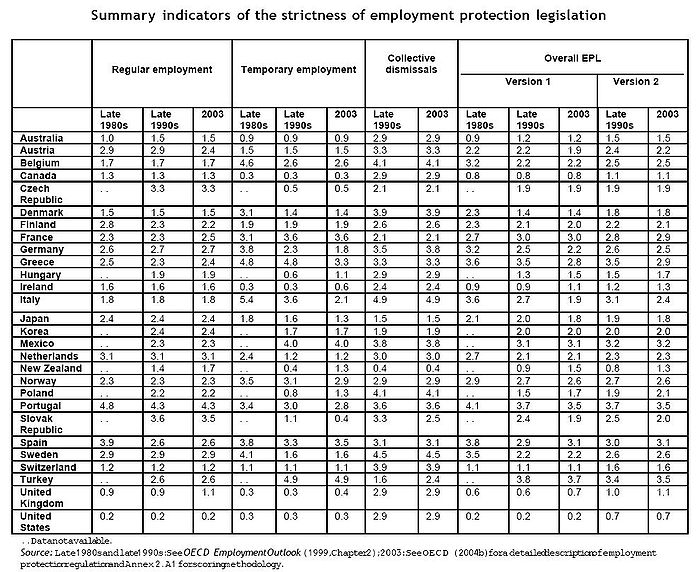
Employment Protection Legislation Index by the OECD
One of the more frequently used measures of the strictness of the EPL in each country and through different years is the so-called Employment Protection Legislation Index elaborated by the OECD. This index is calculated along 18 basic items, which can be classified in three main areas:- Employment protection of regular workers against individual dismissal;
- Specific requirements for collective dismissals; and
- Regulation of temporary forms of employment.
The 18 first-digit inputs are then expressed in either of the following forms:
- Units of time (e.g. delays before notice can start, or months of notice and severance pay);
- As a number (e.g. maximum number of successive fixed-term contracts allowed); or
- As a score on an ordinal scale specific to each item (0 to 2, 3, 4 or simply yes/no).
Then, these different scoring is converted into cardinal scores that are normalized to range from 0 to 6, with higher scores representing stricter regulation. Therefore, each of the different items is normalized according to weighted averages, thus constructing three sets of summary indicators that correspond to successively more aggregated measures of EPL strictness.
The last step of the procedure involves computing, for each country, an overall summary indicator based on the three subcomponents:
- Strictness of regulation for regular contracts,
- Temporary contracts, and
- Collective dismissals.
The summary measure for collective dismissals is attributed just 40% of the weight assigned to regular and temporary contracts. The rationale for this is that the collective dismissals indicator only reflects additional employment protection triggered by the collective nature of the dismissal. In most countries, these additional requirements are quite modest. Moreover, summary measures for collective dismissals are only available since the late 1990s. An alternative overall index, so-called Version 1, has been thus calculated as an unweighted average of the summary measures for regular and temporary contracts only. While more restrictive than the previous one (so-called Version 2), this alternative measure of the overall EPL strictness allows comparisons over a longer period of time (since the late 1980s compared with the late 1990s).

On the duality of the labour market
Some economists have claimed that empirical evidence gives support to their theories, according to which EPL leads to a segmentationMarket segment
Market segmentation is a concept in economics and marketing. A market segment is a sub-set of a market made up of people or organizations with one or more characteristics that cause them to demand similar product and/or services based on qualities of those products such as price or function...
in the labour market between the so-called insiders, the workers with a protected job, and the outsiders, who are people that are either unemployed
Unemployment
Unemployment , as defined by the International Labour Organization, occurs when people are without jobs and they have actively sought work within the past four weeks...
or employed
Employment
Employment is a contract between two parties, one being the employer and the other being the employee. An employee may be defined as:- Employee :...
with fixed-term, part-time or temporary contracts, or even in the black economy, and face big difficulties to find a job covered by EPL because of the firms’ reduced propensity to hire. This latter group is mainly constituted by youths, women, racial minorities and unskilled workers
Skilled worker
A skilled worker is any worker who has some special skill, knowledge, or ability in their work. A skilled worker may have attended a college, university or technical school. Or, a skilled worker may have learned their skills on the job...
.
On unemployment
Whether EPL has any effect on unemployment is an issue of contention between economists. On the one hand, assuming that the cyclical wage pattern is not affected by mandated firing costs, EPL reduces the propensity to hire by employers, since they fear that such decisions will be difficult to reverse in the future, in case of a recession. On the other hand, EPL also leads firms during downswings to keep more workers employed, than they would have otherwise done. Therefore, EPL reduces both job creation and job destruction, so that the net effects on average employmentEmployment
Employment is a contract between two parties, one being the employer and the other being the employee. An employee may be defined as:- Employee :...
and unemployment
Unemployment
Unemployment , as defined by the International Labour Organization, occurs when people are without jobs and they have actively sought work within the past four weeks...
are not identifiable a priori. What is instead agreed among economists, is that more stringent EPL lowers the fluctuations in the quantity of labour demand
Demand
- Economics :*Demand , the desire to own something and the ability to pay for it*Demand curve, a graphic representation of a demand schedule*Demand deposit, the money in checking accounts...
ed over the business cycle
Business cycle
The term business cycle refers to economy-wide fluctuations in production or economic activity over several months or years...
, leading to smoother dynamic patterns of those aggregates.
Economists considering that EPL has no effect on unemployment include Blanchard and Portugal (2000). In their article they compare two opposite countries as regards their EPL stance: Portugal
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
with one of the more strict legislations in the world and the US with one of the more flexible ones. In spite of these differences, both countries have similar unemployment rates which undermines the argument considering that EPL has any effect on unemployment. Instead, the authors claim that EPL does affect two other variables: job flows and unemployment duration. EPL would reduce job flows (from employment to unemployment: employers are less willing to fire, given that they must pay indemnizations to workers) therefore reducing unemployment but would increase unemployment duration, increasing the unemployment rate. These two effects would neutralize each other, explaining why overall, EPL has no effect on unemployment.
Nickell (1997) arrived to similar conclusions when stating that labor market rigidities that do not appear to have serious implications for average levels of unemployment included strict employment protection legislation and general legislation on labor market standards.
Among those that have found evidence suggesting that EPL increases unemployment are Lazear
Edward Lazear
Edward Paul "Ed" Lazear is an award-winning American economist, considered the founder of personnel economics, and was the chief economic advisor to President George W. Bush.-Career:...
(1990). The author argued that mandated severance pay seemed to increase unemployment rates. His estimates suggested that an increase from zero to three months of severance pay would raise the unemployment rate by 5.5 percent in the United States.
On employment
Lazear (1990) once again argues he has evidence suggesting that EPL reduces the Employment-to-Population ratioEmployment-to-population ratio
The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development defines the employment rate as the employment-to-population ratio. This is a statistical ratio that measures the proportion of the country's working-age population that is employed...
. In his article he claims that the best estimates suggest that moving from no required severance pay to three months of required severance pay to employees with ten years of service would reduce the employment-population ratio by about one percent. In the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
that would mean over a million jobs. Lazear argues that the young could bear a disproportionate amount of the burden.
To the contrary, Bertola and Bentolila (1990) found evidence supporting the idea that firing costs have a larger effect on firms' propensity to fire than to hire, and therefore (slightly) increase average long-run employment
Employment
Employment is a contract between two parties, one being the employer and the other being the employee. An employee may be defined as:- Employee :...
.
On wages
Several authors have found that EPL has significant effects on wages. As stated by Lazear (1990), in a perfect labor market, severance payments can have no real effects as they can be undone by a properly designed labor contract. Leonardi and Pica (2006) found evidence supporting this claim. They suggest that in the case of ItalyItaly
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
an EPL reform in 1990 had as effect to reduce entry wages by 6 percent, implying that firms tend to transfer the increase in the cost of firing (due to EPL) onto workers. In fact, in their study they find that 25 percent of the firing cost was shifted onto lower wages in the case of Italy.
On firm efficiency and profits
In principle the effects on profits are ambiguous. Because of EPL, firms engage themselves in labour hoarding practices, which lead them to employ a lower quantity of workers during upswings, while keeping inefficient levels of employment in downturns. For a given level of wages, this loss of productive efficiency would result in lower average profitProfit (economics)
In economics, the term profit has two related but distinct meanings. Normal profit represents the total opportunity costs of a venture to an entrepreneur or investor, whilst economic profit In economics, the term profit has two related but distinct meanings. Normal profit represents the total...
s. On the other hand, if firms
operated in a context of efficiency wages, by inducing more stable relationships with the workers and reducing their job and income insecurity, EPL could allow them to pay lower wages, without reducing the effort provided by the labour force employed, with beneficial effects on profits.
On product market regulation
There appears to be agreement among economists on the positive correlationCorrelation
In statistics, dependence refers to any statistical relationship between two random variables or two sets of data. Correlation refers to any of a broad class of statistical relationships involving dependence....
between product market and employment regulation
Regulation
Regulation is administrative legislation that constitutes or constrains rights and allocates responsibilities. It can be distinguished from primary legislation on the one hand and judge-made law on the other...
. Although employment protection legislation is only one aspect of the wide range of regulatory interventions in the labour market, Nicoletti et al. (2000) find evidence suggesting that, across countries, restrictive regulatory environments in the product market tend to be associated with restrictive employment protection policies. They claim that the indicators presented in their paper are closely related, with a statistical correlation
Correlation
In statistics, dependence refers to any statistical relationship between two random variables or two sets of data. Correlation refers to any of a broad class of statistical relationships involving dependence....
of 0.73 (significant
Statistical significance
In statistics, a result is called statistically significant if it is unlikely to have occurred by chance. The phrase test of significance was coined by Ronald Fisher....
at the 1% level). In other words, according to these results, restrictive product market regulations are matched by analogous EPL restrictions to generate a tight overall regulatory environment for firms in their product market as well as in the allocation of labour inputs. The strong correlation between regulatory regimes in
the product market and EPL also suggests that their influence may have compounded effects on labour market outcomes, making regulatory reform in only one market less effective than simultaneous reform in the two markets.
Kugler and Pica (2003) find similar results in the case of the Italian economy
Economy of Italy
Italy has a diversified industrial economy with high gross domestic product per capita and developed infrastructure. According to the International Monetary Fund, the World Bank and the CIA World Factbook, in 2010 Italy was the seventh-largest economy in the world and the third-largest in Europe...
. They present a matching model which illustrates how barriers to entry
Barriers to entry
In theories of competition in economics, barriers to entry are obstacles that make it difficult to enter a given market. The term can refer to hindrances a firm faces in trying to enter a market or industry - such as government regulation, or a large, established firm taking advantage of economies...
in the product market
Product market
Product market is a mechanism that allows people to easily buy and sell products. Services are often included in the scope of the term. Product market regulation is an economic term that describes restrictions in the market....
(product market regulation) mitigate the impact of labor market deregulation
Deregulation
Deregulation is the removal or simplification of government rules and regulations that constrain the operation of market forces.Deregulation is the removal or simplification of government rules and regulations that constrain the operation of market forces.Deregulation is the removal or...
, (that is, mitigate the effects of a reduction in the strictness of EPL). In the author's opinion, this means that there are economic complementarities between labor and product market policies in their model, in the sense that the effectiveness of one policy depends on the implementation of the other policy. Thus, an important implication of their model is that labor market deregulation will be less effective in the presence of heavier regulations of entry. Similar results are obtained by Koeniger and Vindigni (2003).
On hours per worker
Whereas EPL may have not a significantStatistical significance
In statistics, a result is called statistically significant if it is unlikely to have occurred by chance. The phrase test of significance was coined by Ronald Fisher....
effect on unemployment, strict EPL gives incentives to the firms to resort to other sources of flexibility
Labour market flexibility
Labour market flexibility refers to the speed with which labour markets adapt to fluctuations and changes in society, the economy or production.-Definition:In the past, the most common definition of labour market flexibility was the neo-liberal definition...
like overtime, which, as shown by Abraham and Houseman (1994), indeed tends to be used much more in Continental European countries, where the variability of hours per worker is significantly higher than in the Anglo-Saxon labour markets.
See also
- Labour lawLabour lawLabour law is the body of laws, administrative rulings, and precedents which address the legal rights of, and restrictions on, working people and their organizations. As such, it mediates many aspects of the relationship between trade unions, employers and employees...
- Labour market
- Labour market flexibilityLabour market flexibilityLabour market flexibility refers to the speed with which labour markets adapt to fluctuations and changes in society, the economy or production.-Definition:In the past, the most common definition of labour market flexibility was the neo-liberal definition...
- MicroeconomicsMicroeconomicsMicroeconomics is a branch of economics that studies the behavior of how the individual modern household and firms make decisions to allocate limited resources. Typically, it applies to markets where goods or services are being bought and sold...
- Important publications in labour economics
- UnemploymentUnemploymentUnemployment , as defined by the International Labour Organization, occurs when people are without jobs and they have actively sought work within the past four weeks...

