
Energy Systems Language
Encyclopedia
Howard T. Odum
Howard Thomas Odum was an American ecologist...
and colleagues in the 1950s during studies of the tropical forests funded by the United States Atomic Energy Commission
United States Atomic Energy Commission
The United States Atomic Energy Commission was an agency of the United States government established after World War II by Congress to foster and control the peace time development of atomic science and technology. President Harry S...
. They are used to compose energy flow diagrams in the field of systems ecology
Systems ecology
Systems ecology is an interdisciplinary field of ecology, taking a holistic approach to the study of ecological systems, especially ecosystems. Systems ecology can be seen as an application of general systems theory to ecology. Central to the systems ecology approach is the idea that an ecosystem...
.
Design intent
The design intent of the energy systems language was to facilitate the generic depiction of energy flows through any scale system while encompassing the laws of physics, and in particular, the laws of thermodynamicsThermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a physical science that studies the effects on material bodies, and on radiation in regions of space, of transfer of heat and of work done on or by the bodies or radiation...
(see energy transformation for an example).
In particular H.T. Odum aimed to produce a language which could facilitate the intellectual analysis, engineering synthesis and management of global systems such as the geobiosphere, and its many subsystems. Within this aim, H.T. Odum had a strong concern that many abstract mathematical models of such systems were not thermodynamically valid. Hence he used analog computers to make system models due to their intrinsic value
Intrinsic value
Intrinsic value can refer to:*Intrinsic value , of an option or stock.*Intrinsic value , of a coin.*Intrinsic value , in ethics and philosophy.*Intrinsic value , in philosophy....
; that is, the electronic circuits are of value for modelling natural systems which are assumed to obey the laws of energy flow, because, in themselves the circuits, like natural systems, also obey the known laws of energy flow, where the energy form is electrical. However Odum was interested not only in the electronic circuits themselves, but also in how they might be used as formal analogies for modeling other systems which also had energy flowing through them. As a result, Odum did not restrict his inquiry to the analysis and synthesis of any one system in isolation. The discipline that is most often associated with this kind of approach, together with the use of the energy systems language is known as Systems Ecology
Systems ecology
Systems ecology is an interdisciplinary field of ecology, taking a holistic approach to the study of ecological systems, especially ecosystems. Systems ecology can be seen as an application of general systems theory to ecology. Central to the systems ecology approach is the idea that an ecosystem...
.
General characteristics
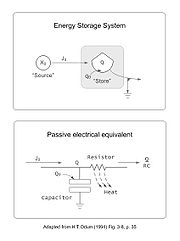
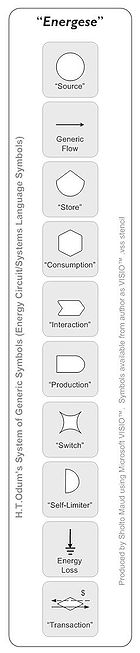
Depicted to the left is what the generic symbol for storage, which Odum named the Bertalanffy module, in honor of the general systems theorist Ludwig von Bertalanffy
Ludwig von Bertalanffy
Karl Ludwig von Bertalanffy was an Austrian-born biologist known as one of the founders of general systems theory . GST is an interdisciplinary practice that describes systems with interacting components, applicable to biology, cybernetics, and other fields...
.
For Odum, in order to achieve a holistic understanding of how many apparently different systems actually effect each other, it was important to have a generic language with a massively scalable modeling capacity - to model global-to-local, ecological, physical and economic systems. The intention was, and for those who still apply it, is, to make biological, physical, ecological, economic and other system models thermodynamically, and so also energetically
Energetics
Energetics is the study of energy under transformation. Because energy flows at all scales, from the quantum level to the biosphere and cosmos, energetics is a very broad discipline, encompassing for example thermodynamics, chemistry, biological energetics, biochemistry and ecological energetics...
, valid
Valid
Valid is a Brazilian engraving company headquartered in Rio de Janeiro that provides security printing services to financial institutions, telecommunication companies, state governments, and public agencies in Brazil, Argentina, and Spain....
and verifiable. As a consequence the designers of the language also aimed to include the energy metabolism of any system within the scope of inquiry.
Pictographic icons
In order to aid learning, in Modeling for all Scales Odum and Odum (2000) suggested systems might first be introduced with pictographic icons, and then later defined in the generic symbolism. Pictograms have therefore been used in software programs like ExtendSim(tm) to depict the basic categories of the Energy Systems Language. Some have argued that such an approach shares similar motivations to Otto NeurathOtto Neurath
Otto Neurath was an Austrian philosopher of science, sociologist, and political economist...
's isotype
Isotype (pictograms)
Isotype is a method of showing social, technological, biological and historical connections in pictorial form...
project, Leibniz's (Characteristica Universalis
Characteristica universalis
The Latin term characteristica universalis, commonly interpreted as universal characteristic, or universal character in English, is a universal and formal language imagined by the German philosopher Gottfried Leibniz able to express mathematical, scientific, and metaphysical concepts...
) Enlightenment
Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment was an elite cultural movement of intellectuals in 18th century Europe that sought to mobilize the power of reason in order to reform society and advance knowledge. It promoted intellectual interchange and opposed intolerance and abuses in church and state...
Project and Buckminster Fuller
Buckminster Fuller
Richard Buckminster “Bucky” Fuller was an American systems theorist, author, designer, inventor, futurist and second president of Mensa International, the high IQ society....
's works.
See also
- EmergyEmergyEmergy is the available energy of one kind that is used up in transformations directly and indirectly to make a product or service. Emergy accounts for, and in effect, measures quality differences between forms of energy. Emergy is an expression of all the energy used in the work processes that...
- Embodied energyEmbodied energyEmbodied energy is defined as the sum of energy inputs that was used in the work to make any product, from the point of extraction and refining materials, bringing it to market, and disposal / re-purposing of it...
- Universal languageUniversal languageUniversal language may refer to a hypothetical or historical language spoken and understood by all or most of the world's population. In some circles, it is a language said to be understood by all living things, beings, and objects alike. It may be the ideal of an international auxiliary language...
- Characteristica universalisCharacteristica universalisThe Latin term characteristica universalis, commonly interpreted as universal characteristic, or universal character in English, is a universal and formal language imagined by the German philosopher Gottfried Leibniz able to express mathematical, scientific, and metaphysical concepts...
- Principles of energetics
- Unified Modelling Language
- SysML
External links
- D.Cevolatti and S.Maud (2004) Realising the Enlightenment: H.T. Odum’s Energy Systems Language qua G.W.v Leibniz’s Characteristica Universalis, Ecological Modelling 178, pp. 279–292.
- A series of flash animations using the energy systems language (ecolanguage) on YouTube by Lee Arnold

