Energy intensity
Encyclopedia
Energy intensity is a measure
Measurement
Measurement is the process or the result of determining the ratio of a physical quantity, such as a length, time, temperature etc., to a unit of measurement, such as the metre, second or degree Celsius...
of the energy efficiency of a nation's economy
Economic system
An economic system is the combination of the various agencies, entities that provide the economic structure that defines the social community. These agencies are joined by lines of trade and exchange along which goods, money etc. are continuously flowing. An example of such a system for a closed...
. It is calculated as units of energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
per unit of GDP.
- High energy intensities indicate a high price or cost of converting energy into GDP.
- Low energy intensity indicates a lower price or cost of converting energy into GDP.
- Energy Intensity as defined here is not to be confused with Energy Use Intensity (EUI), a measure of building energy use per unit area. For Energy Use Intensity, see the definition on the Energy Star webpage or the article in HPB magazine.
Overview
Many factors influence an economy's overall energy intensity. It may reflect requirements for general standards of living and weather conditions in an economy. It is not atypical for particularly cold or hot climates to require greater energy consumptionDomestic Energy Consumption
Domestic energy consumption is the amount of energy that is spent on the different appliances used within housing. The amount of energy used per household varies widely depending on the standard of living of the country, climate, and the age and type of residence...
in homes and workplaces for heating (furnace
Furnace
A furnace is a device used for heating. The name derives from Latin fornax, oven.In American English and Canadian English, the term furnace on its own is generally used to describe household heating systems based on a central furnace , and sometimes as a synonym for kiln, a device used in the...
s, or electric heaters) or cooling (air conditioning
Air conditioning
An air conditioner is a home appliance, system, or mechanism designed to dehumidify and extract heat from an area. The cooling is done using a simple refrigeration cycle...
, fans
Fan (mechanical)
A mechanical fan is a machine used to create flow within a fluid, typically a gas such as air.A fan consists of a rotating arrangement of vanes or blades which act on the air. Usually, it is contained within some form of housing or case. This may direct the airflow or increase safety by preventing...
, refrigeration
Refrigeration
Refrigeration is a process in which work is done to move heat from one location to another. This work is traditionally done by mechanical work, but can also be done by magnetism, laser or other means...
). A country with an advanced standard of living is more likely to have a wider prevalence of such consumer goods and thereby be impacted in its energy intensity than one with a lower standard of living.
Energy efficiency of appliances and buildings (through use of building materials and methods, such as insulation
Building insulation
building insulation refers broadly to any object in a building used as insulation for any purpose. While the majority of insulation in buildings is for thermal purposes, the term also applies to acoustic insulation, fire insulation, and impact insulation...
), fuel economy of vehicles, vehicular distances travelled (frequency of travel or larger geographical distances), better methods and patterns of transportation, capacities and utility of mass transit, energy rationing
Energy rationing
Energy rationing primarily involves measures that are designed to force energy conservation as an alternative to price mechanisms in energy markets...
or conservation efforts
Energy demand management
Energy demand management, also known as demand side management , is the modification of consumer demand for energy through various methods such as financial incentives and education...
, 'off-grid' energy sources, and stochastic economic shocks such as disruptions of energy due to natural disaster
Natural disaster
A natural disaster is the effect of a natural hazard . It leads to financial, environmental or human losses...
s, wars, massive power outage
Power outage
A power outage is a short- or long-term loss of the electric power to an area.There are many causes of power failures in an electricity network...
s, unexpected new sources, efficient uses of energy or energy subsidies may all impact overall energy intensity of a nation.
Thus, a nation that is highly economically productive, with mild and temperate weather, demographic patterns of work places close to home, and uses fuel efficient vehicles, supports carpools, mass transportation or walks or rides bicycles, will have a far lower energy intensity than a nation that is economically unproductive, with extreme weather conditions requiring heating and cooling, long commutes, and extensive use of generally poor fuel economy vehicles. Paradoxically, some activities that may seem to promote high energy intensities, such as long commutes, could in fact result in lower energy intensities by causing a disproportionate increase in GDP output.
Figures of energy consumption used in statistics are energy sources marketed through major energy industries. Therefore some small scale but frequent consumption of energy source like firewood
Firewood
Firewood is any wood-like material that is gathered and used for fuel. Generally, firewood is not highly processed and is in some sort of recognizable log or branch form....
, charcoal
Charcoal
Charcoal is the dark grey residue consisting of carbon, and any remaining ash, obtained by removing water and other volatile constituents from animal and vegetation substances. Charcoal is usually produced by slow pyrolysis, the heating of wood or other substances in the absence of oxygen...
peat
Peat
Peat is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation matter or histosol. Peat forms in wetland bogs, moors, muskegs, pocosins, mires, and peat swamp forests. Peat is harvested as an important source of fuel in certain parts of the world...
, water wheel
Water wheel
A water wheel is a machine for converting the energy of free-flowing or falling water into useful forms of power. A water wheel consists of a large wooden or metal wheel, with a number of blades or buckets arranged on the outside rim forming the driving surface...
, wind mill are not in its count.
In countries, which does not have such developed energy industries or people with highly self energy efficient life style, report smaller energy consumption figures.
Examples
- U.S.United StatesThe United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
energy consumption in 2004 was estimated at 99.74 quadrillion Btus (1.05 × 1011 GJ) (referred to as 'quads') from all sources (US DoE). Total GDP was estimated at $11.75 trillion in 2004 and US GDP per capita was estimated at roughly $40,100 in 2004 (CIA Factbook). Using a population of 290,809,777 (as per US Census Bureau). This would produce an Energy Intensity of 8,553 Btus (9 MJ) consumed to produce a single dollar of GDP (about 9,023 kJ/$).
Various nations have significantly higher or lower energy intensities.
- BangladeshBangladeshBangladesh , officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh is a sovereign state located in South Asia. It is bordered by India on all sides except for a small border with Burma to the far southeast and by the Bay of Bengal to the south...
, with a population of 144 million and a GDP of $275.5 billion therefore has a GDP per capita of approximately $2,000. Its annual energy consumption was only 0.61 quads, making its Energy Intensity a mere 2,113 kJ/$ (a quarter of the US value). Low standards of living and economic performance primarily accounts for such a meager number.
- RussiaRussiaRussia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
, with a population of 143 million and a GDP of $1.408 trillion therefore has a GDP per capita of approximately $9,800. Its annual energy consumption was 29.6 quads, for an Energy Intensity of 20,676 kJ/$(more than twice the US value), largely due to harsh climatic conditions in most of Eastern Russia and the country's vast territorial space.
- ItalyItalyItaly , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
, with a population of 60 million and a GDP of $1.8 trillion therefore has a GDP per capita of approximately $31,000. Its annual Energy Intensity of 122.8 tons of oil equivalent makes it the most energy efficient country in the G8 and one of the most energy efficient in the industrial world, largely due to traditionally high energy prices which have resulted in more efficient company and consumer behaviours.
Of course, these numbers were produced with a mix of 2003 and 2004 figures, many of which are estimates. Actual mathematical models should use precise data of appropriate matching periods of study.
Economic Energy Efficiency

- Referring to the above examples, 1 million Btus consumed with an energy intensity of 8,553 produced $116.92 of GDP for the US. Whereas, each million Btus of energy consumed in Bangladesh with an Energy Intensity of 2,113 produced $473 of GDP, or over four times the effective US rate. Russia, on the other hand, produced only $48.37 GDP per 1 million Btu based on an energy intensity of 20,676. Thus, Bangladesh could be perceived as having nearly ten times the economic energy efficiency of Russia.
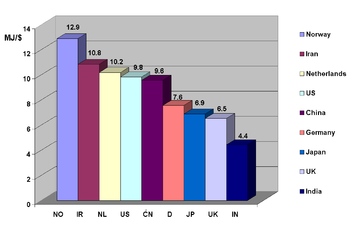
It is not directly causal that a high GDP per capita must have lower economic energy efficiencies. See the accompanying chart for examples based on the top 40 national economies.
Energy intensity can be used as a comparative measure between countries; whereas the change in energy consumption required to raise GDP in a specific country over time is described as its energy elasticity
Energy elasticity
Energy elasticity is a term used with reference to the energy intensity of Gross Domestic Product. It is "the percentage change in energy consumption to achieve one per cent change in national GDP"....
.
See also
- List of countries by energy intensity
- Over-illuminationOver-illuminationOver-illumination is the presence of lighting intensity beyond that required for a specified activity. Over-illumination was commonly ignored between 1950 and 1995, especially in office and retail environments; only since then has the interior design community begun to reconsider this practice.The...
- World energy resources and consumptionWorld energy resources and consumption]World energy consumption in 2010: over 5% growthEnergy markets have combined crisis recovery and strong industry dynamism. Energy consumption in the G20 soared by more than 5% in 2010, after the slight decrease of 2009. This strong increase is the result of two converging trends...
- carbon intensity
- energy use intensity
General Reference
- Energy Intensity (UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs)

